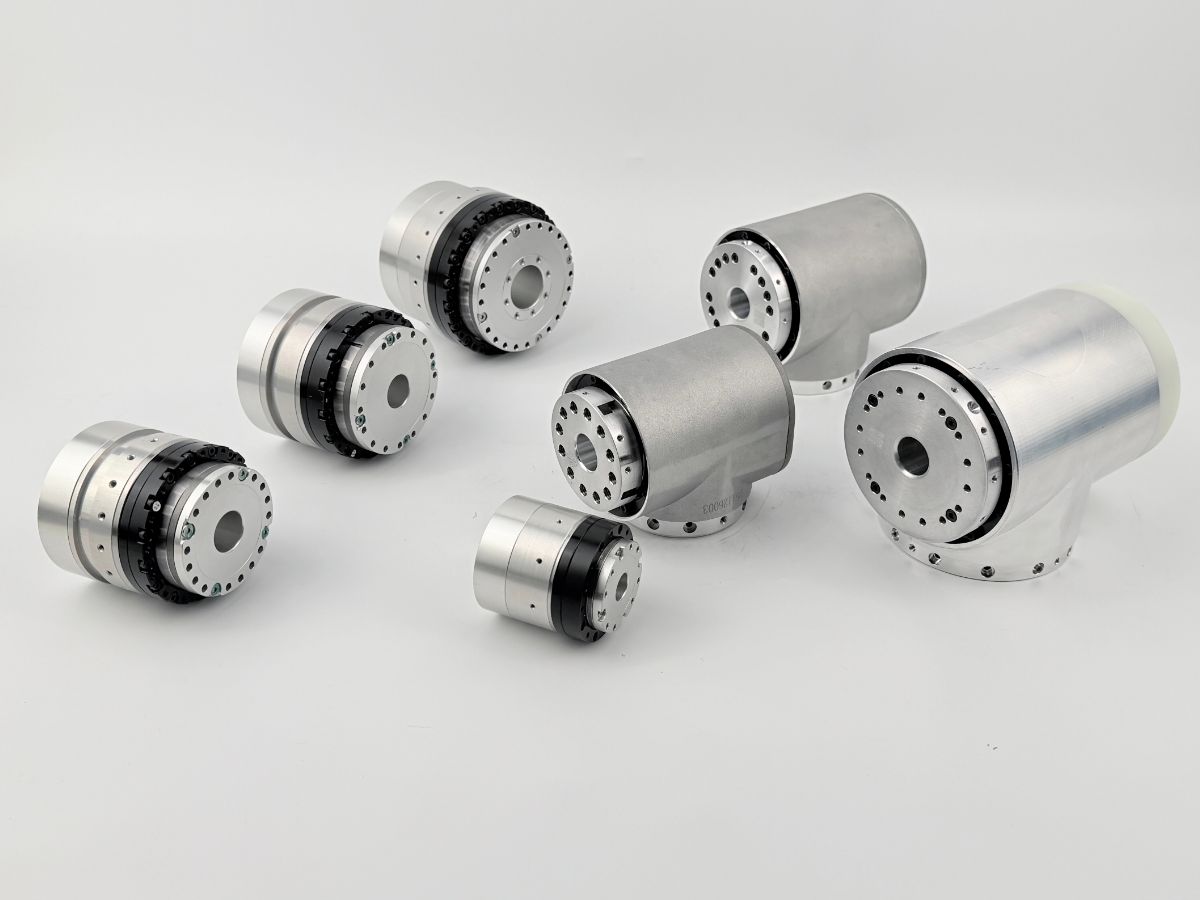
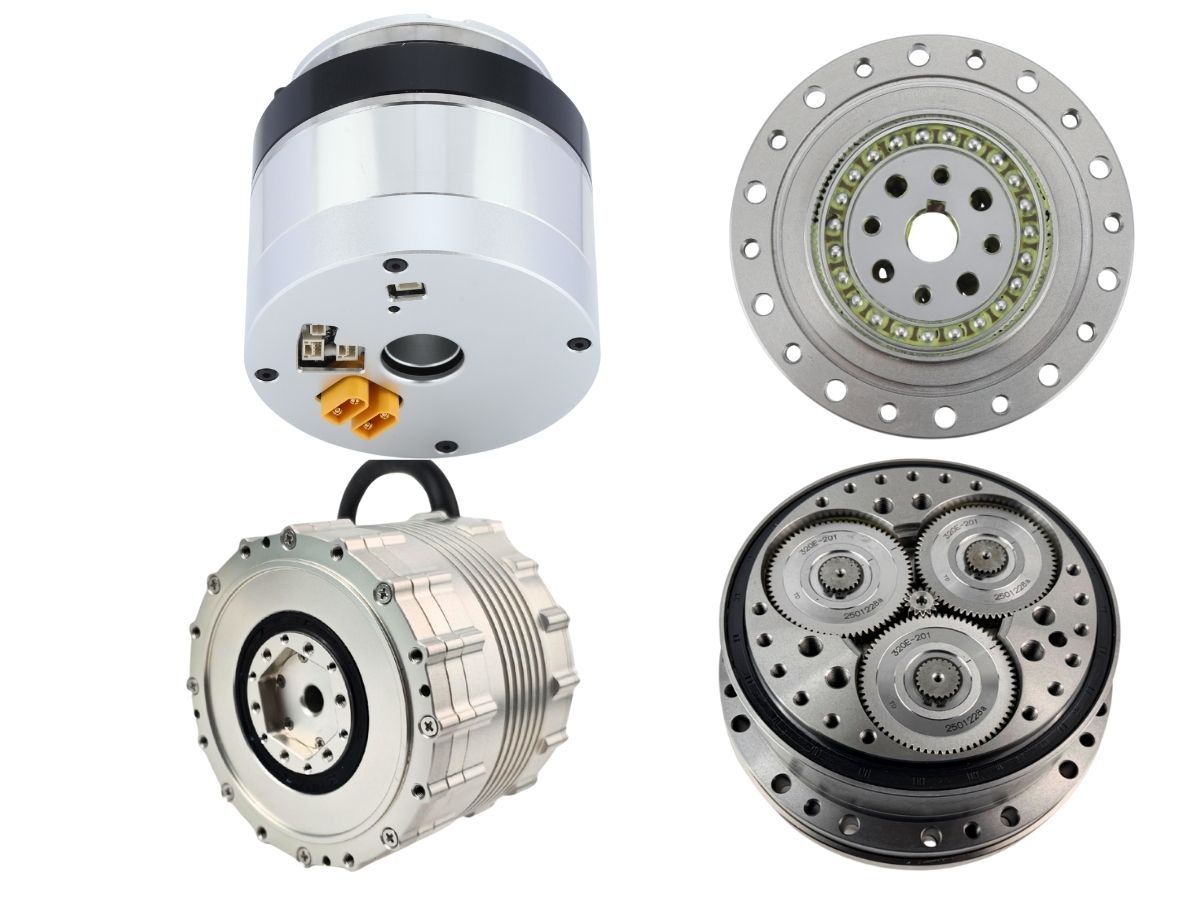
