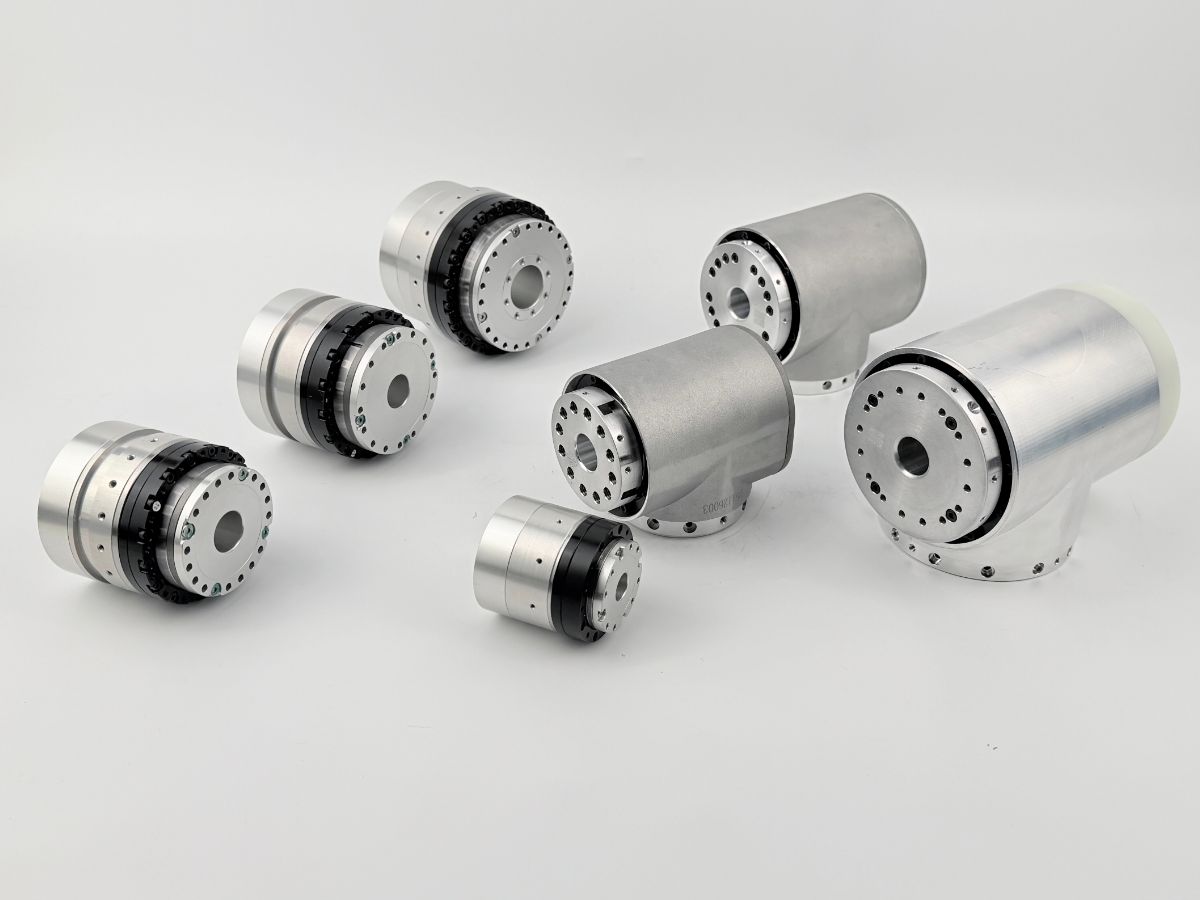
5 Key Factors When Selecting a Precision Robot Joint Motors
As robotics technology continues to evolve toward higher precision and higher dynamic performance, robot joint motors—often referred to as the “motion cells” of robots—play a critical role in determining overall flexibility, payload capacity, and system reliability. Analyzing their core performance indicators is essential for optimized design and proper selection.
