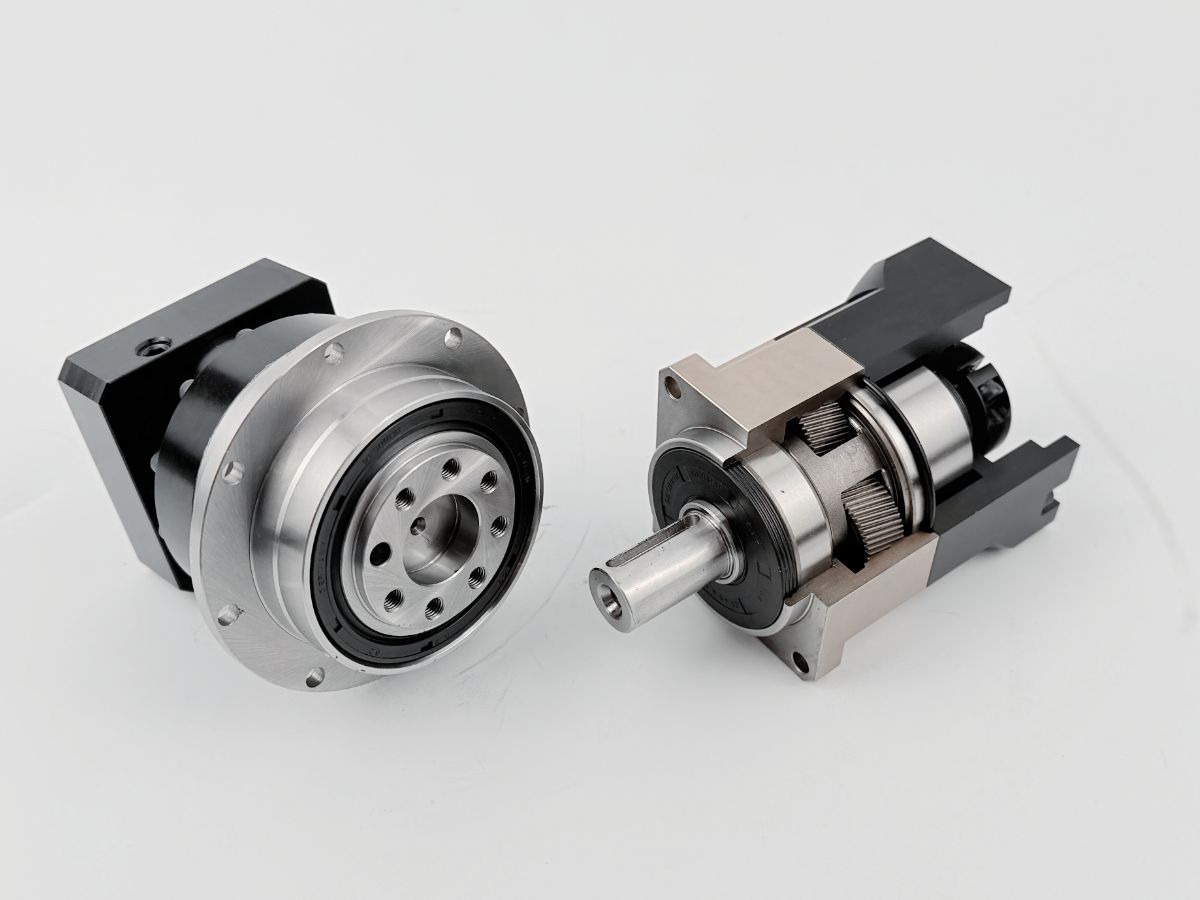
Precision Reducers and Motors Comprehensive Analysis
This article provides the most comprehensive analysis and introduction of the four major categories of precision reducers and explains their future development trends especially precision motors.
Classification of Precision Reducers
Precision reducers are mainly classified into harmonic reducers, planetary reducers, RV reducers, and cycloidal pinwheel reducers.