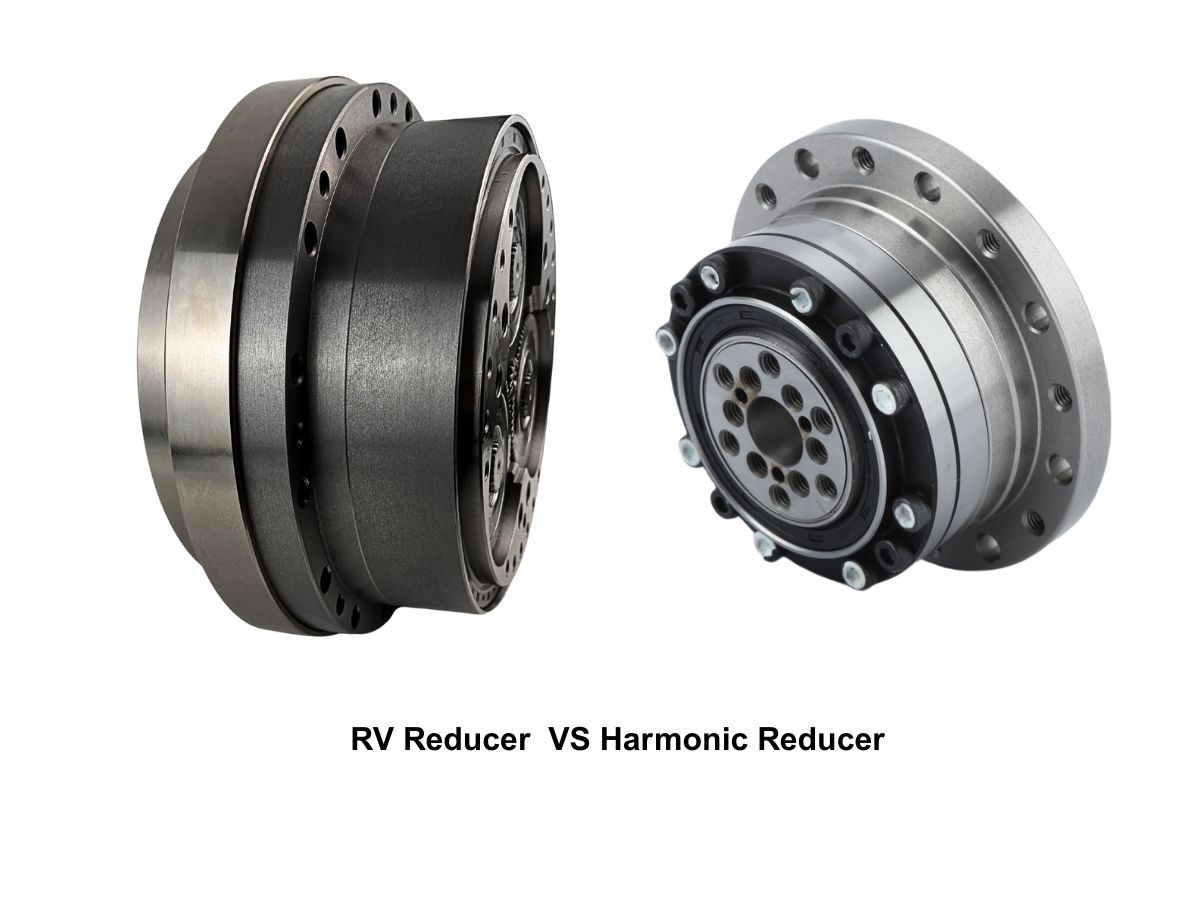
What is the Difference Between RV Reducer and Harmonic Reducer?
