Harmonic Drive Gearbox – Complete Introduction and Analysis
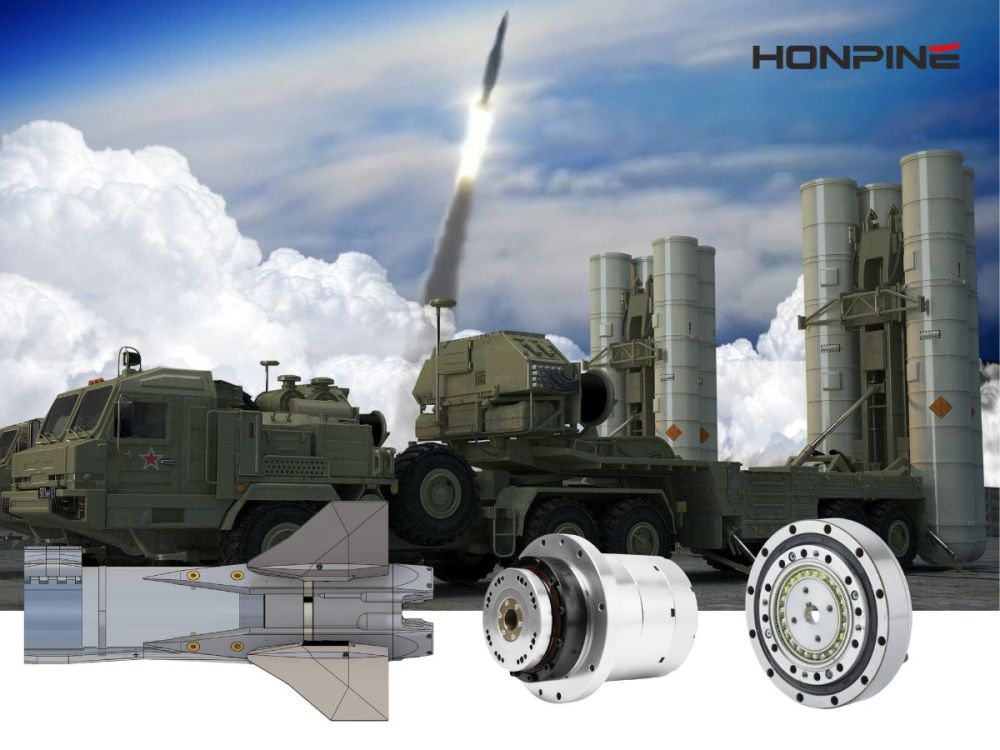
The Harmonic Drive Gearbox, also known as a Strain Wave Gearbox, is irreplaceable in applications requiring high precision, compact size, and low load.It is widely used in collaborative robots, servo systems, precision positioning and scanning equipment, aerospace, defense, and other high-precision systems.Thanks to its zero backlash, high reduction ratio, lightweight design, high positioning accuracy, and excellent repeatability, the harmonic drive has become an essential precision transmission solution in many advanced fields.
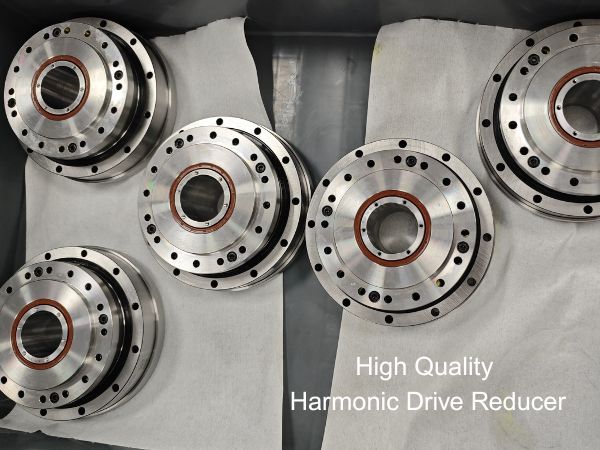
Basic Structure of a Harmonic Drive Gearbox
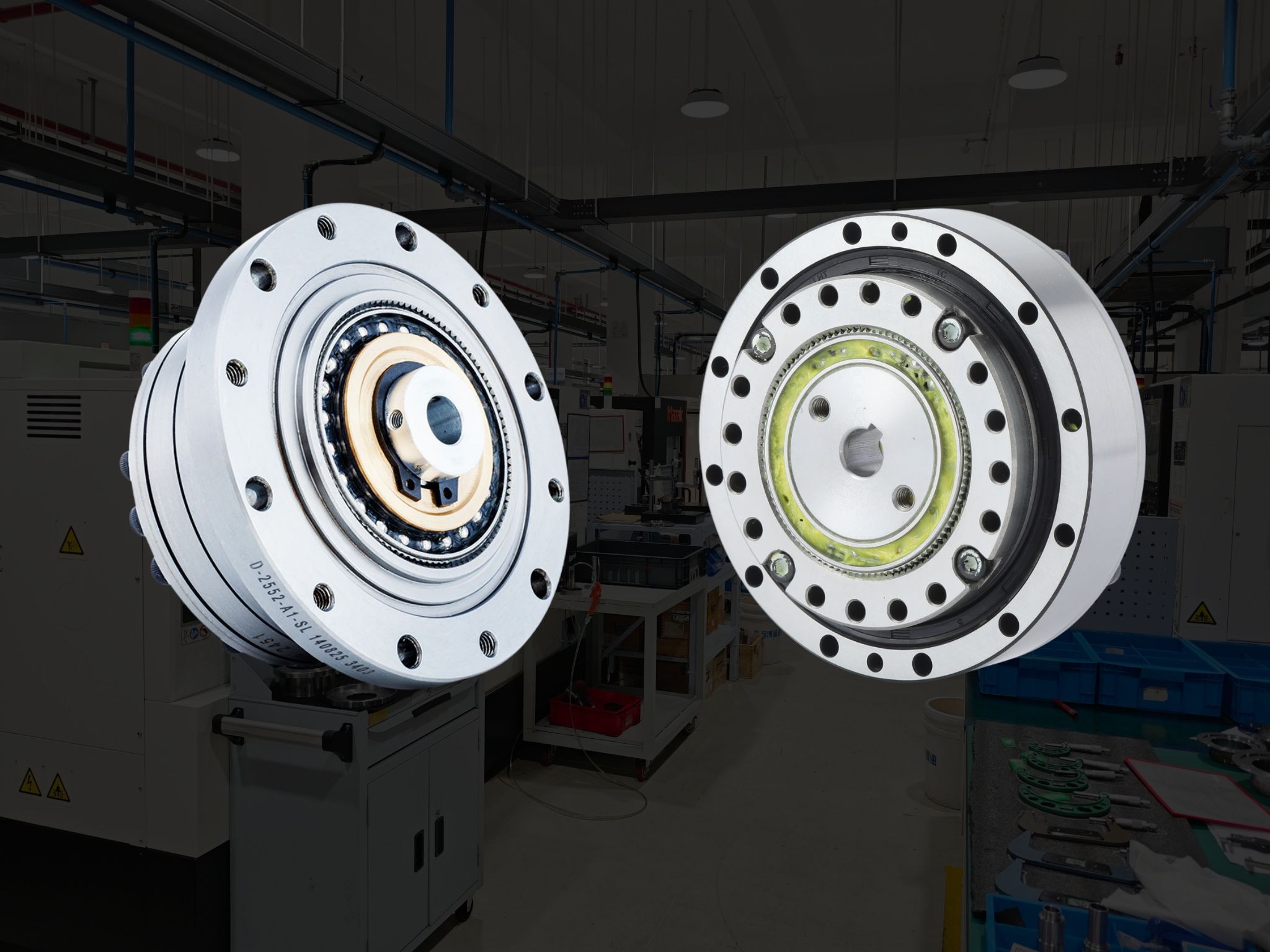
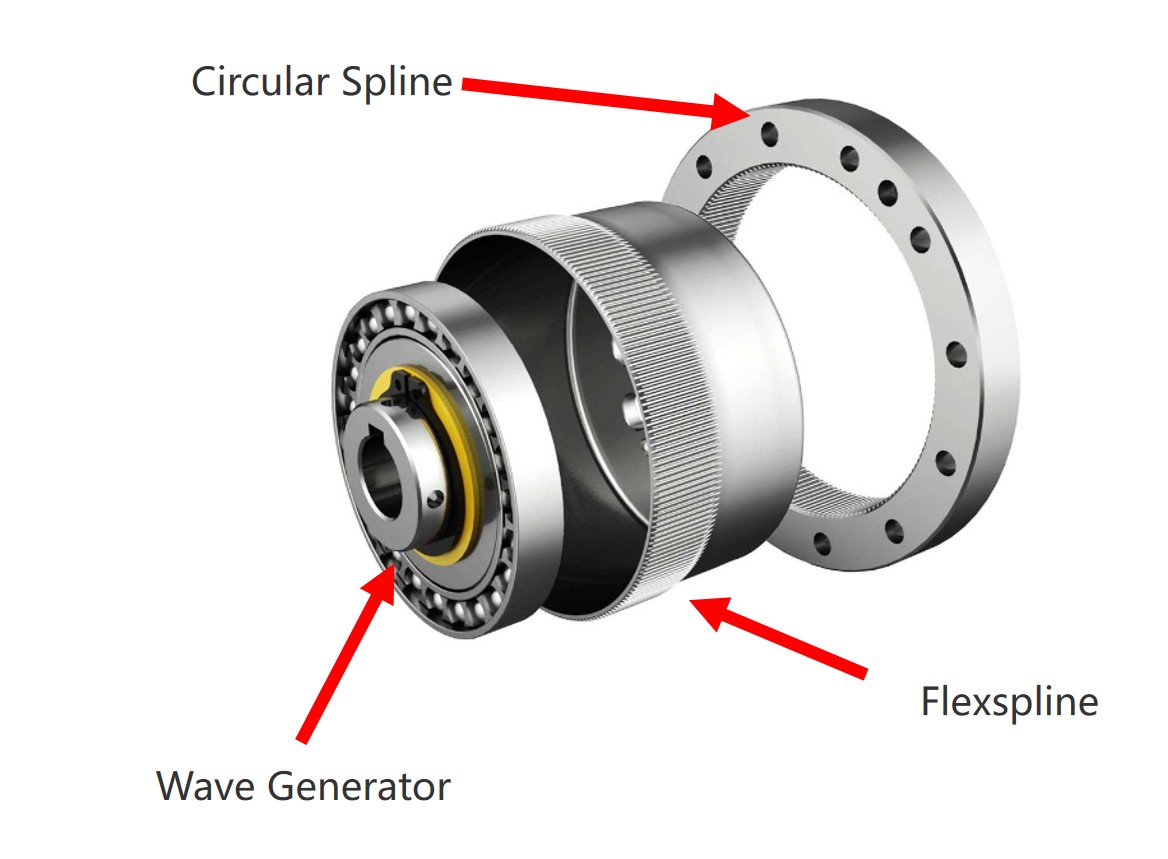
A harmonic drive mechanism mainly consists of three core components: the Wave Generator, Flexspline, and Circular Spline.
Wave Generator
Composed of a flexible bearing and an elliptical cam, the wave generator is typically mounted on the input side of the gearbox.