Precision Harmonic Reducer
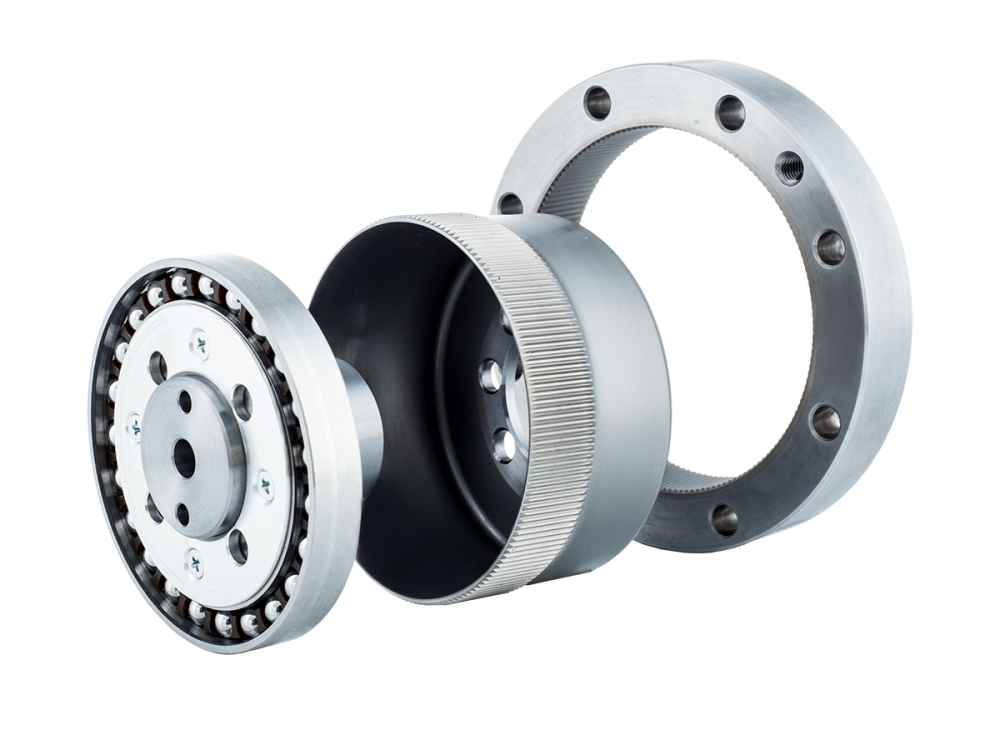
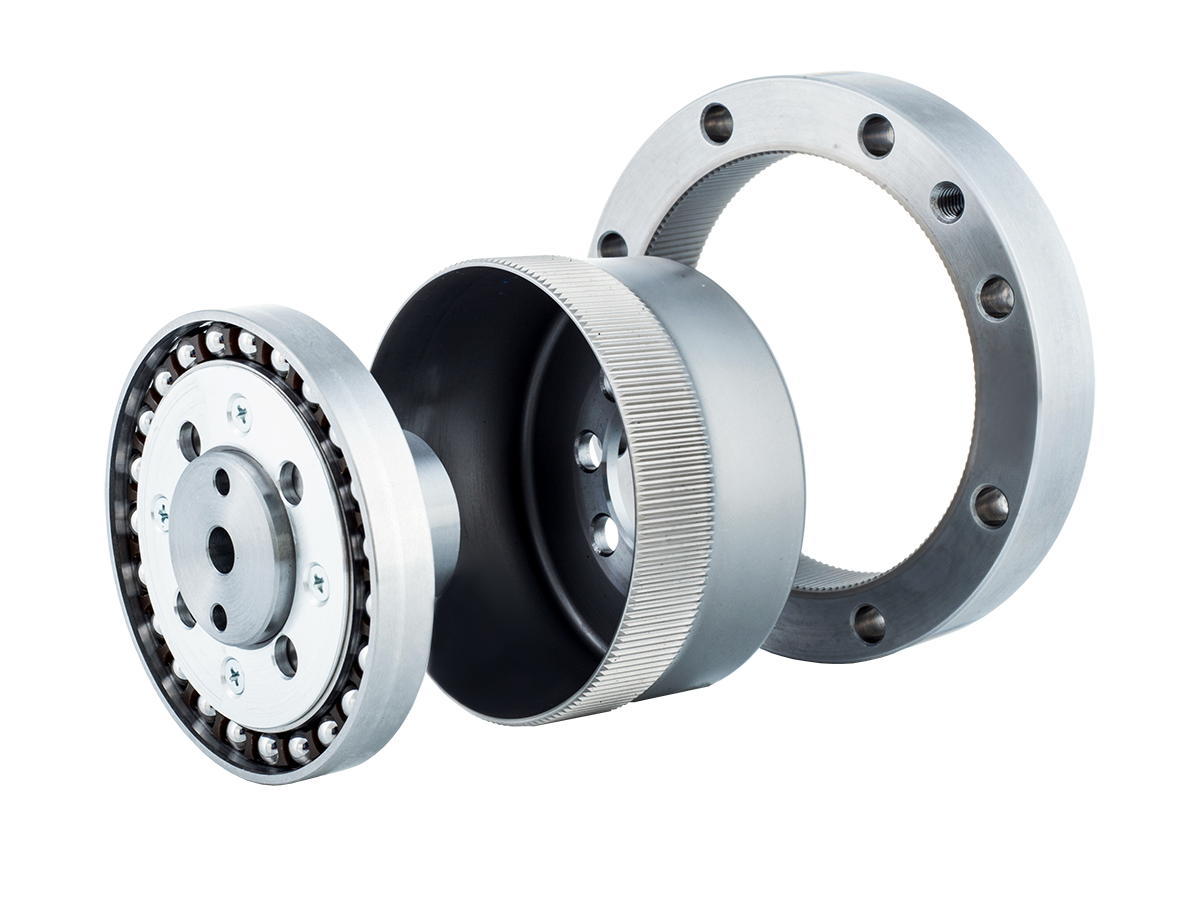
A harmonic reducer is a new type of reduction mechanism that achieves transmission through elastic deformation. It breaks away from the traditional rigid mechanical transmission mode and uses flexible components to realize mechanical power transmission. A harmonic reducer mainly consists of three basic components: a wave generator, a rigid gear with an internal tooth profile (circular spline), and a flexible gear with an external tooth profile (flexspline).