This article provides an in-depth comparison between RV reducers and harmonic reducers, analyzing their differences from multiple perspectives, including working principles, performance characteristics, application fields, installation methods, and long-term maintenance.
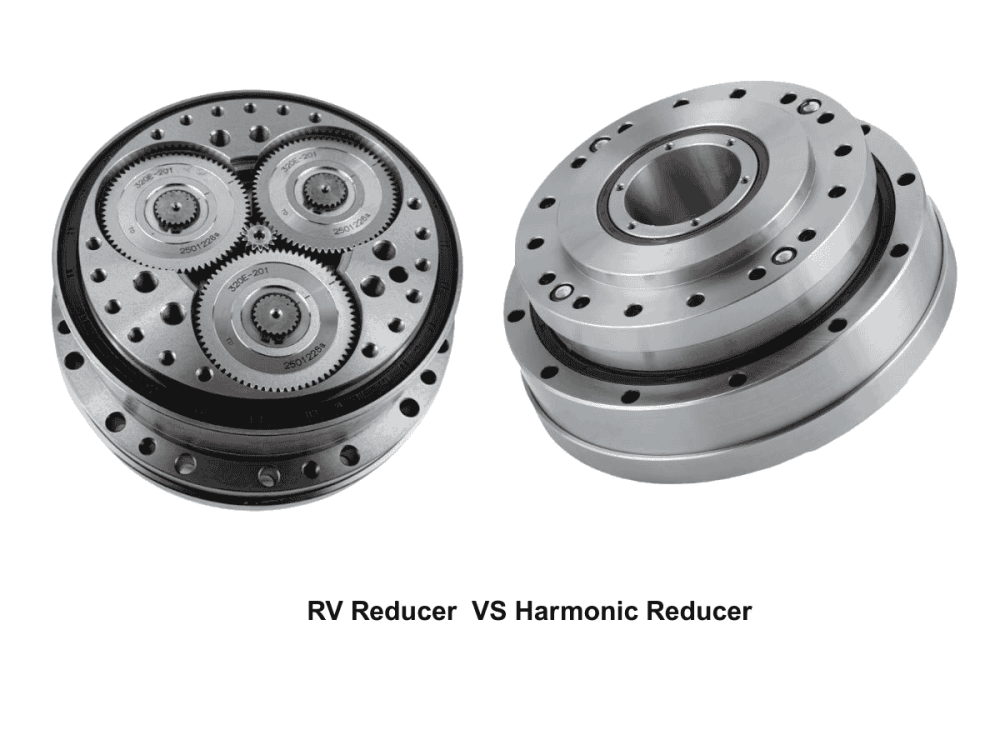
Differences in Working Principles Between RV Reducers and Harmonic Reducers
RV reducers operate based on rigid multi-tooth meshing transmission, while harmonic reducers rely on elastic deformation differential transmission.
