How to Select the Most Suitable Harmonic Drive Gearbox Based on Specific Applications
When mechanical engineers select a harmonic drive gearbox, they typically evaluate its performance characteristics and operating environment, confirming the most appropriate model through drawings and key specifications.
Beyond these basic parameters, there are many additional details that should be carefully considered.
1. Fully Consider the Torque Requirements of the Harmonic Drive
When assisting customers with model selection, the HONPINE engineering team usually reserves 20%–30% torque margin to ensure that the harmonic drive can withstand the load during continuous operation.
It is also important to consider maximum torque, since startup, emergency stops, and short-term impact loads often occur in real applications.
In scenarios with frequent acceleration/deceleration or high-inertia loads, the inherent torque ripple characteristics of harmonic drives may be affected. Excessive torque fluctuation can, in turn, reduce positioning accuracy.
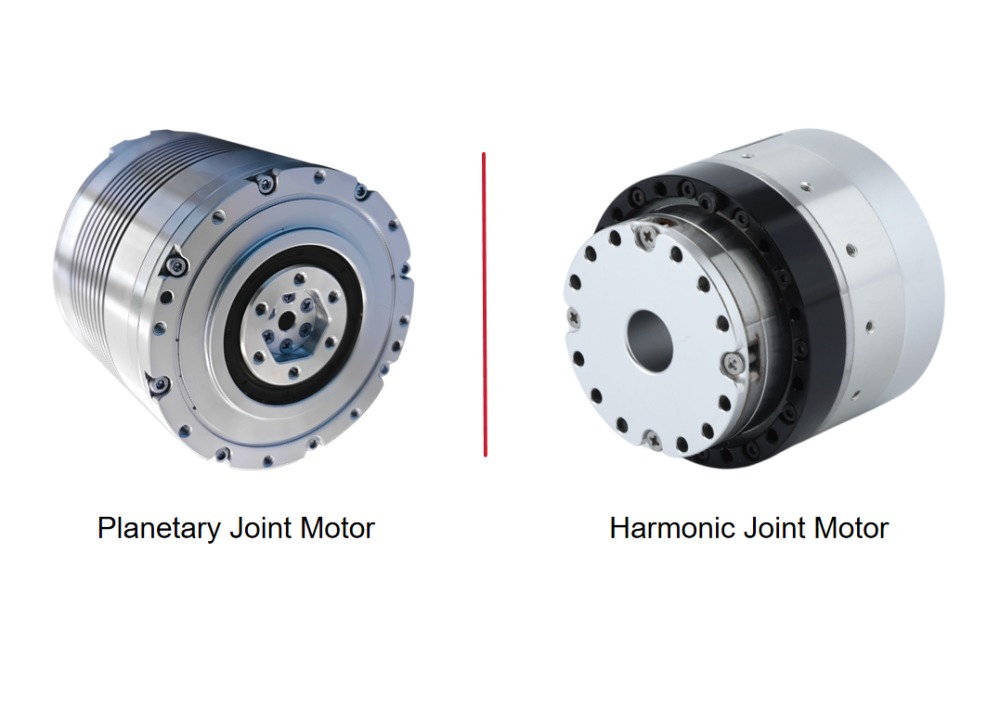
2. Choose the Optimal Harmonic Drive Structure for the Application Environment
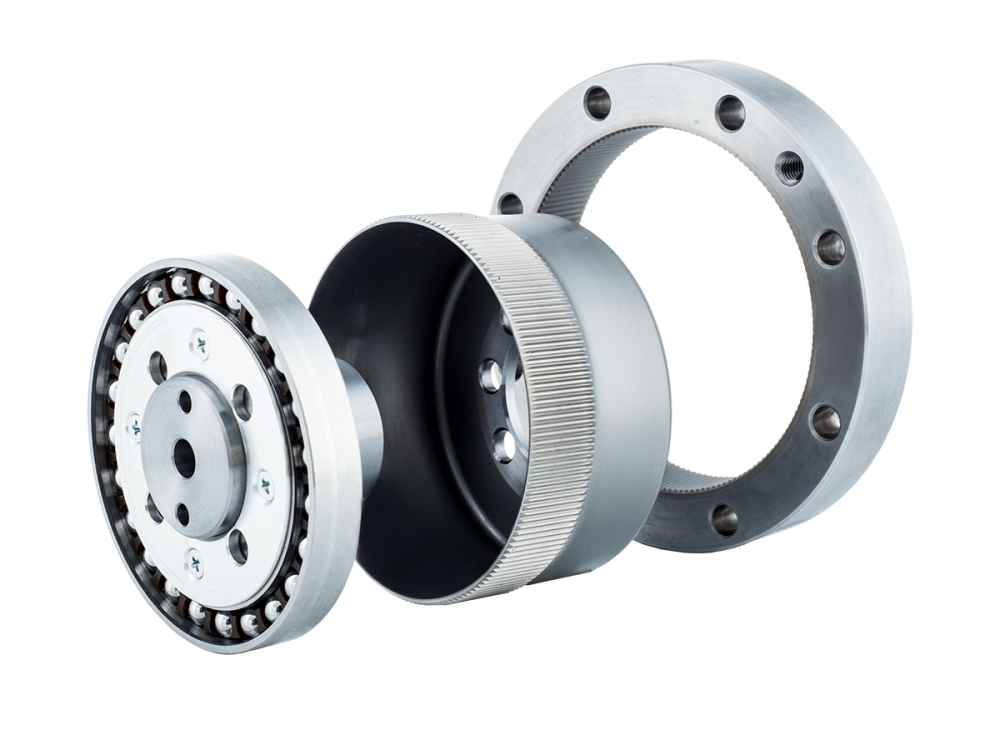
Cup Type Harmonic Drive
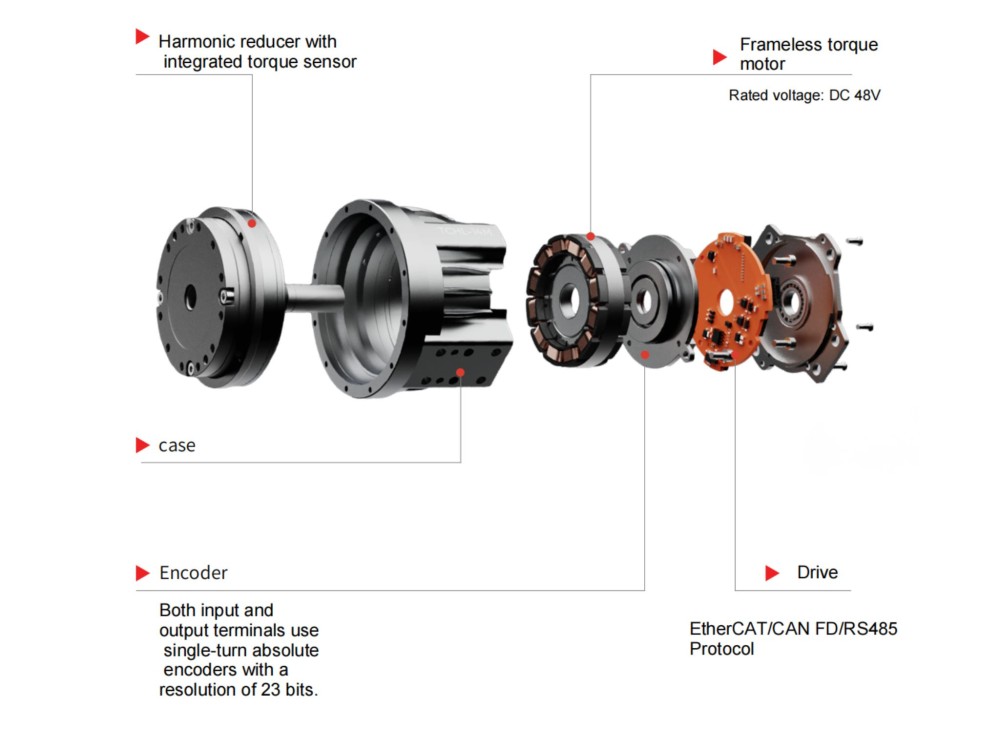
When used in robot joints or medical devices, where high precision is required, the cup type harmonic drive is typically preferred.
Hat Type Harmonic Drive
For machine tools or heavy-load applications, the hat type variant—with higher rigidity—is recommended.
Hollow Shaft Design Harmonic Drive
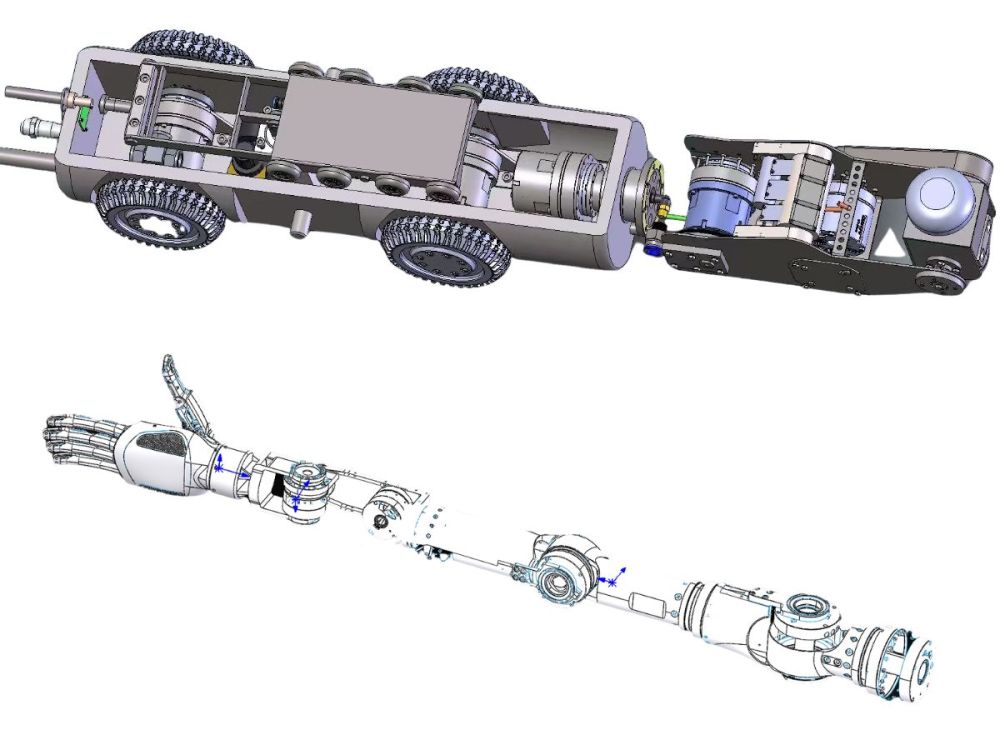
In robotic applications that require higher degrees of freedom, a hollow-through design is suggested. It allows cable routing through the center, reducing the risk of wire bending, interference, and breakage.