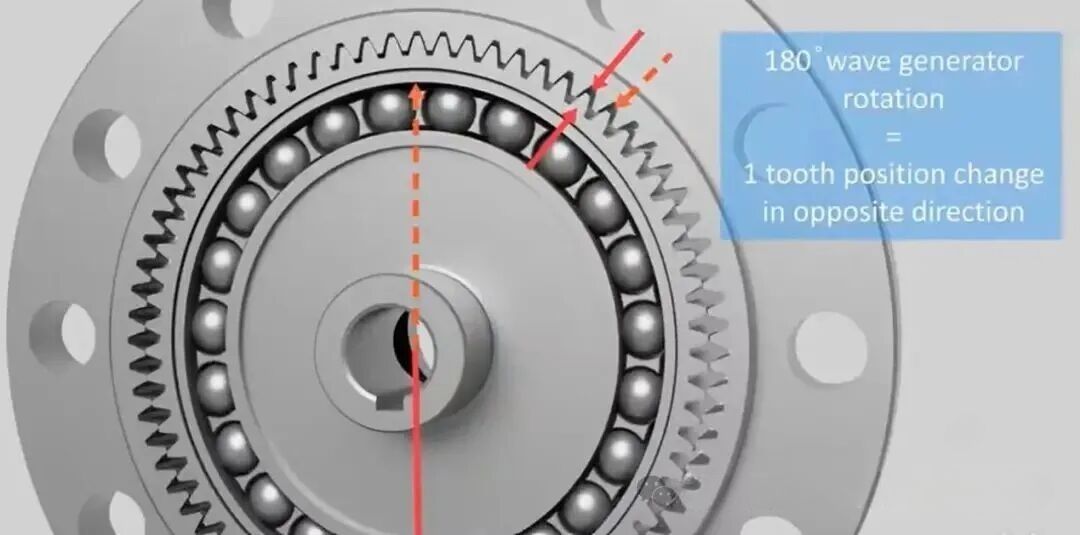
The wave generator is a cam component whose two ends press tightly against the inner wall of the flexspline. The flexspline is a thin-walled gear capable of large elastic deformation. When the wave generator is inserted into the flexspline, it forces the cross-section of the flexspline to change from a circular shape to an elliptical shape. At the two ends of the major axis, the teeth of the flexspline fully mesh with the teeth of the circular spline, while near the two ends of the minor axis, the teeth are completely disengaged from the circular spline.
Harmonic reducers feature large reduction ratios, compact outlines, a small number of components, and high transmission efficiency. They are typically installed in the forearm, wrist, or hand of robots.
Harmonic reducers achieve speed reduction and torque amplification through differential tooth motion. The typical working principle adopts a configuration in which the wave generator is the input, the circular spline is fixed, and the flexspline is the output. The elliptical wave generator is connected to the motor shaft and installed inside the circular flexspline, forcing elastic deformation. At the major axis, the flexspline teeth fully engage with the circular spline teeth, while at the minor axis they are completely disengaged, with the remaining regions in transitional engagement. As the wave generator rotates continuously, the flexspline repeatedly deforms and produces differential tooth motion. The engagement state continuously changes through engagement, full meshing, disengagement, and re-engagement, causing the flexspline to rotate slowly relative to the circular spline in the opposite direction of the wave generator, thereby transmitting motion.
Precision Planetary Reducer
A precision planetary reducer mainly consists of a sun gear, planet gears, a planet carrier, and a ring gear. Its reduction principle is based on gear transmission. During operation, a servo motor or other prime mover drives the sun gear to rotate. The meshing between the sun gear and the planet gears causes the planet gears to rotate about their own axes. At the same time, the planet gears mesh with the internal ring gear fixed to the housing, causing them to roll along the ring gear while rotating, forming a “revolution” motion around the sun gear.
The planet gears transmit motion to the planet carrier, which is connected to the output shaft and delivers output torque. Typically, multiple planet gears operate simultaneously, sharing the load and jointly driving the output.
Precision planetary reducers are mainly available in single-stage and multi-stage structures. Multi-stage planetary reducers add multiple stages based on a single-stage design, with each stage consisting of a sun gear, planet gears, and a ring gear, forming a cascaded structure to further reduce output speed and increase torque. While multiple planet gears distribute the load and improve load capacity, each additional gear mesh reduces transmission efficiency. To maintain compactness, multi-stage planetary reducers usually share a common ring gear, which also serves as the housing.