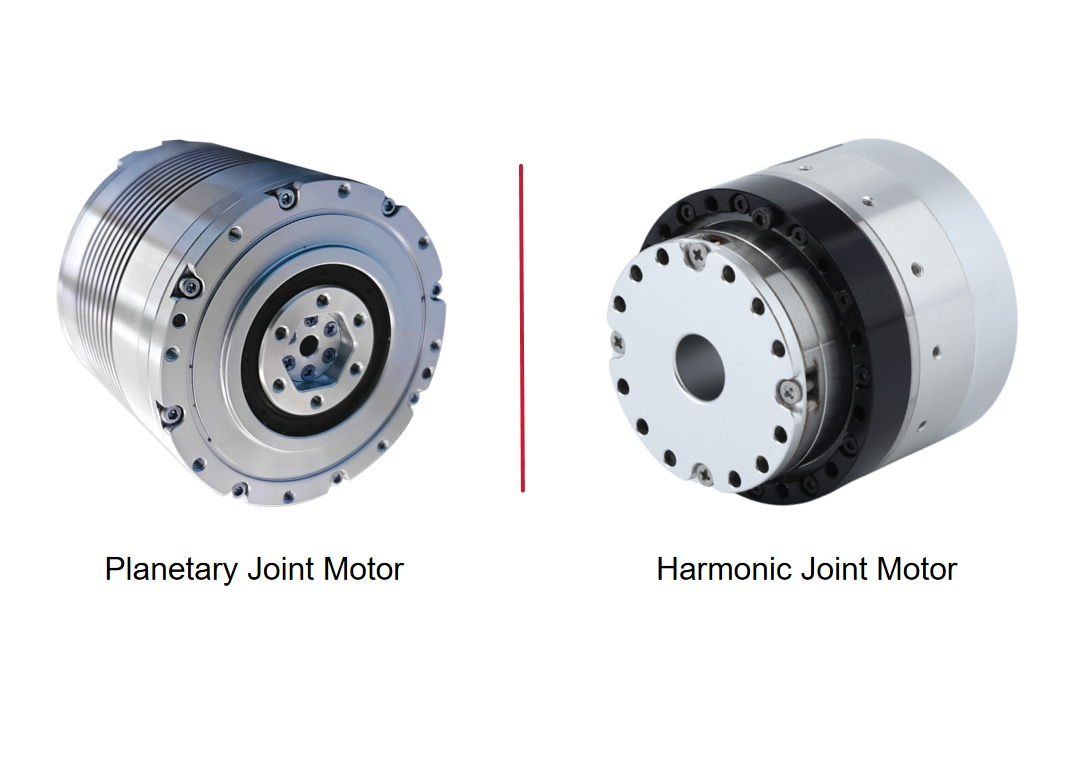
Working Principle of an RV Reducer
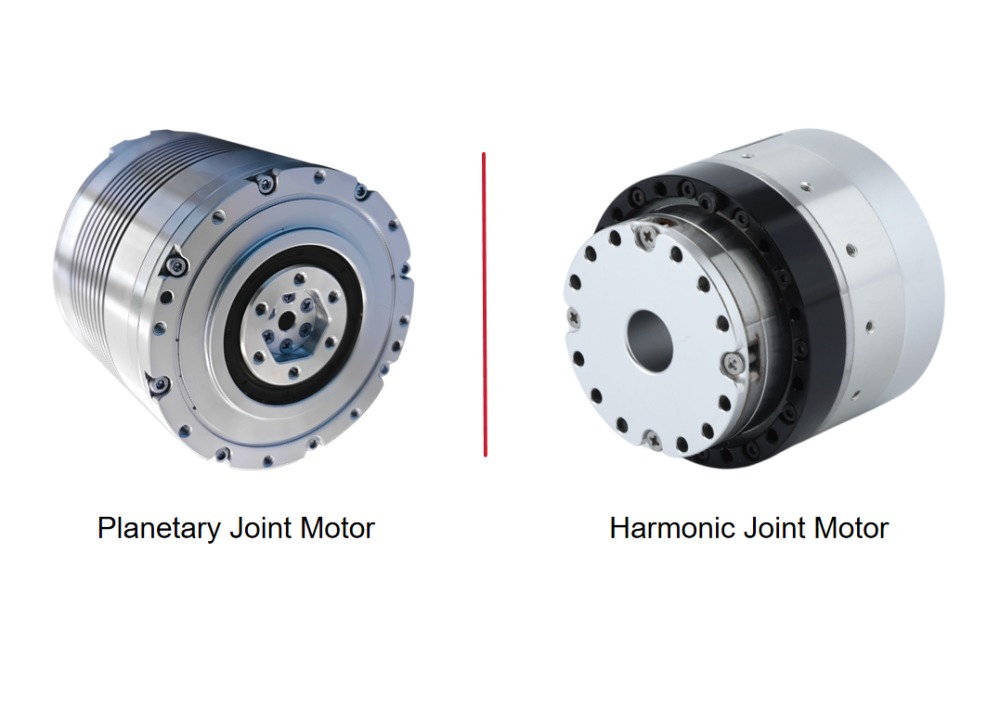
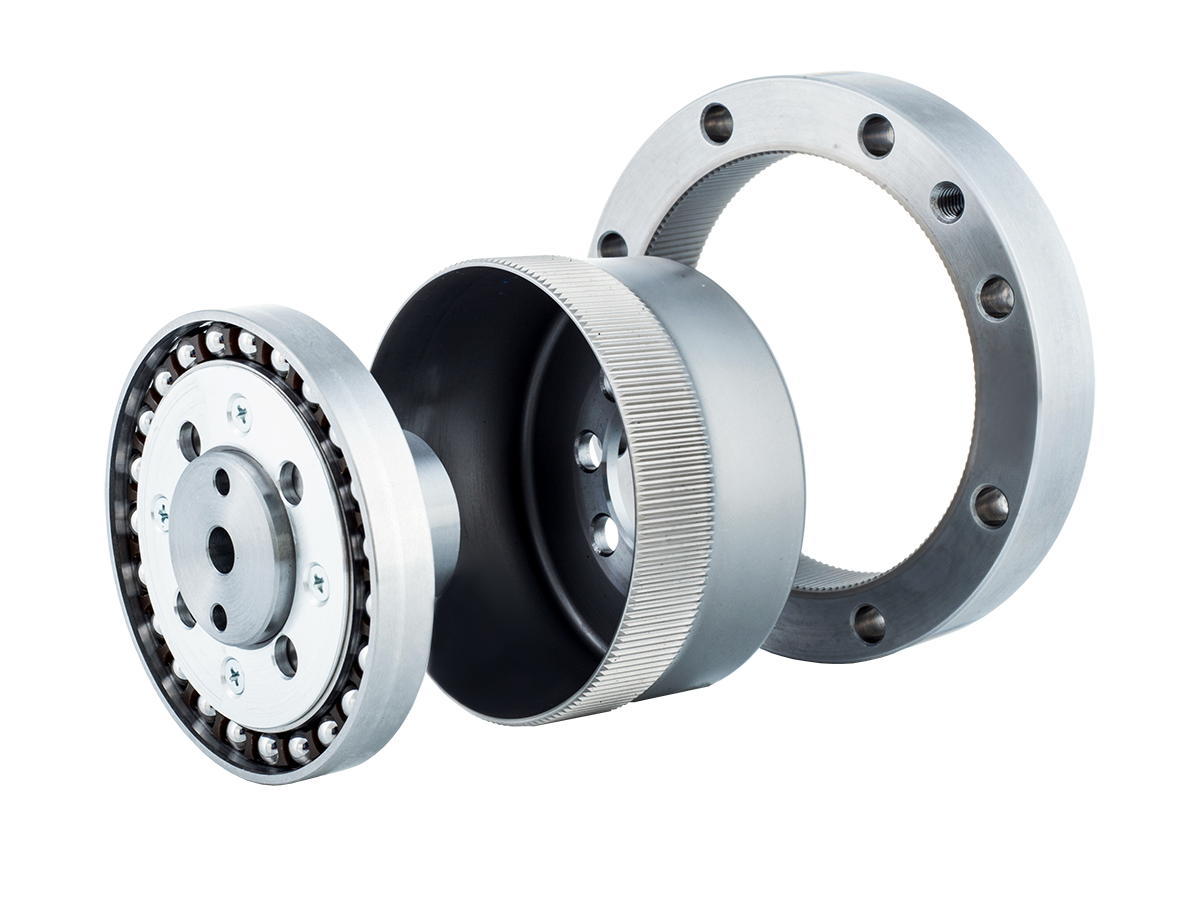
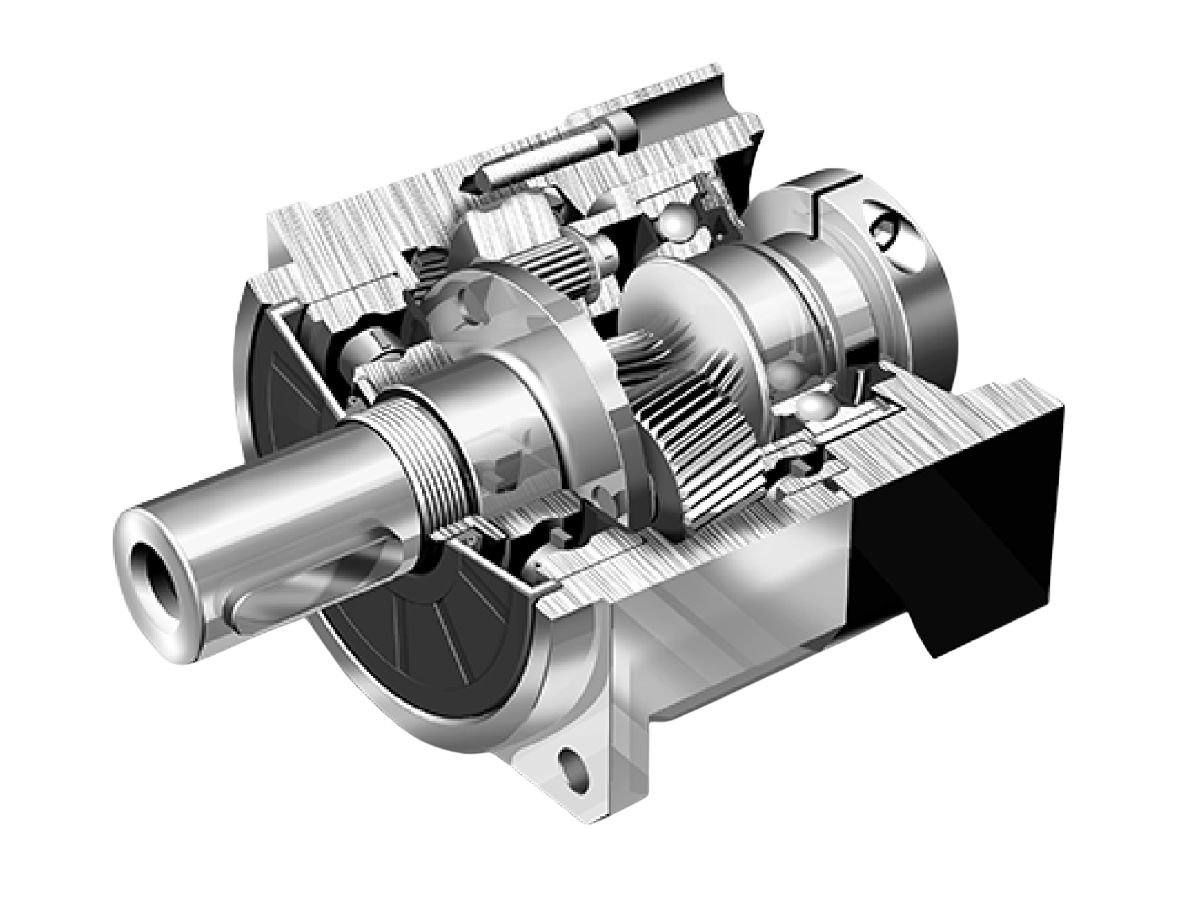
An RV reducer adopts a two-stage differential transmission structure composed of a planetary gear stage and a cycloidal pinwheel stage.The input shaft drives the planetary gear, which in turn rotates