The inner ring of the bearing is fixed to the cam, while the outer ring deforms elastically into an elliptical shape through the rolling elements.
Flexspline
A thin-walled, flexible cup-shaped component with external teeth. It is usually mounted on the output side of the gearbox.
Circular Spline
A rigid ring with internal teeth, typically having two more teeth than the flexspline and fixed to the housing.
Operating Principle of the Harmonic Drive
In a standard harmonic drive configuration, the wave generator acts as the input, the circular spline is fixed, and the flexspline serves as the output.When the wave generator is inserted into the flexspline, it deforms the flexspline into an elliptical shape.At the major axis of the ellipse, the teeth of the flexspline and circular spline are fully engaged;at the minor axis, the teeth are completely disengaged.Between these two axes, the teeth are either engaging or disengaging.
As the wave generator rotates continuously, the flexspline undergoes a cyclic deformation, causing its teeth to progressively mesh and unmesh with those of the circular spline.This results in a relative motion between the wave generator and flexspline, thereby achieving motion transmission and speed reduction through the so-called strain wave effect.
For a detailed explanation of the harmonic drive principle, please refer to the following article on the HONPINE official website:
Features of the Harmonic Drive Gearbox
High Precision
Multiple teeth are engaged simultaneously at two symmetrical positions (180° apart), which averages out pitch errors and ensures exceptionally high positioning and rotational accuracy.
Large Reduction Ratio
A single-stage harmonic drive can achieve reduction ratios of i = 30–500 with a simple structure consisting of only three coaxial components.
High Load Capacity
The tooth engagement is surface contact, and multiple teeth are engaged simultaneously, resulting in low unit stress and high torque capacity.
Compact and Lightweight
Compared with conventional gear mechanisms, harmonic drives offer significant size and weight reduction, enabling miniaturization and lightweight designs.