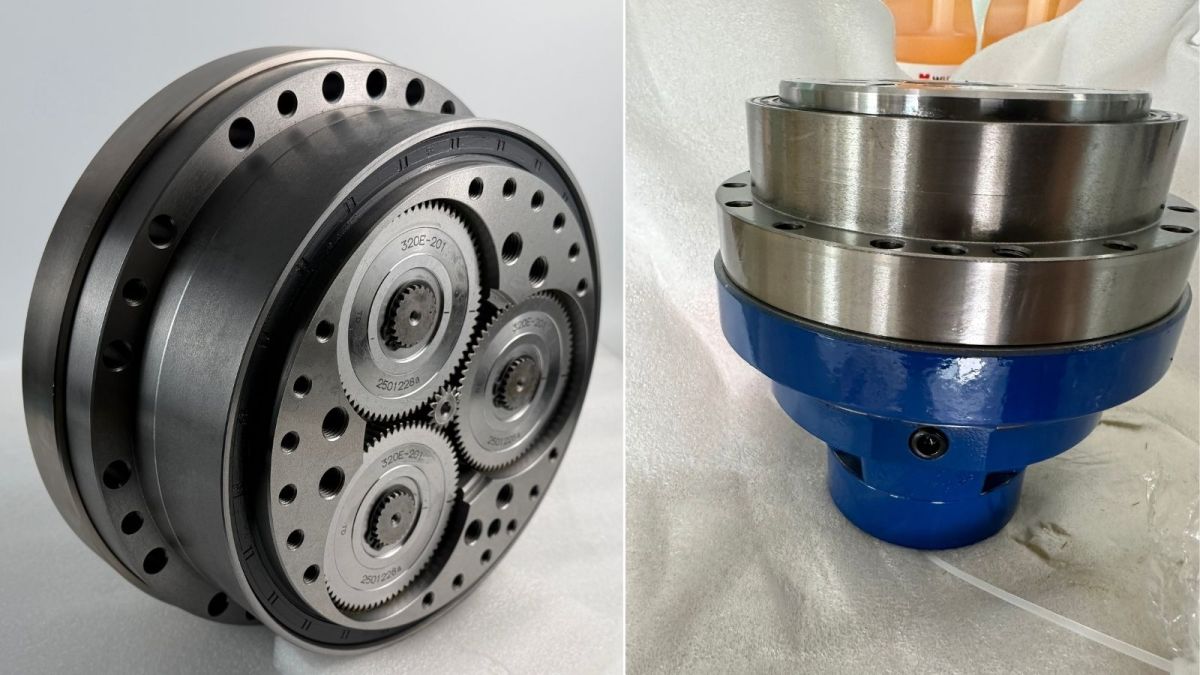
Precision RV Reducer
An RV reducer is a two-stage reduction system composed of a first-stage planetary gear reducer and a second-stage cycloidal pinwheel reducer.
First-stage reduction: The sun gear is connected to the motor, and the motor drives the sun gear to rotate. The sun gear drives the planet gears, which are connected to a crankshaft whose front and rear ends are connected to the planet gears and the RV gears (cycloidal discs). As the planet gears rotate, the crankshaft rotates at the same speed. Due to the higher tooth count of the planet gears, their rotational speed is lower than that of the input gear, achieving the first-stage reduction.
Second-stage reduction: The input shaft is the crankshaft from the first stage. Two cycloidal discs (RV gears) are mounted on the eccentric portion of the crankshaft via needle bearings. The number of pins in the housing’s pin ring is one more than the number of teeth on the cycloidal discs. When the crankshaft rotates one revolution, the cycloidal discs complete one eccentric motion cycle and rotate one tooth in the opposite direction of the crankshaft, achieving further reduction.

Cycloidal Pinwheel Reducer
The cycloidal pinwheel reducer adopts precision cycloidal transmission technology, first proposed by German engineer Lorenz Braren in 1926. It is a small-tooth-difference planetary transmission using an epicycloidal tooth profile. Because its key components are cycloidal discs and pinwheels, it is known as a cycloidal pinwheel reducer and is a type of RV reducer.
Specifically, “cycloidal” refers to the actual profile of the cycloidal disc, which is an equidistant curve of a short epicycloid. According to the internal rolling method, a rolling circle rolls without slipping inside a fixed base circle, creating a cycloidal trajectory. A point fixed to the rolling circle traces a short epicycloid during rolling. By drawing equal-radius circles centered on points along this trajectory, the envelope of these circles forms the actual tooth profile of the cycloidal disc.
Characteristics and Application Scenarios of Different Reducers
RV reducers feature high precision, large reduction ratios, high rigidity, strong overload capacity, long service life, and high fatigue strength, with low vibration, low noise, and low energy consumption. They are commonly used in robot joints with large torque requirements, such as the leg, waist, and elbow joints, and in heavy-load industrial robots. The first, second, and third axes typically use RV reducers. Due to their wide reduction ratio range, stable precision, high fatigue strength, and high rigidity and torque capacity, RV reducers are particularly advantageous in heavy-load positions such as robot arms and bases.
Harmonic reducers feature large and flexible reduction ratios, high precision, compact size, light weight, smooth transmission, low noise, and the ability to transmit motion in sealed spaces. Compared with conventional reducers, harmonic reducers achieve the same output torque with smaller size and lower weight, giving them advantages in robot forearms, wrists, and hands. However, their motion accuracy decreases over time, so they are generally used in light-load industrial robots or the terminal axes of large robots, as well as in aerospace, precision machining, and medical equipment.
Planetary reducers are widely used in servo, stepper, and DC drive systems due to their compact size and long service life. However, single-stage planetary reducers have limited reduction ratios, and achieving high torque requires multi-stage configurations, which increase size and weight. Applications include mobile robots, new energy equipment, high-end machine tools, and intelligent transportation. Tesla’s Optimus robot uses planetary reducers in dexterous hands, while some robot manufacturers apply planetary reducers in legs and hip joints.
