Harmonic Drive Gearbox Advantages,Disadvantages,Backlash,Devices Comprehensive Analysis
This article will provide a comprehensive analysis of harmonic drive gearboxes, including their introduction, advantages and disadvantages, backlash, application scenarios, and installation precautions.
What is a harmonic drive gearbox?
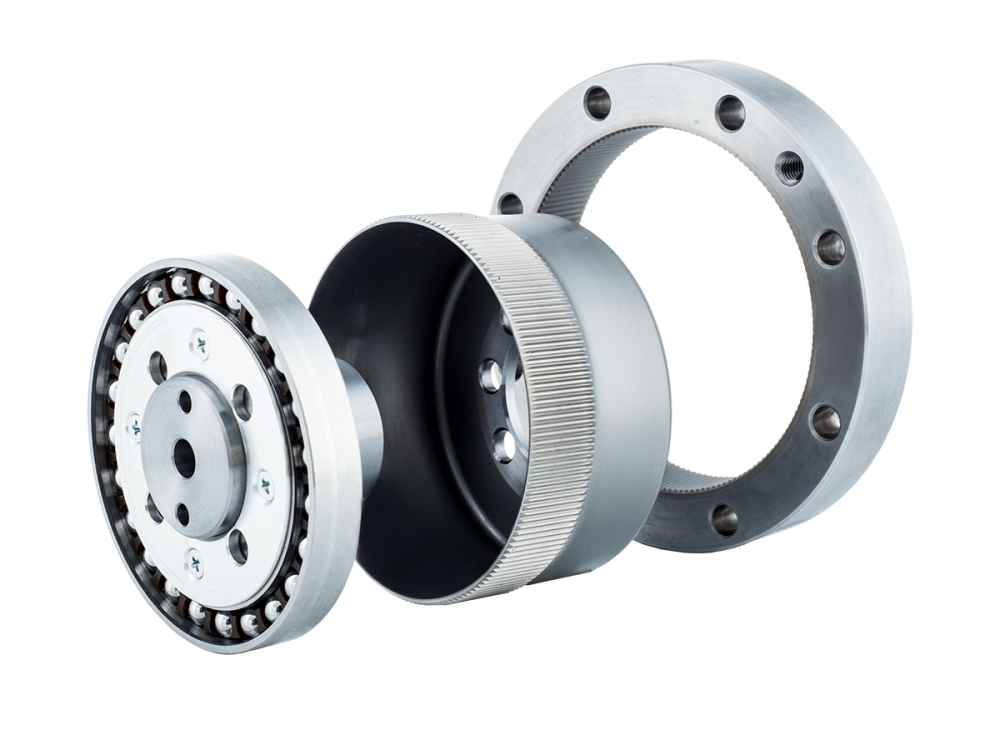
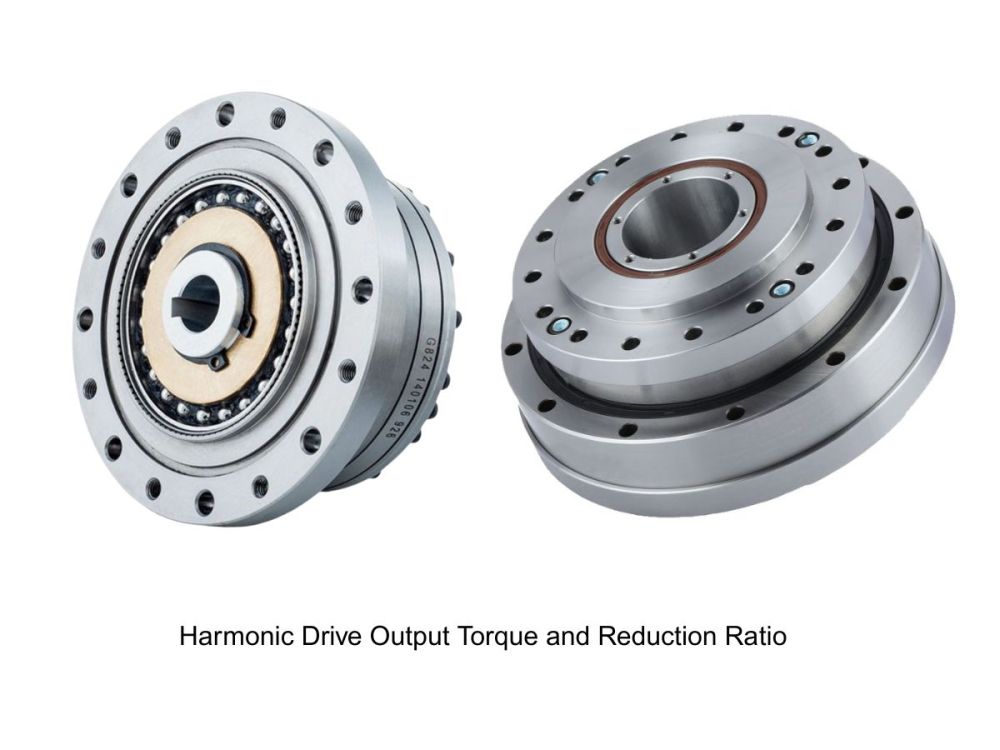
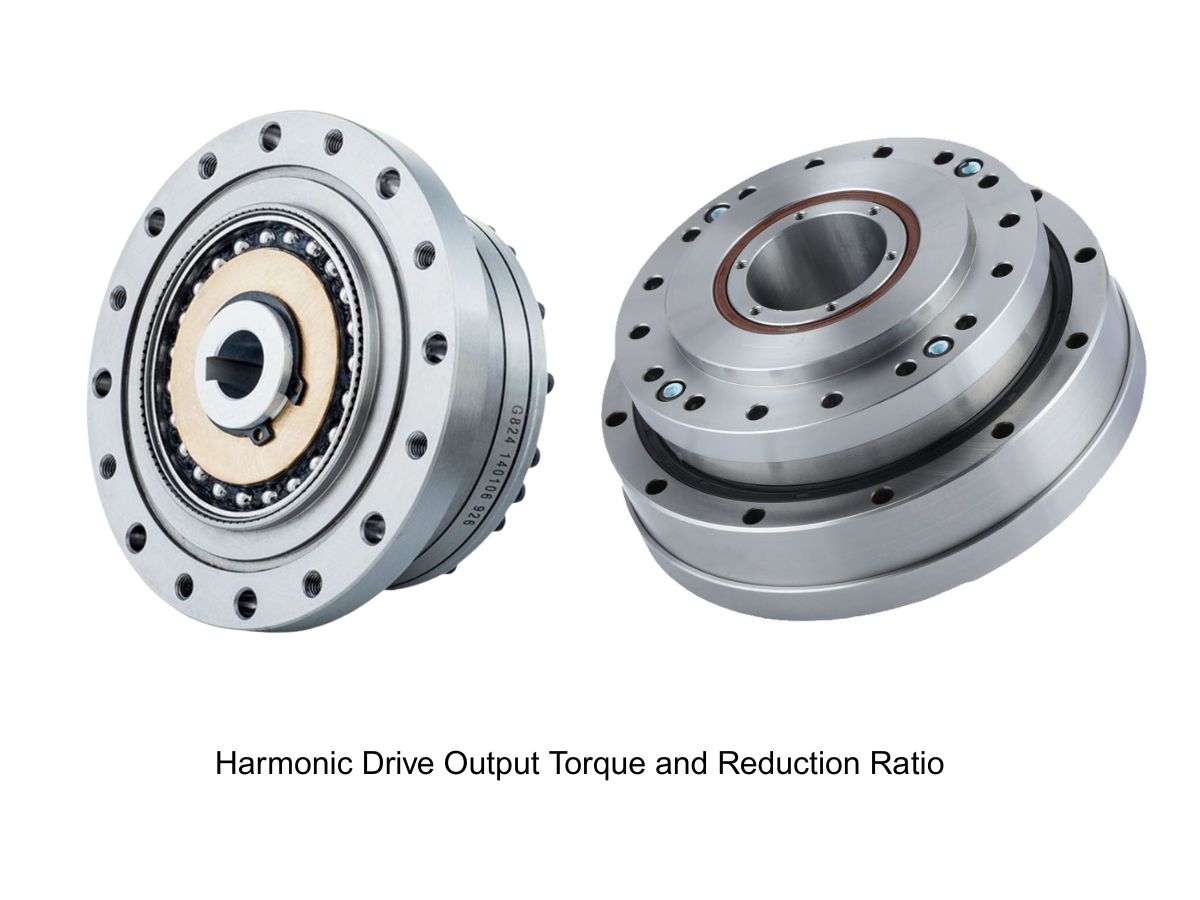
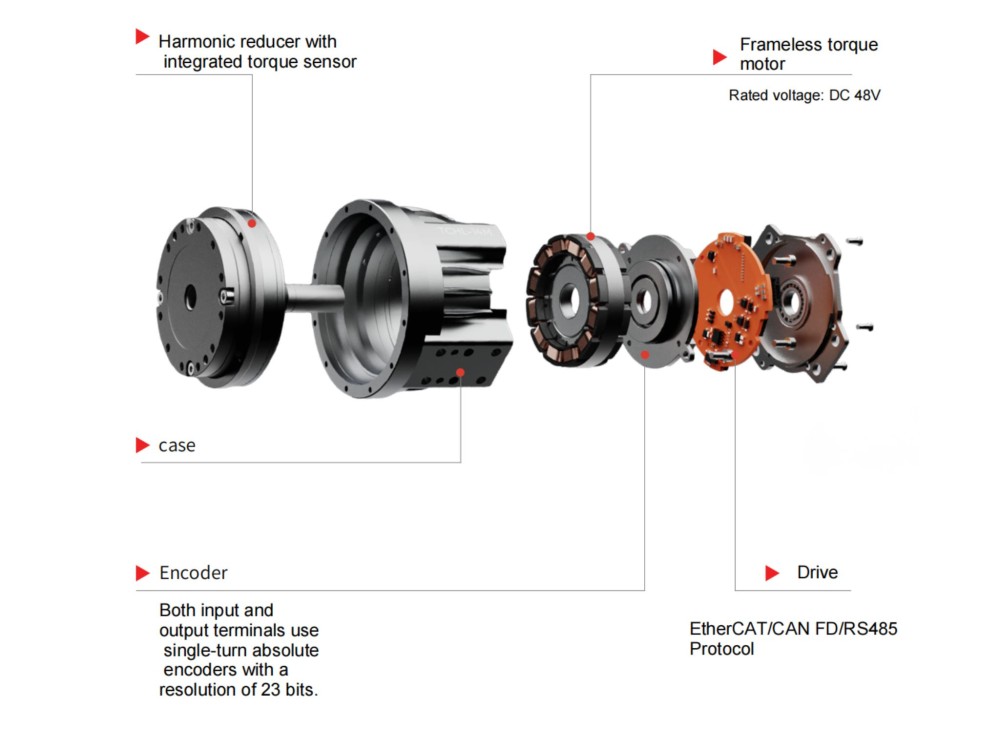
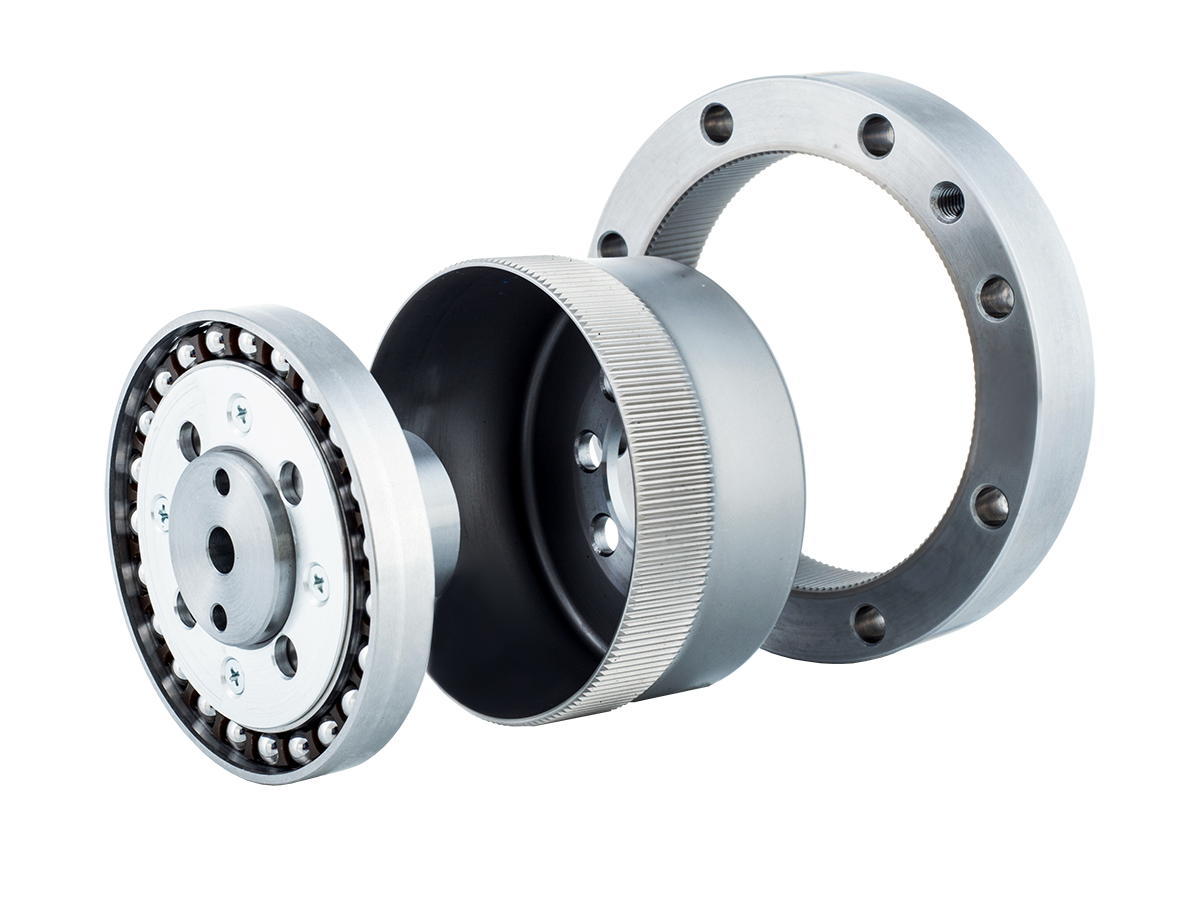
A harmonic drive gearbox, as a flexible gear reducer, has a core consisting of a wave generator, a flexible spline, and a circular spline. The precise coordination of these three components is key to its stable transmission. The wave generator, typically elliptical or hyperbolic in shape, is often connected to the input shaft and serves as the "power source" that induces deformation. The rolling bearings on its periphery allow for smoother deformation and reduce component wear.