High Transmission Efficiency and Long Service Life
Smooth Operation with Low Noise and Minimal Vibration
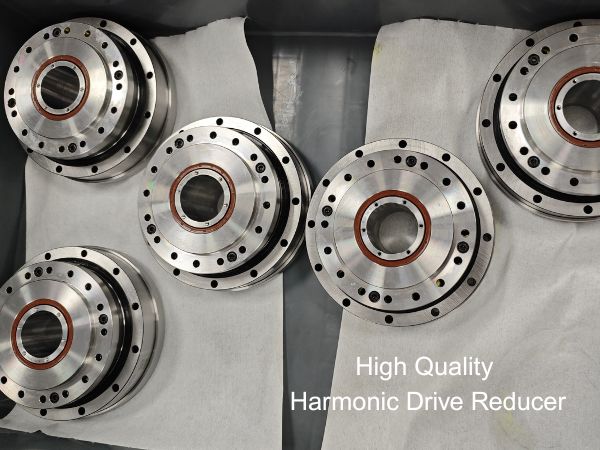
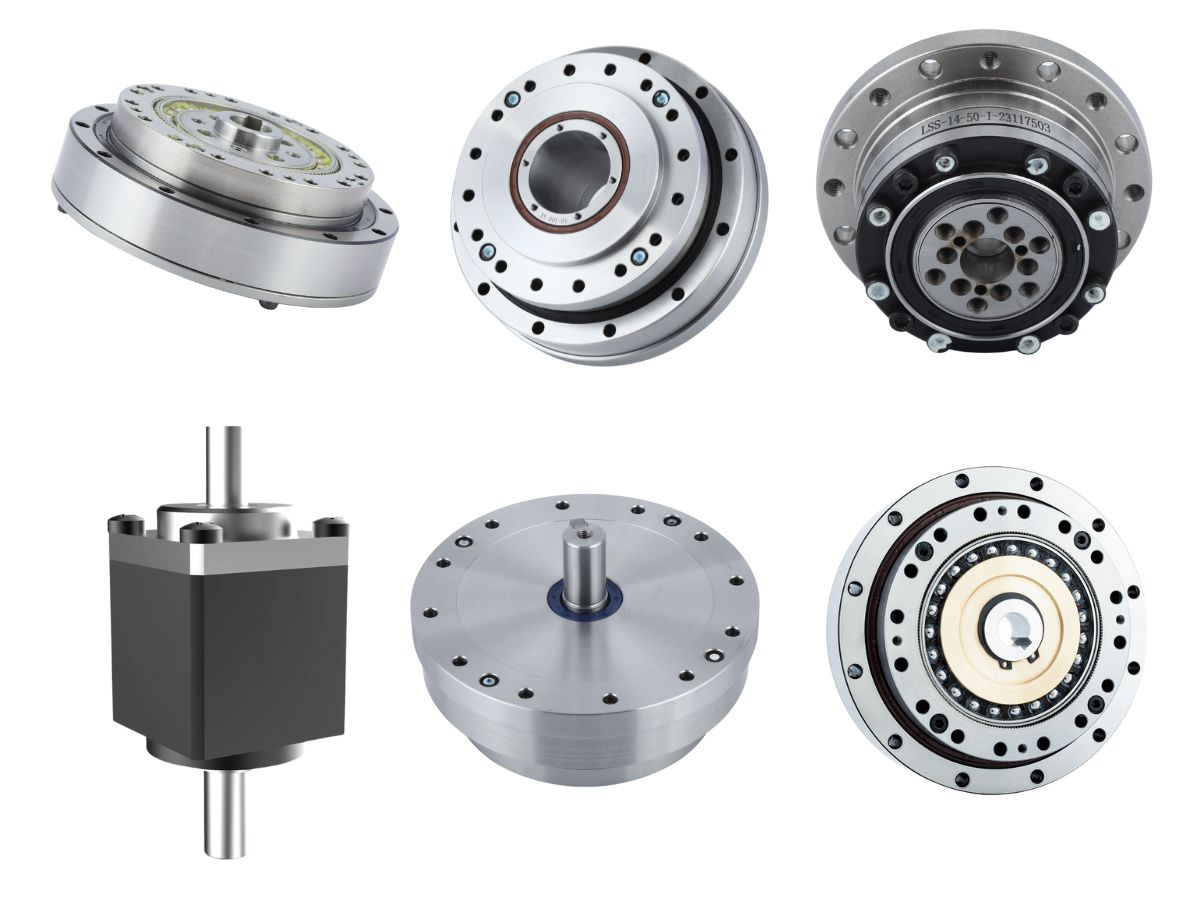
Classification of HONPINE Harmonic Drive Gearboxes
HONPINE harmonic drives are mainly categorized into five series
Direct Drive Harmonic Drive
Hollow Type Harmonic Drive
Input Shaft Harmonic Drive
Ultra-Thin Harmonic Drive
Mini Harmonic Drive

Each type is optimized for different installation configurations, transmission interfaces, spatial orientations, weight requirements, and functional demands—ensuring the most suitable solution for every application.