Cycloidal pinwheel reducers offer high load capacity, relatively high transmission accuracy, compact size, light weight, and smooth transmission due to multi-tooth engagement. Although their structure is complex and their precision is slightly lower than that of harmonic reducers, their high load capacity gives them strong potential for use in high-load joints such as humanoid robot waists and hips.
Comparison of Different Precision Reducers
Harmonic reducer: working principle involves wave generator motion driving flexspline deformation and meshing with the circular spline through a small tooth difference to achieve reduction; structure consists of wave generator, flexspline, and circular spline; higher unit price; lower weight; high transmission accuracy; relatively high efficiency; high reduction ratio; long design life; relatively high torsional rigidity; advantages include high reduction ratio, high precision, compact structure, and light weight; disadvantages include limited load capacity and shorter service life.
Planetary reducer: working principle involves planet gears rotating under the drive of the sun gear; simple structure consisting of sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear; lower unit price; lower weight; average transmission accuracy; high efficiency; moderate reduction ratio; long design life; high torsional rigidity; advantages include simple structure and compact single-stage design; disadvantages include lower reduction ratio and lower output torque.
RV reducer: two-stage transmission with planetary and cycloidal stages; complex structure with many components; high unit price; higher weight; high transmission accuracy; high efficiency; high reduction ratio; long design life; high torsional rigidity; advantages include strong load capacity, high torsional rigidity, and stable precision; disadvantages include large size and limited application scenarios.
Cycloidal pinwheel reducer: working principle involves eccentric motion driving cycloidal discs to revolve around pinwheels using a small tooth difference; structure includes cycloidal discs, pinwheels, and eccentric shafts; relatively high unit price; lower weight; relatively high transmission accuracy; high efficiency; high reduction ratio; long design life; high torsional rigidity; advantages include large load capacity, compact size, light weight, and smooth transmission; disadvantages include complex manufacturing and lower precision compared to harmonic reducers.
Principles, Parameters, Advantages, and Disadvantages of Precision Reducers
Key technical indicators of precision reducers include torsional rigidity, reduction ratio, transmission efficiency, transmission accuracy, transmission error, starting torque, lost motion, and backlash.
Torsional rigidity refers to the ability of a component to resist torsional deformation under torque, or the ratio of rated load torque to elastic angular deformation, influenced by structural design, bearing support method, bearing type, gear stiffness and accuracy, and reduction ratio.
Reduction ratio is the ratio of input speed to output speed; a larger reduction ratio results in lower output speed and higher torque, influenced by gear tooth numbers and the number of reduction stages.
Transmission efficiency is the ratio of output power to input power and is affected by reduction ratio, speed, load torque, temperature, lubrication conditions, material selection, transmission stages, structural design, gear accuracy, gear positioning, and assembly quality.
Transmission accuracy and transmission error describe how closely the actual output angle matches the theoretical angle during unidirectional input rotation; they are influenced by design, machining, assembly, and lubrication.
Starting torque is the torque required for no-load startup and is influenced by structural design, reduction ratio, friction coefficients, and bearing quality.
Lost motion refers to the angular lag of the output shaft when the input shaft reverses direction and is influenced by design, manufacturing quality, wear, installation, and adjustment.
Backlash refers to the small angular displacement at the input when the output and housing are fixed and ±2% rated torque is applied alternately; it is affected by gear accuracy, bearing precision, oil film thickness, machine tool accuracy, assembly precision, and operating temperature.
Why Precision Motors Are the Future Trend
A precision motor is an integrated module that combines a precision reducer with a motor. With the rapid development of industrial automation, humanoid robots, semiconductor equipment, and medical devices, demand for integrated reducer–motor solutions continues to grow.