The flexible spline is cup-shaped or ring-shaped, usually made of high-strength alloy steel with excellent elasticity. It undergoes periodic deformation under the action of the wave generator. The gear teeth are distributed on its outer or inner circumference, acting as the "bridge" for power transmission. The circular spline is a fixed component with teeth on its inner or outer wall. It has 2 more teeth (or a specific integer difference) than the flexible spline. By meshing with the deforming flexible spline, it achieves power output.
During operation, the rotation of the wave generator pushes the flexible spline to deform, causing the teeth of the two components to engage and disengage sequentially. The speed reduction is achieved through the tooth difference. The three major components each perform their own functions, enabling transmission with both high precision and stability.
What are the advantages of harmonic drive?
Harmonic drive gearboxes offer the following significant advantages:
1. High Reduction Ratio:
Single-stage reduction ratios typically range from 30 to 500, while multi-stage ratios can exceed 30,000. This allows for significant speed reduction in a single stage, meeting the needs of high-precision and high-torque transmission, suitable for scenarios requiring high reduction ratios.
2. High Transmission Precision:
The multi-tooth meshing mechanism averages out errors, with transmission error being only about 1/4 that of ordinary gear transmissions. It can achieve near-zero backlash motion, ensuring precise movement, making it ideal for fields with extremely high precision requirements such as surgical robots and semiconductor equipment.
3. Compact Size and Light Weight:
Compared to traditional reducers, with the same output torque, the volume can be reduced by 2/3 and the weight by 1/2. Its compact structure is suitable for space-constrained applications, like light-load joints in humanoid robots.
4. High Load Capacity:
The flexspline is made of high-strength material, and tooth contact is surface-to-surface. The number of simultaneously meshing teeth can reach over 30% of the total teeth, resulting in low unit area load and enabling the transmission of relatively high torque, suitable for high-load scenarios.
5. High Transmission Efficiency:
During transmission, the flexspline teeth move uniformly in the radial direction with very low relative sliding speed, leading to minimal wear. Efficiency can reach 69% to 96%, maintaining relatively high efficiency even at high speeds, reducing energy loss.
6. Smooth Operation and Low Noise:
Both sides of the teeth participate in engagement and disengagement, resulting in no impact phenomenon. Operation produces minimal noise and vibration, suitable for noise-sensitive applications.