1. Accuracy and Repeatability
Accuracy and repeatability are the core criteria for evaluating joint control capability. Absolute accuracy refers to the deviation between the actual position and the target position, and is influenced by encoder resolution, transmission backlash, and mechanical deformation. Repeatability describes the consistency when repeatedly reaching the same target point and better reflects system stability.
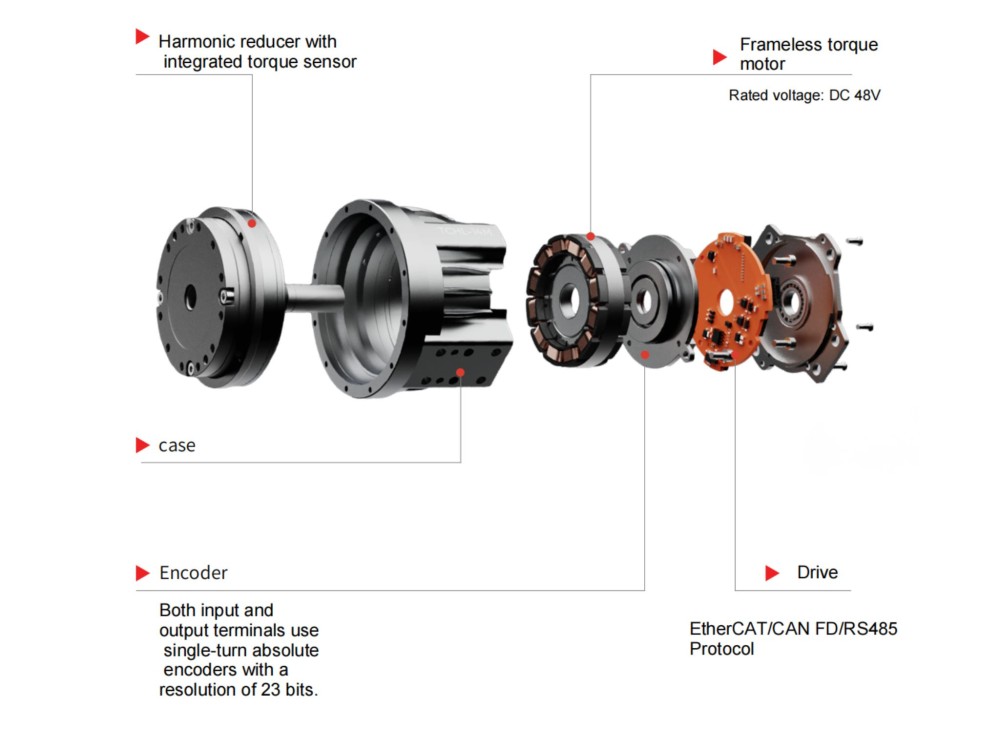
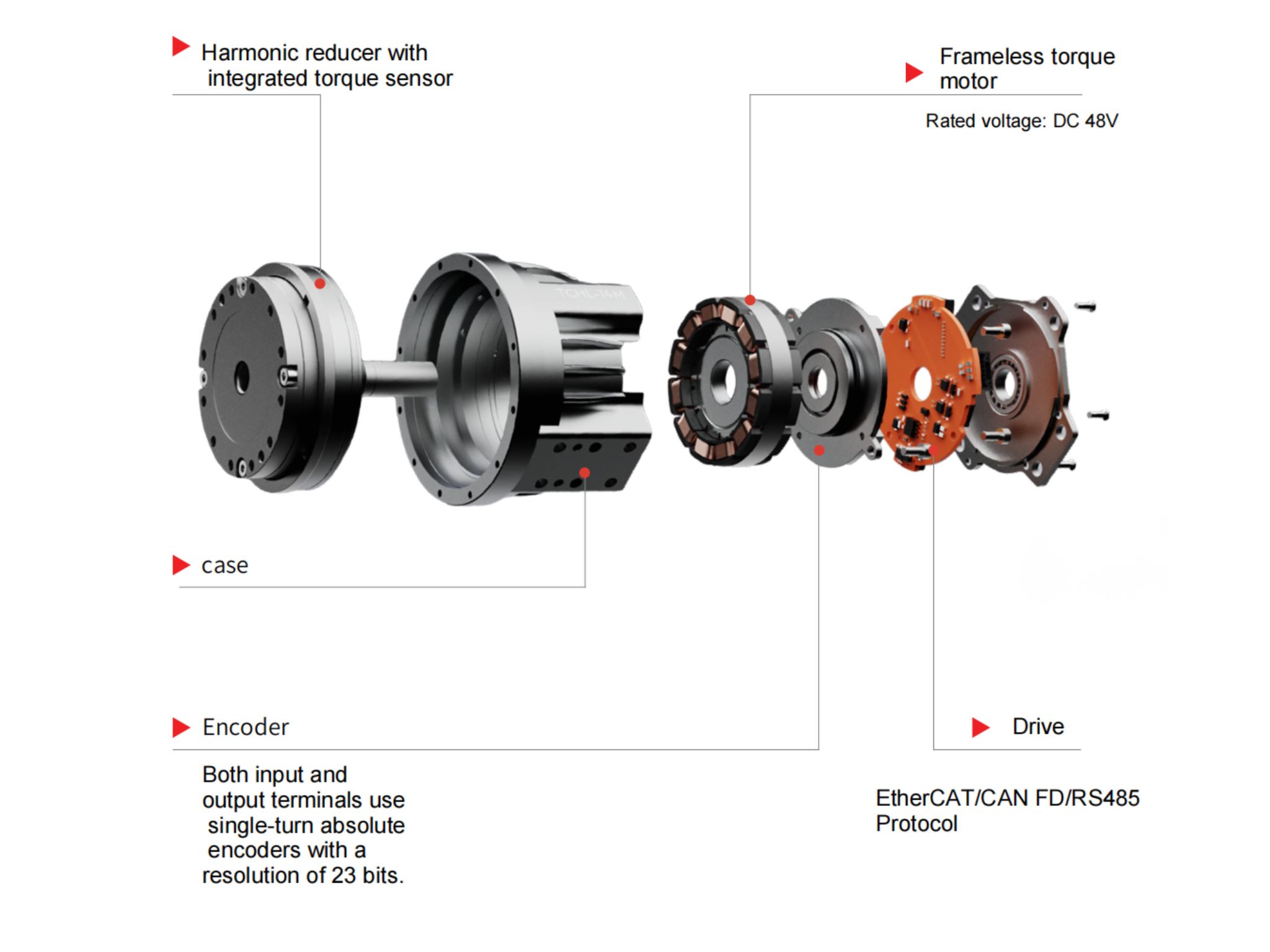
Industrial collaborative robots typically require repeatability at the ±0.02 mm level, while precision assembly applications demand sub-millimeter accuracy or even higher. This performance relies on the combination of high-resolution encoders (such as 23-bit absolute encoders) and low-backlash reducers.
2. Torque Density and Output Capability
Torque density and output capability determine the load potential of a joint. Torque density refers to the torque output per unit mass or volume (Nm/kg or Nm/L), directly affecting robot lightweight design and payload-to-weight ratio.