an eccentric shaft. This eccentric motion causes the cycloidal disc to perform an orbital movement. The cycloidal disc meshes simultaneously with multiple pins in the pin gear housing, achieving speed reduction and torque output.Because the transmission mainly depends on rigid contact, RV reducers feature high rigidity, high load capacity, strong impact resistance, and excellent torque transmission capability.
Working Principle of a Harmonic Reducer
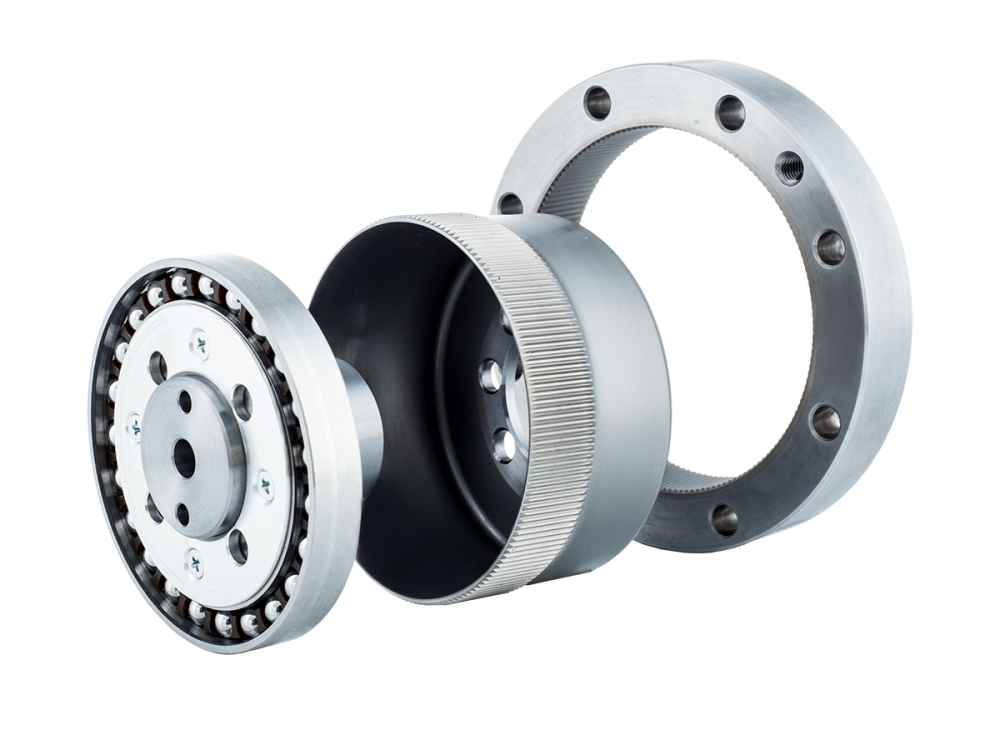
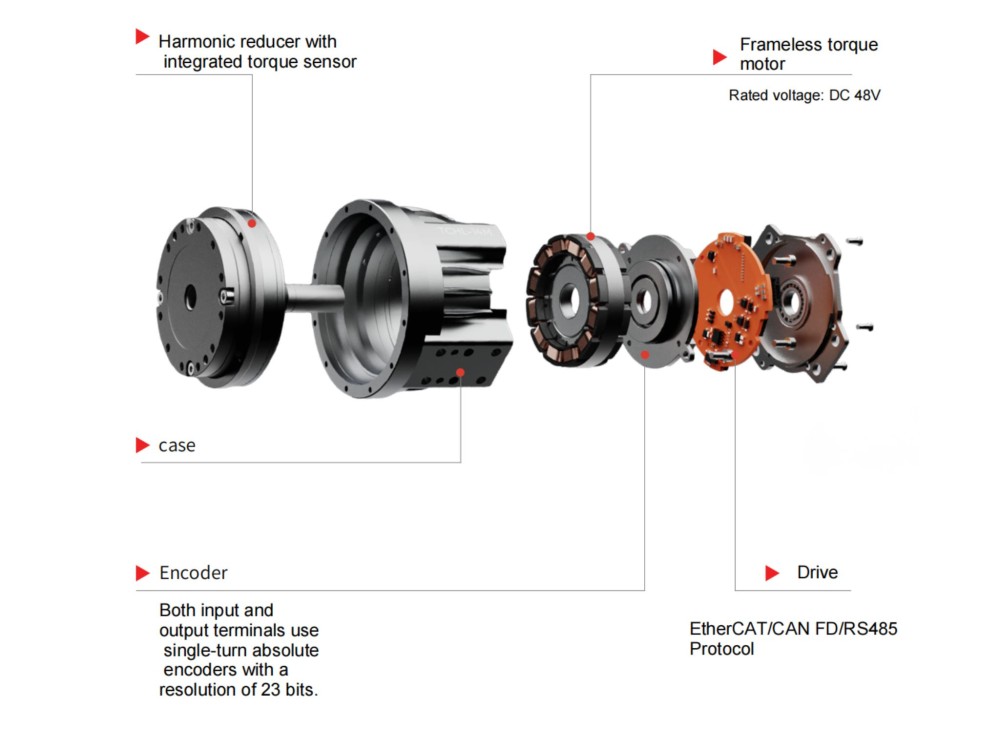
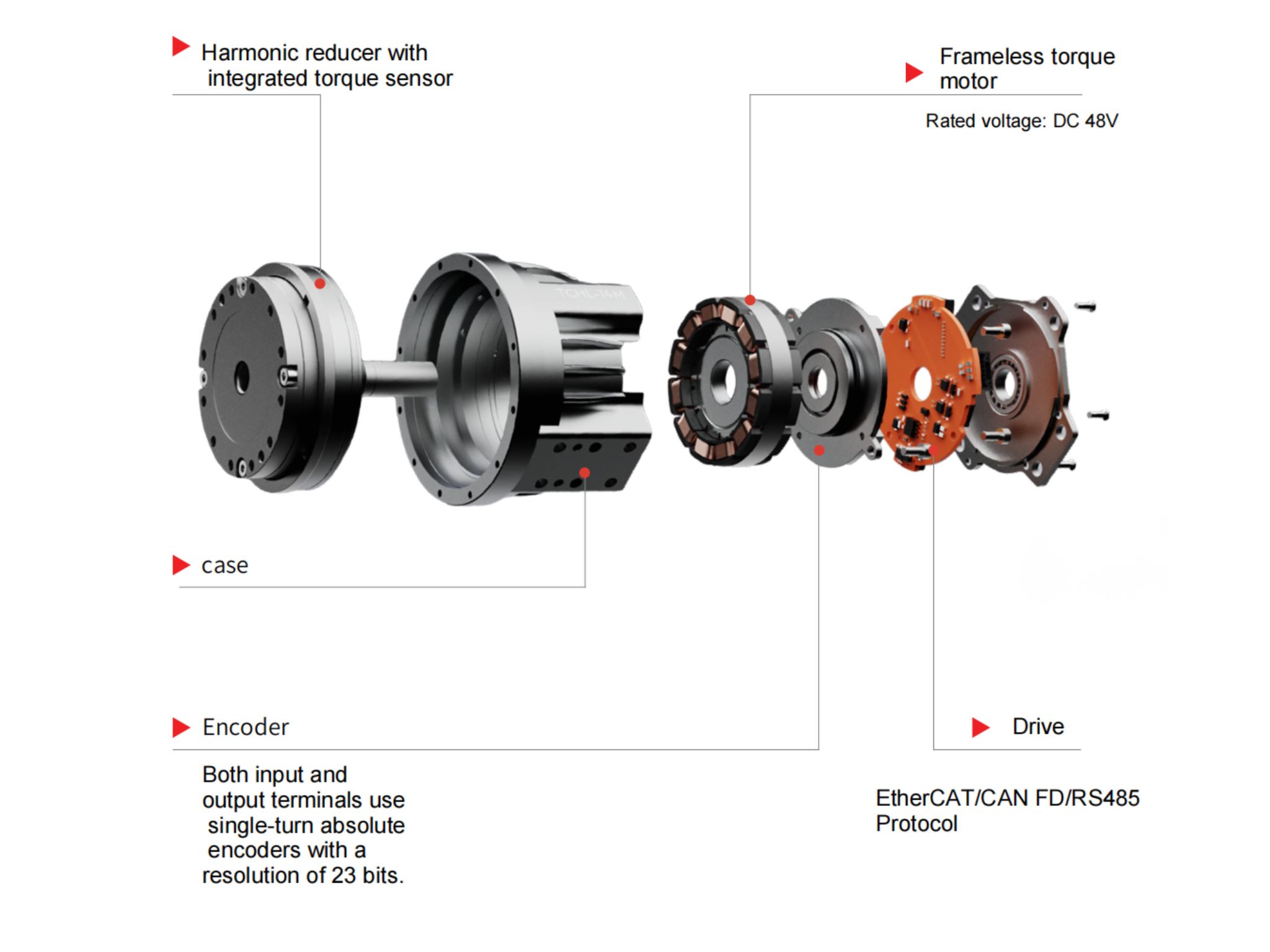
A harmonic reducer consists of three main components: a wave generator, a flexspline, and a circular spline.The input shaft drives the wave generator, causing the flexspline to undergo periodic elastic deformation. The flexspline only meshes with the circular spline at two symmetrical regions, and the difference in tooth count between the two components produces a large reduction ratio.Since power transmission depends on material elastic deformation, harmonic reducers are compact and capable of very high reduction ratios, but their rigidity and load capacity are relatively lower compared to RV reducers.