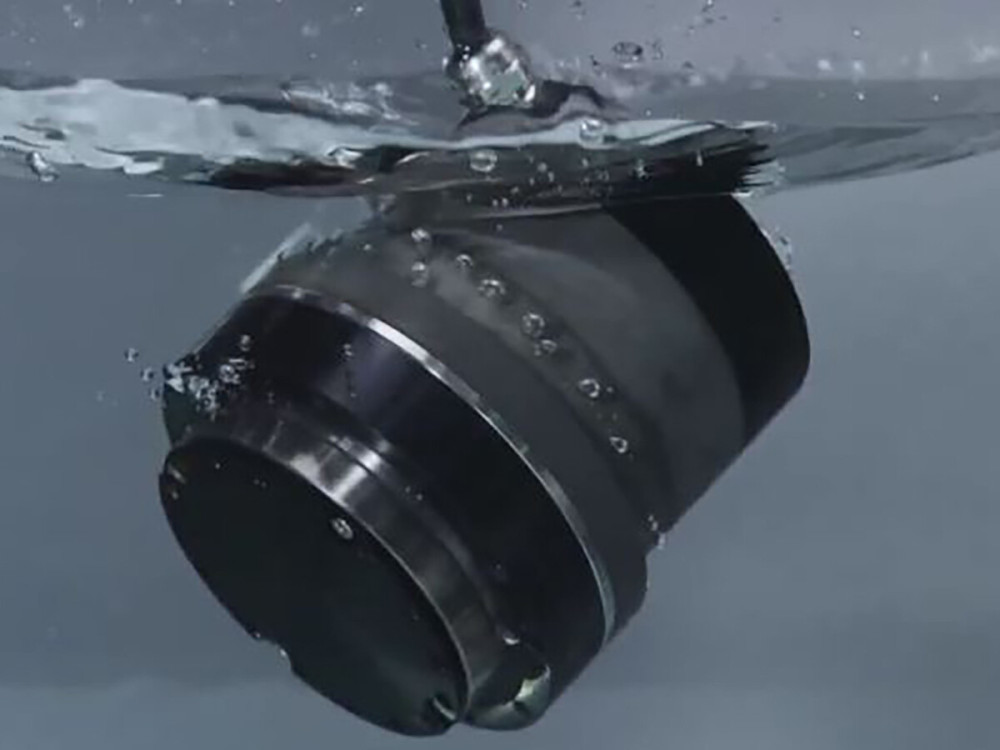
7. Ability to Transmit Motion into Sealed Spaces:
Utilizing the flexible nature of the flexspline, motion can be transmitted through sealed walls, suitable for equipment like aerospace and medical devices that need to operate in enclosed environments.
These advantages make harmonic drive gearboxes an ideal transmission solution for high-tech fields such as robotics, CNC machine tools, aerospace, and medical equipment.
What are the disadvantages of harmonic drive?
As a precision transmission device, while harmonic drives offer advantages like high precision, high reduction ratio, and compact size, they also have some limitations, including:
1. Limited Flexspline Fatigue Life:
The flexspline undergoes periodic elastic deformation during operation, generating alternating stress. Long-term use can easily lead to material fatigue, causing cracks or even fracture. Especially in high-load, high-frequency operation scenarios, the flexspline's lifespan can be a limiting factor, requiring regular replacement or maintenance.