Pancake Type Harmonic Drive
When space constraints are a key factor—such as in robotic end-axis joints—the ultra-flat pancake harmonic drive is the ideal choice.

3. Select the Appropriate Connection Method for the Operating Conditions
Belt Connection
The motor and harmonic drive are connected via a belt transmission, allowing flexible placement without requiring them to be on the same axis.
This setup is suitable for space-limited or offset-mounted equipment, such as compact automation systems or lightweight handling robots.
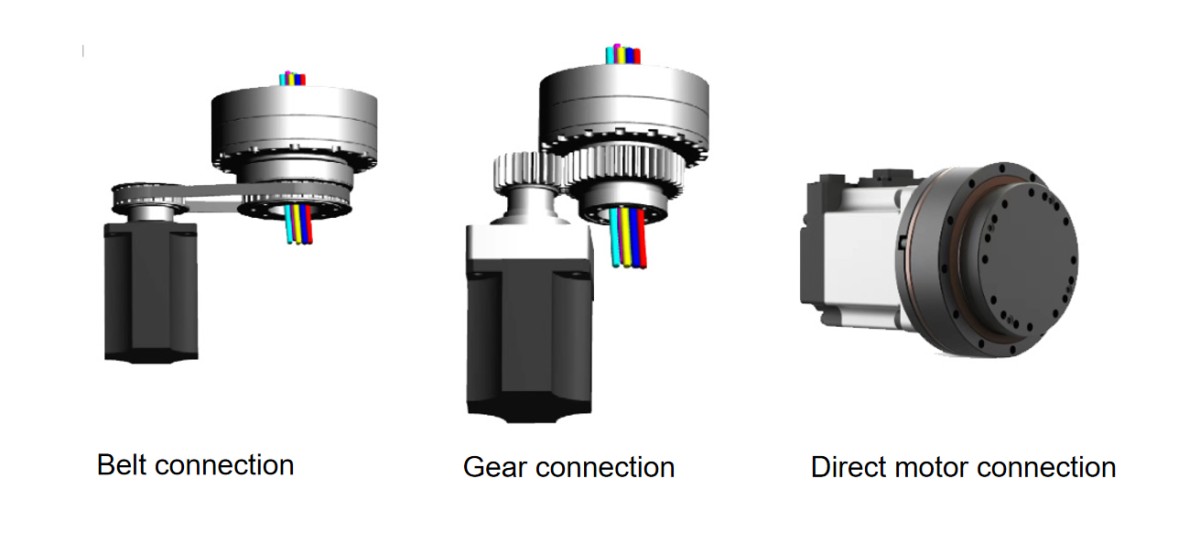
Gear Connection
Here, the motor and harmonic drive are connected through gear meshing, typically used when the motor and drive are not coaxially aligned.
Compared with belt transmission, this configuration offers higher rigidity, making it suitable for medium to heavy-load applications, such as machine tool auxiliary axes or automated production equipment.
Direct Motor Coupling
The motor is directly connected to the input side of the harmonic drive via a flange or coupling, forming an integrated motor-drive assembly.
This provides easy installation, high efficiency, and is ideal for applications that demand high precision and rigidity, such as robot joints, semiconductor manufacturing equipment, and medical machinery.
4. Comprehensive Considerations for Reliable Long-Term Performance
When selecting a harmonic drive, in addition to the basic parameters such as torque, reduction ratio, and precision, engineers must also consider:
rigidity, efficiency, service life, lubrication, installation method, and environmental adaptability.
Only by evaluating all these factors together can the system maintain stable and reliable operation over long-term use.
Read More
Learn more about the story of HONPINE and industry trends related to precision transmission.
Double Click
We provide harmonic drive reducer,planetary reducer,robot joint motor,robot rotary actuators,RV gear reducer,robot end effector,dexterous robot hand