Performance Differences Between RV Reducers and Harmonic Reducers
RV Reducers
RV reducers are characterized by:
High transmission efficiency
Large torque capacity
High positioning accuracy
Strong rigidity
Excellent impact resistance
Long service life
However, they are relatively larger and heavier in size and weight.
Harmonic Reducers
Harmonic reducers offer:
Very large reduction ratios
Compact and lightweight structure
High precision
High power density
Fast dynamic response
Low noise
Their torque capacity and transmission efficiency are relatively lower. To address this limitation, HONPINE’s harmonic AC motors and harmonic DC motors adopt an integrated design, successfully mitigating these disadvantages.
Differences in Application Fields
Applications of RV Reducers
RV reducers are commonly used in high-load joints of industrial robots, such as the base, shoulder, and upper arm, typically on axes 1–4.
When the robot’s end payload exceeds approximately 20 kg, all six joints often use RV reducers to ensure overall rigidity and long-term accuracy stability.
Beyond robotics, RV reducers are widely applied in:
Heavy-duty robotic arms
CNC rotary tables
Precision indexing tables
Automated production line positioning mechanisms
Engineering and construction equipment
They are especially suitable for applications involving impact loads and continuous operation.
Applications of Harmonic Reducers
Harmonic reducers are mainly used in light-load robot joints, such as the wrist and end-effector, typically on axes 5–6.
They are widely applied in:
Collaborative robots
Medical robots
Service robots
Semiconductor manufacturing equipment
Optical positioning platforms
Aerospace and radar systems
Due to their low inertia, low noise, and high precision, harmonic reducers are highly favored. However, under long-term heavy load or high-impact conditions, the flexspline is prone to fatigue, limiting service life and long-term accuracy retention.
Installation and Mounting Differences
RV Reducers
RV reducers are typically mounted using flange connections with locating pilots. The output side usually features a flange plate, requiring high coaxiality and mounting surface flatness.HONPINE’s flange-integrated RV reducers simplify installation and provide higher overall system rigidity after mounting. Custom motor shafts are supported based on application requirements—please contact HONPINE for selection guidance.
Harmonic Reducers
Harmonic reducers are usually fixed using flexspline and circular spline flanges and often require external bearings to handle radial and axial loads. They are highly sensitive to installation stress, and improper mounting can significantly affect performance and lifespan.

Long-Term Maintenance and Durability
RV Reducers
RV reducers use cycloidal pinwheel and planetary gear rigid multi-tooth meshing. Loads are distributed across multiple teeth simultaneously, resulting in low unit tooth surface stress. Wear mainly occurs as gear surface fatigue and rolling contact wear, leading to slow, predictable performance degradation.They are well suited for continuous operation and heavy-load applications.
Harmonic Reducers
Harmonic reducers rely on repeated elastic deformation of the flexspline. The flexspline is the core wear component and is subject to material fatigue and micro-crack formation over long-term operation. Performance degradation is cumulative and may occur suddenly.
RV reducers and harmonic reducers are complementary technologies, though advances in structural design and manufacturing processes may lead to localized competition in certain applications.If your priority is heavy load capacity, high rigidity, and strong impact resistance, an RV reducer is the preferred choice.If your priority is lightweight design, high precision, and high reduction ratio, a harmonic reducer is more suitable.Choosing the appropriate reducer should always be based on specific application requirements and operating conditions.
Read More
Learn more about the story of HONPINE and industry trends related to precision transmission.
Double Click
We provide harmonic drive reducer,planetary reducer,robot joint motor,robot rotary actuators,RV gear reducer,robot end effector,dexterous robot hand