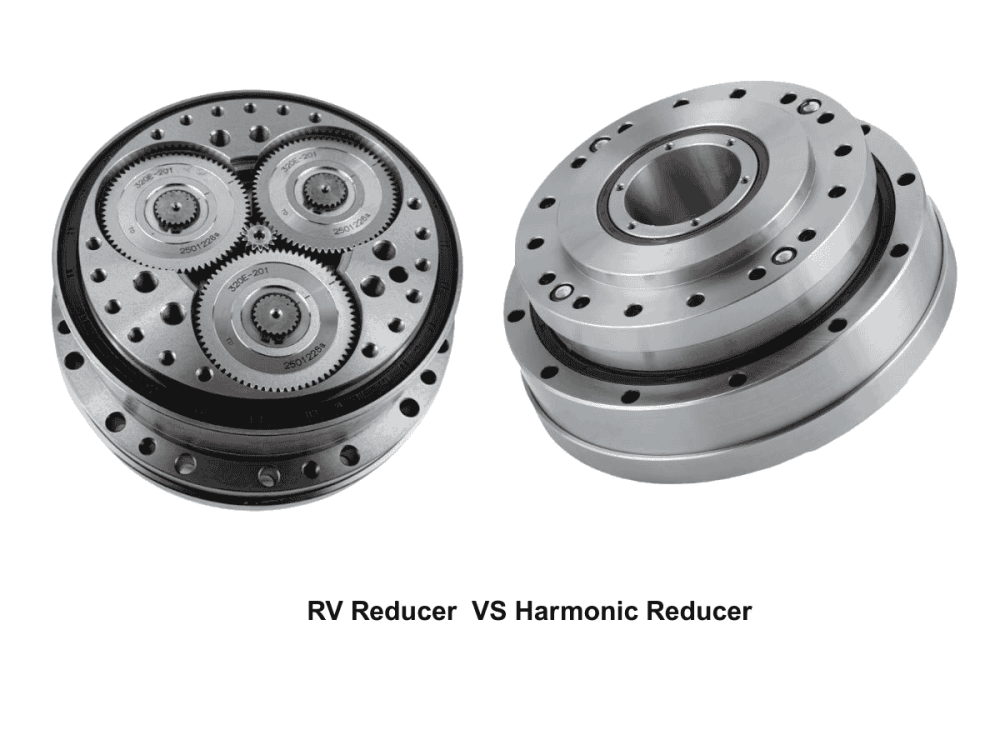
2. Relatively Lower Load Capacity:
Although harmonic drives perform well in low-torque scenarios, compared to reducers like RV reducers, their ability to withstand high torque is weaker. When the load exceeds a certain limit, excessive deformation or poor meshing of the flexspline can affect transmission accuracy and stability. Therefore, they are more suitable for light-load, high-precision applications.
3. Limited Transmission Efficiency:
Due to factors like the elastic deformation of the flexspline and meshing friction, the transmission efficiency of harmonic drives is generally lower than that of planetary or RV reducers, with relatively higher energy loss. Efficiency issues can become more prominent, especially in high-speed or high-power transmission.
4. High Requirements for Installation and Operating Conditions:
Harmonic drives have strict requirements for installation accuracy. Improper installation (e.g., misaligned axes, excessive clearance) can cause uneven stress on the flexspline, accelerating wear or damage. Additionally, they have certain requirements for operating environment temperature, humidity, vibration, etc., which may affect performance and lifespan in harsh conditions.
5. Instantaneous Transmission Ratio Fluctuation:
For harmonic drives using roller wave generators, the instantaneous transmission ratio is not strictly constant. This may affect the smoothness and precision of transmission to some extent, requiring careful consideration in applications with extremely high precision requirements.
6. Heat Dissipation Challenges:
The internal structure of harmonic drives is compact, with relatively poor heat dissipation conditions. Prolonged continuous operation may cause temperature rise, affecting lubrication effectiveness and component performance, even leading to failures. Therefore, heat dissipation design needs attention during high-load or long-term operation.
In summary, harmonic drives are suitable for scenarios with high requirements for precision, size, and weight, but with relatively smaller loads and less stringent demands on lifespan and efficiency, such as robot joints, precision instruments, and aerospace. When selecting a reducer, a comprehensive evaluation of its pros and cons based on specific application needs is necessary.
Does Harmonic Drive have backlash?
Harmonic drive gearboxes can achieve near-zero backlash under ideal conditions. However, in practical applications, due to factors like manufacturing precision, material properties, and wear, it is difficult to achieve absolutely zero backlash completely. There is usually an extremely minute gap, but compared to traditional reducers, their backlash is significantly reduced and can often be considered negligible.
Harmonic drives operate by using a wave generator to drive the elastic deformation of the flexspline, causing the flexspline and circular spline to form periodic meshing. Speed reduction is achieved through the tooth difference. Due to the elastic deformation characteristic of the flexspline, it can tightly conform to the tooth surface of the circular spline during meshing, theoretically eliminating clearance between gears. However, in actual production, factors such as machining errors of components, assembly accuracy, and wear from long-term use can lead to the generation of backlash.