If you have previously used other brands such as Harmonic Drive AG, LeaderDrive, or Nabtesco, you can share your model information with us for direct replacement.
HONPINE’s technical team will provide one-on-one selection and customization support.
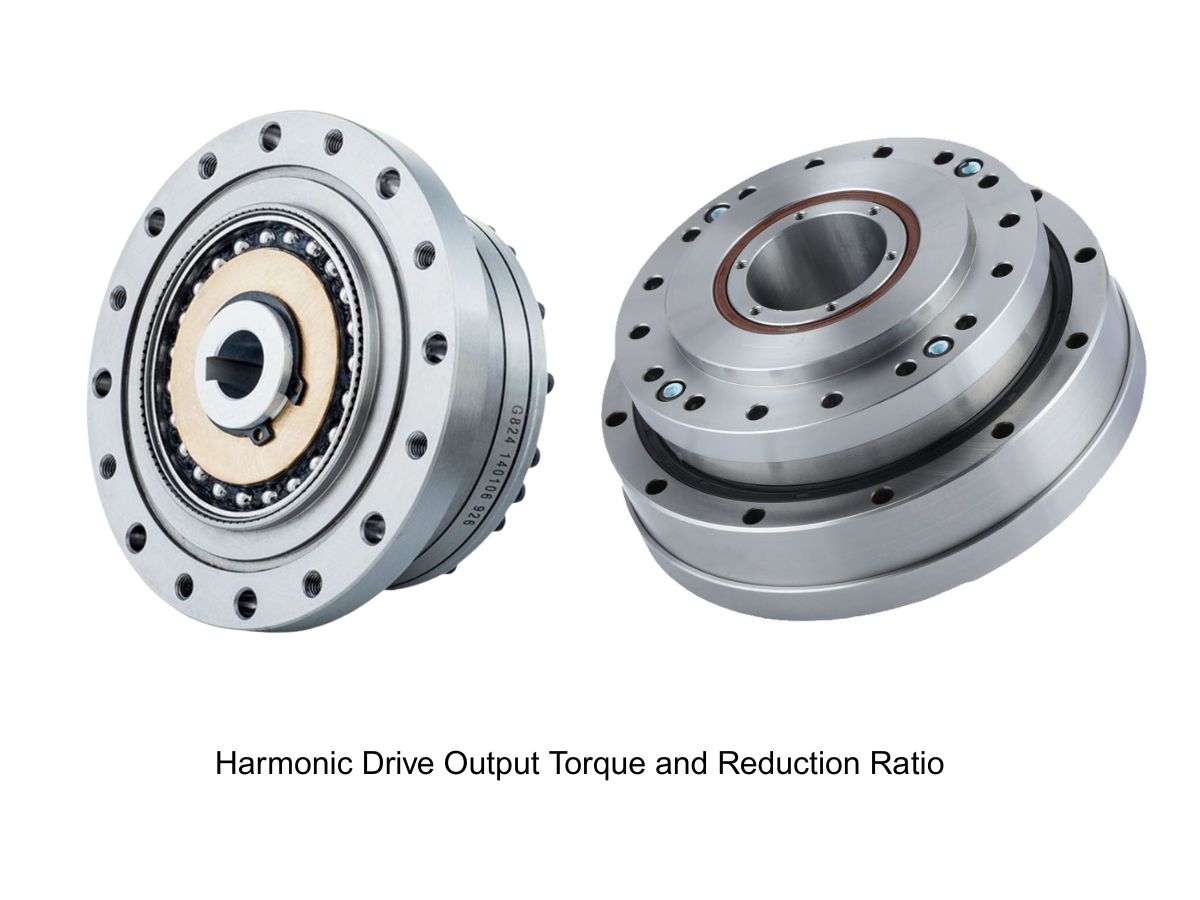
HONPINE Harmonic Drive Gearbox Specifications:
Reduction Ratio Range: 30 – 160
Rated Torque Range: 0.06 – 385 N·m
These specifications cover the majority of industrial applications, and custom designs are available for special requirements.
Contact HONPINE for more information about our Harmonic Drive Gearbox solutions and discover how we can support your precision transmission needs.
Read More
Learn more about the story of HONPINE and industry trends related to precision transmission.
Double Click
We provide harmonic drive reducer,planetary reducer,robot joint motor,robot rotary actuators,RV gear reducer,robot end effector,dexterous robot hand