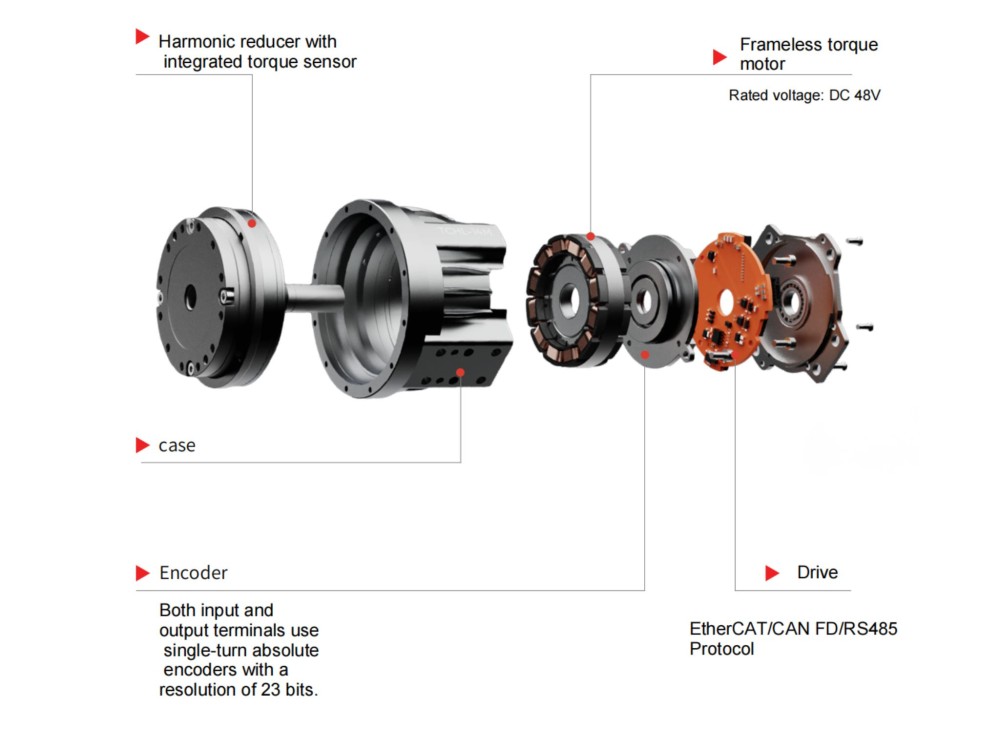
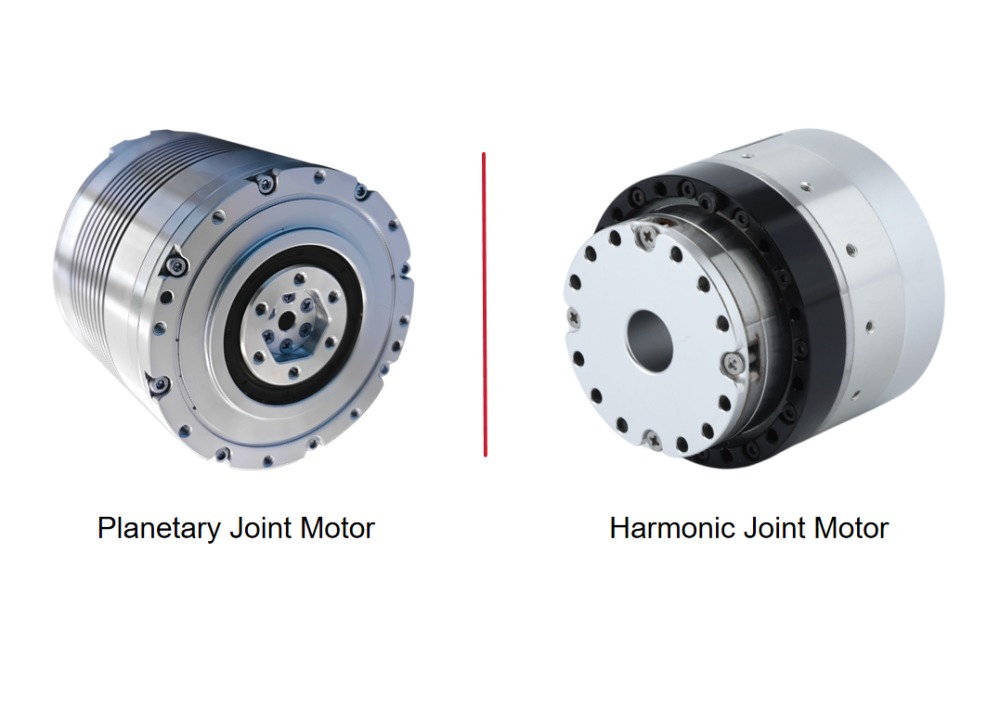
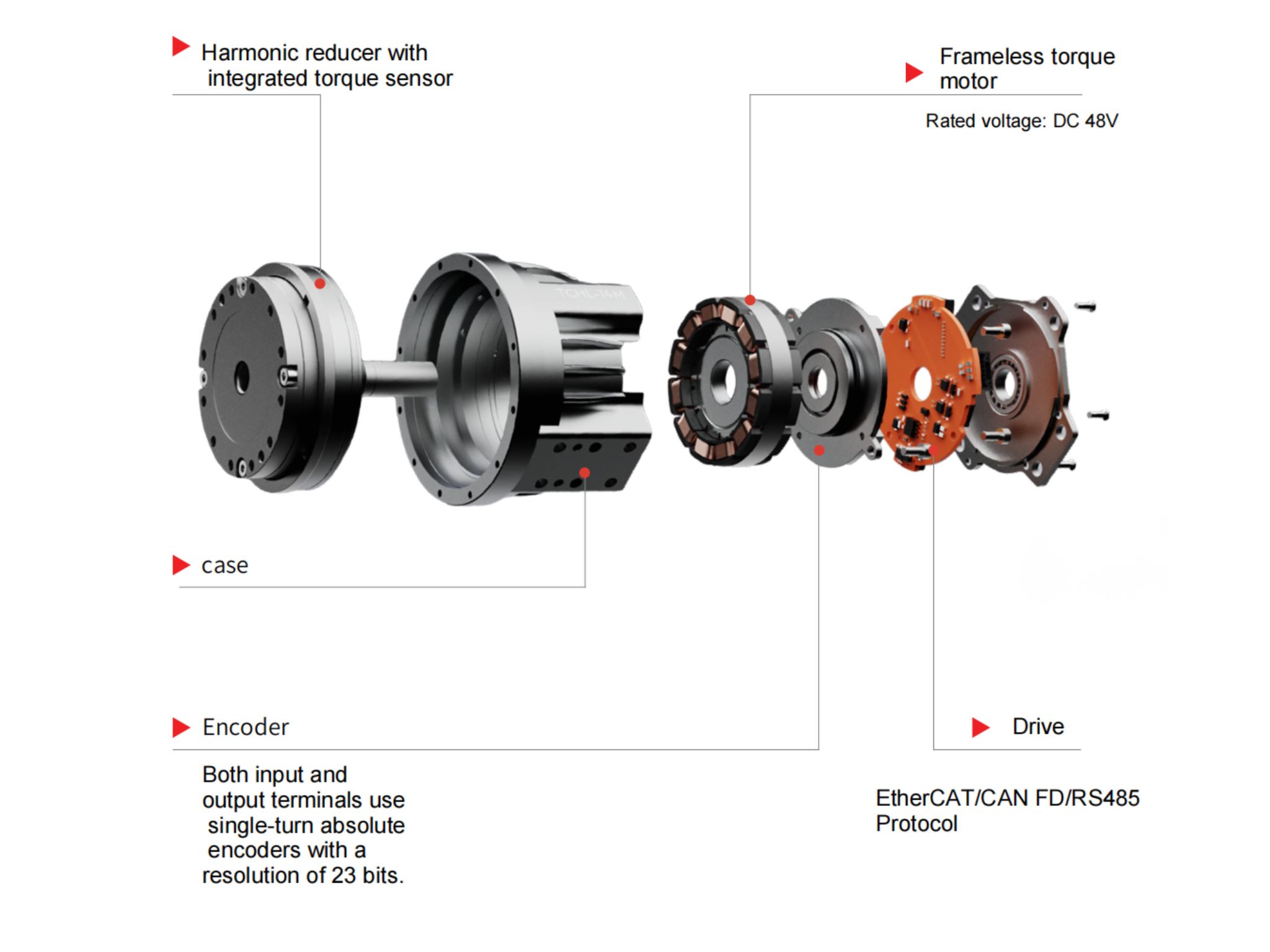
What Is a Harmonic Gear Motor?
A harmonic gear motor consists of a harmonic gear, frameless torque motor, brake, encoder, and drive unit. As a core component in the robotics industry, advancements in harmonic gear motor technology will continue to promote