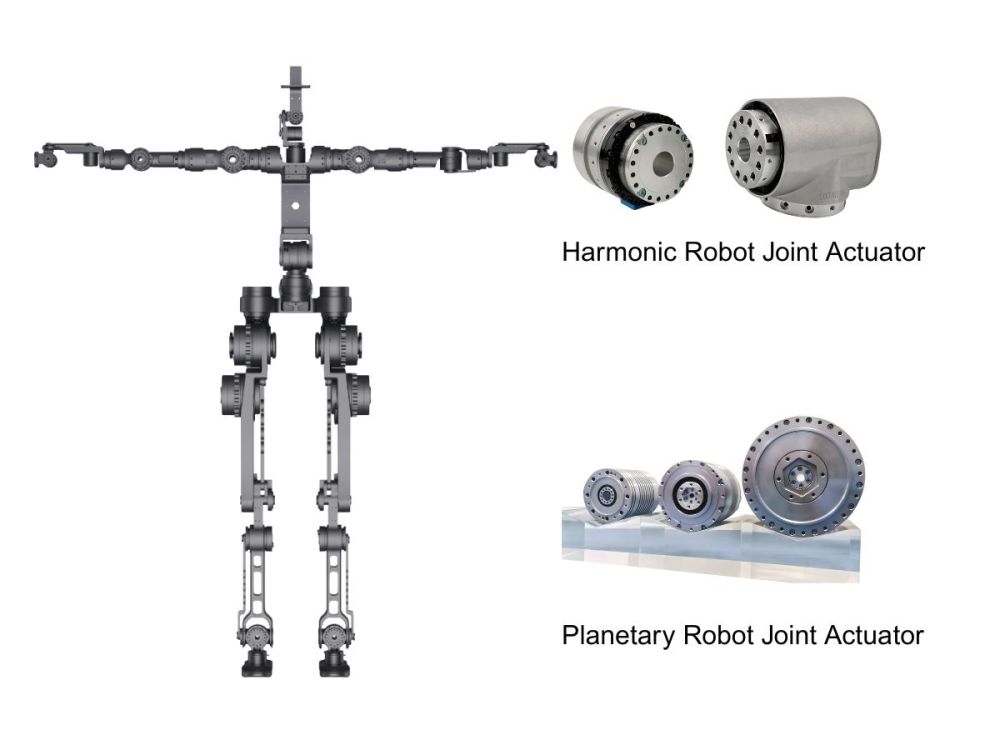
What devices have harmonic drives?
Harmonic drive gearboxes are primarily applied in the following four major industries: industrial robots, service robots, medical equipment, CNC machine tools, and automation equipment.
Machine Tool Industry:
Mainly used for the 4th and 5th axes of machine tools, machine tool fixtures, tool turrets, etc. High-precision equipment predominantly uses harmonic drives.
Small Robotic Arms (under 20KG):
Referring to commonly seen robotic arms, over 50% of the reducers used are harmonic drives.
Home Service Robots:
For high-end robots in home services, logistics sorting, desktop toys, etc., harmonic drives are the only and most effective reducer solution.
Medical Equipment:
Mainly includes medical robots, medical devices, exoskeletons, medical care devices, etc. Harmonic drives are the optimal solution for joints.
Installation Precautions for Harmonic Drive Gearboxes
If bearing support is required during reducer installation, try to select bearings with P6 precision and C2 clearance class to ensure overall machine precision.
Ensure the grease filling amount in the cavity is above 60-70% to avoid poor lubrication during long-term operation.
The installation environment must be clean. Avoid assembly in dusty environments or with particle contamination. Do not use fans in the workshop during installation.
Tools and fixtures used during installation should be tidy and ergonomic to avoid damaging the reducer or creating hidden problems due to tool issues.
Installation personnel should wear rubber gloves whenever possible.
Use industrial lint-free wipes for cleaning the reducer or related parts during installation.
When installing the reducer with the motor rotating, ensure there is sufficient clearance for adjustment regarding the positioning dimensions between the reducer and the mounting flange.
For screw tightening methods and torque, use a torque wrench.
Ensure the screws used are grade 12.9 to guarantee reliability after installation.
Use thread-locking adhesive on installation screws, minimize the use of elastic washers. For blind holes, it's recommended to apply the adhesive into the hole; for through-holes, apply it to the top of the screw.
Ensure sufficient and properly sealed lubricant/grease during installation. For installations with the gear face upward, the cavity should be filled with grease.
After installation, perform a trial run at 100 rpm to observe the reducer's noise, vibration, etc. If any issues are found, stop immediately and check the cause or contact our company's staff.
Is there anything else you'd like to know about harmonic drive gearbox?
Read More
Learn more about the story of HONPINE and industry trends related to precision transmission.
Double Click
We provide harmonic drive reducer,planetary reducer,robot joint motor,robot rotary actuators,RV gear reducer,robot end effector,dexterous robot hand