the development of specialized robots and humanoid robots toward greater flexibility and broader application scenarios. Beyond robotics, robot joint motors are also used in semiconductor equipment, photovoltaic equipment, precision medical equipment, 3C equipment, optical equipment, and other fields.
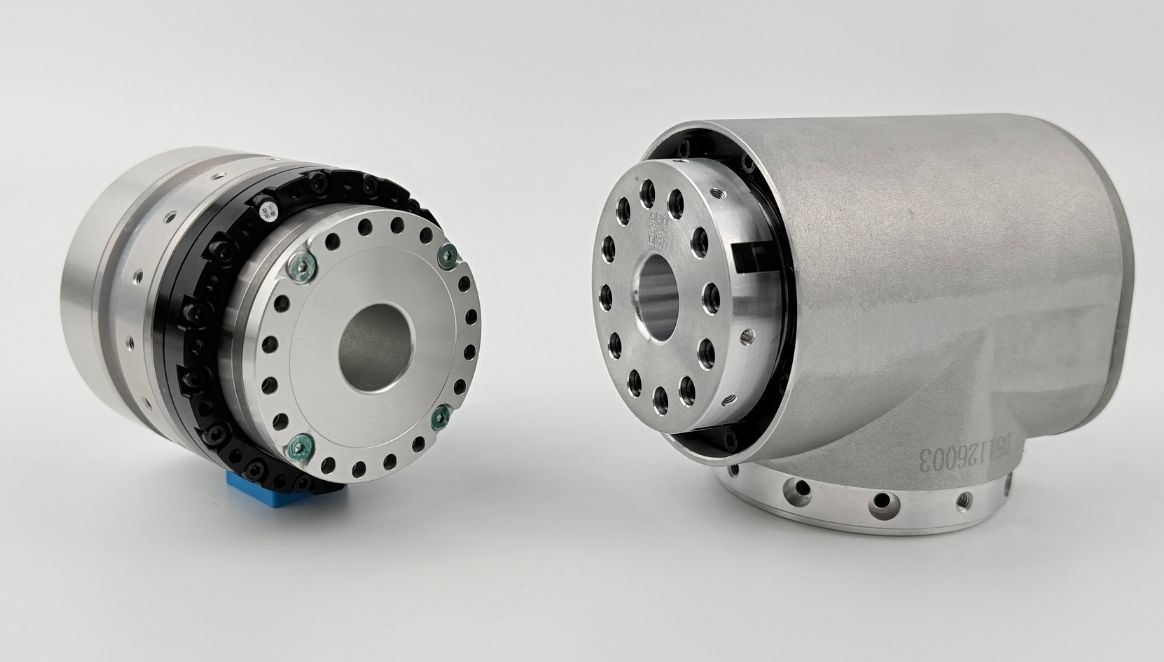

What Is a Planetary Reducer Motor?
The planetary reducer motor is a core component of robotic power systems. Through a highly integrated design combining a planetary reducer, frameless torque motor, brake, encoder, and driver, it achieves significant optimization in volume and weight and enables precise joint motion control. This results in greater torque, smaller size, and lighter weight. Compared with harmonic gear motors, planetary reducer motors feature smaller reduction ratios, higher output speeds, and higher torque density, making them more suitable for medium-to-low load applications. Customization services tailored to specific customer requirements are also available. With advantages such as high-speed performance, impact resistance, and compact lightweight design, standard planetary joint modules have become preferred solutions for humanoid robots, specialized robots, logistics AGVs, and industrial automation, driving improved robotic performance and expanded application scenarios.
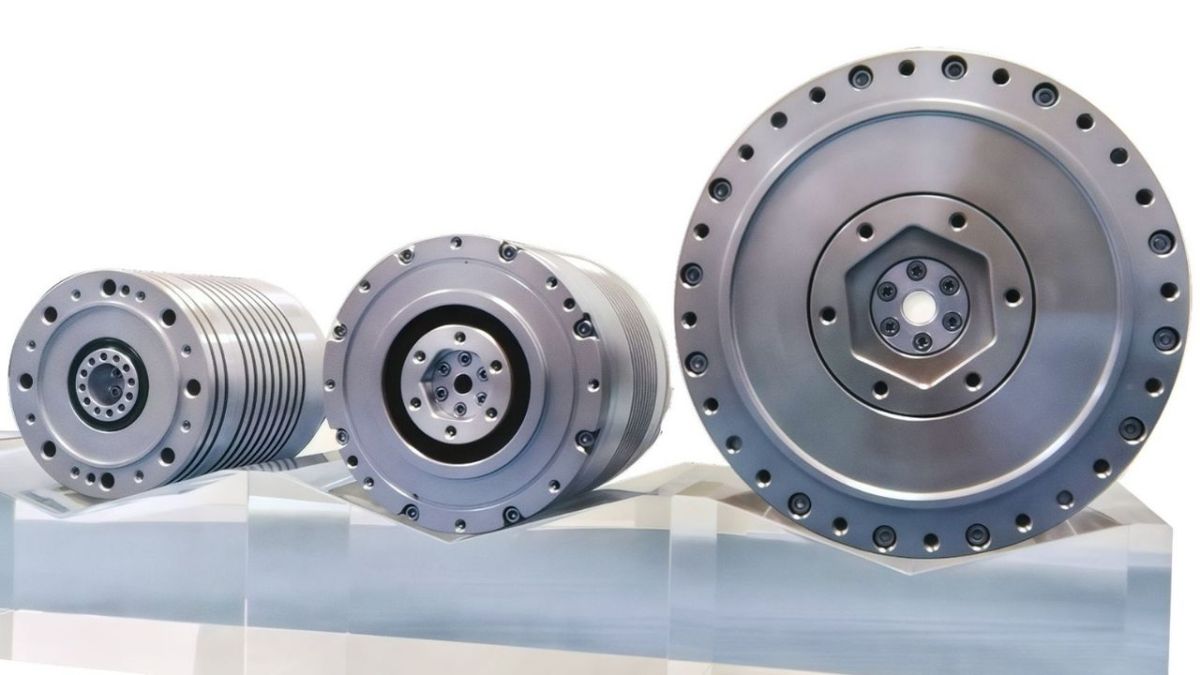

What Is a Flange RV Reducer?
The flange-integrated RV reducer is a high-precision reduction device designed for advanced machinery. Its internal mechanism features a unique two-stage combination of cycloidal and planetary gears enclosed in a sealed unit. The reducer is supplied fully assembled with an integrated flange and pre-lubricated with special grease, allowing direct installation and immediate use with a servo motor without additional preparation.
RV reducers are commonly used in industrial robots, particularly in base and high-load joints (joints 1 to 4) for robotic arms with payloads of 20 kg or less. When the payload exceeds 20 kg, all six joints are typically equipped with RV reducers. These reducers play a critical role in maintaining positioning accuracy.
The flange-integrated RV reducer is a specialized version developed by incorporating a flange seal into the traditional RV reducer design. Similar to standard RV reducers, flange-integrated models are classified into two types: the Flange-Integrated E Series with a solid shaft and the Flange-Integrated C Series with a hollow shaft.
Precision reducers are evolving toward simultaneous performance upgrades and deeper mechatronic integration. In particular, harmonic reducers must adopt mechatronic integration by combining harmonic reducers with motors, encoders, brakes, sensors, and other components to provide high value-added modular products, enabling better applications in humanoid robots, semiconductor equipment, optical systems, and precision measurement industries.
Read More
Learn more about the story of HONPINE and industry trends related to precision transmission.
Double Click
We provide harmonic drive reducer,planetary reducer,robot joint motor,robot rotary actuators,RV gear reducer,robot end effector,dexterous robot hand