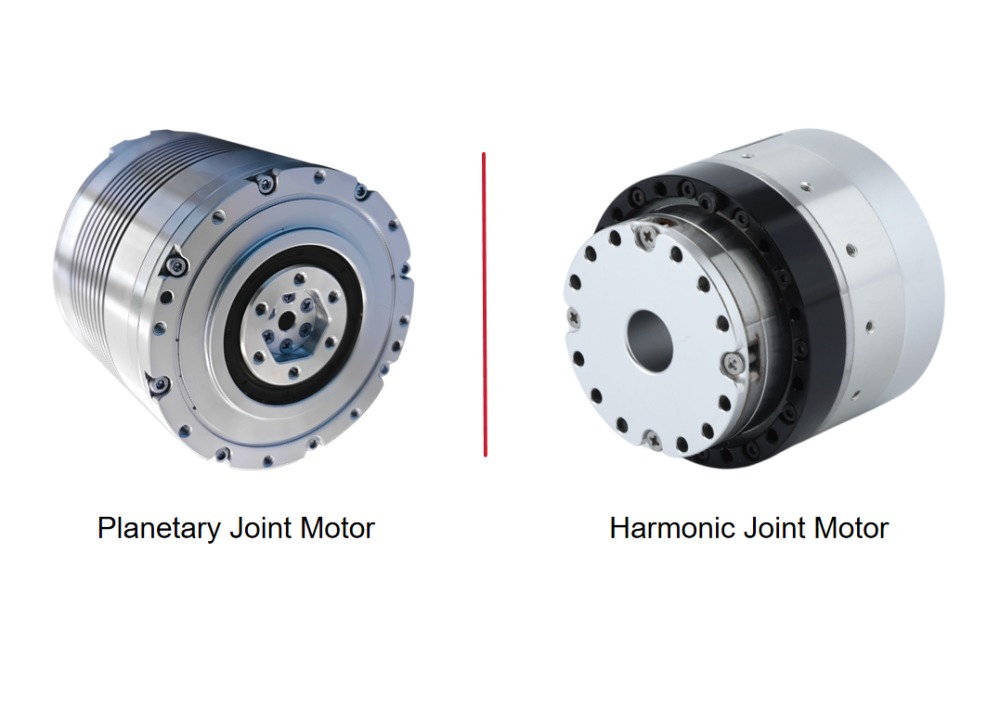
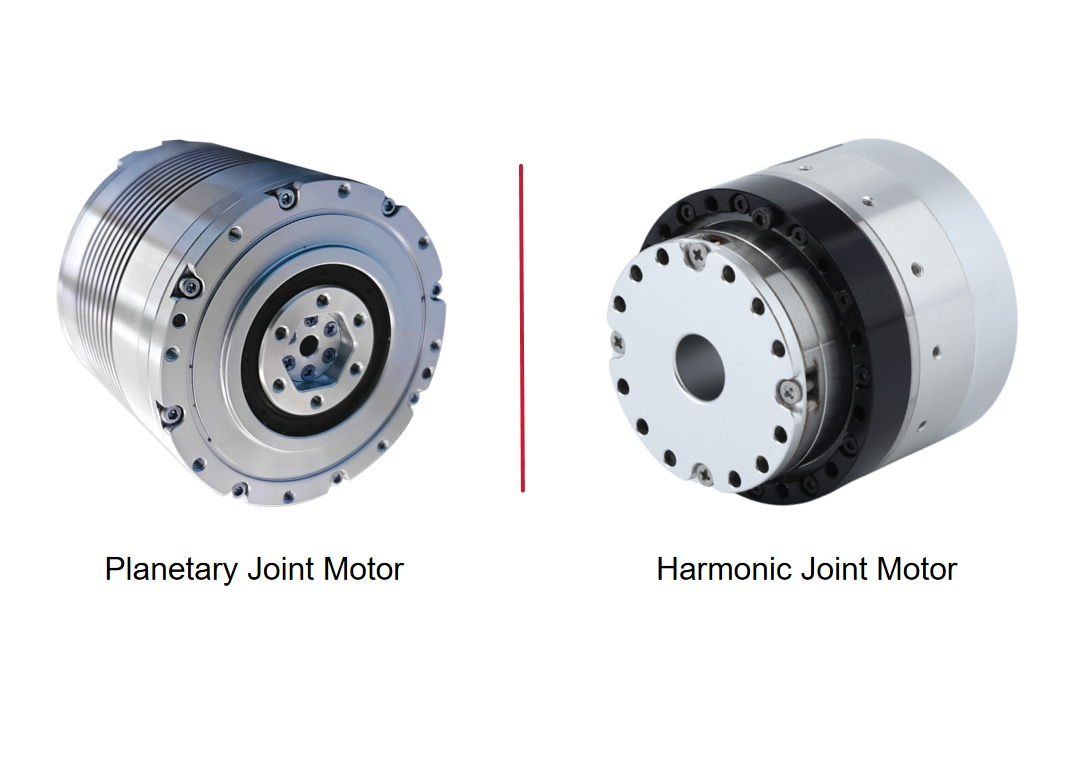
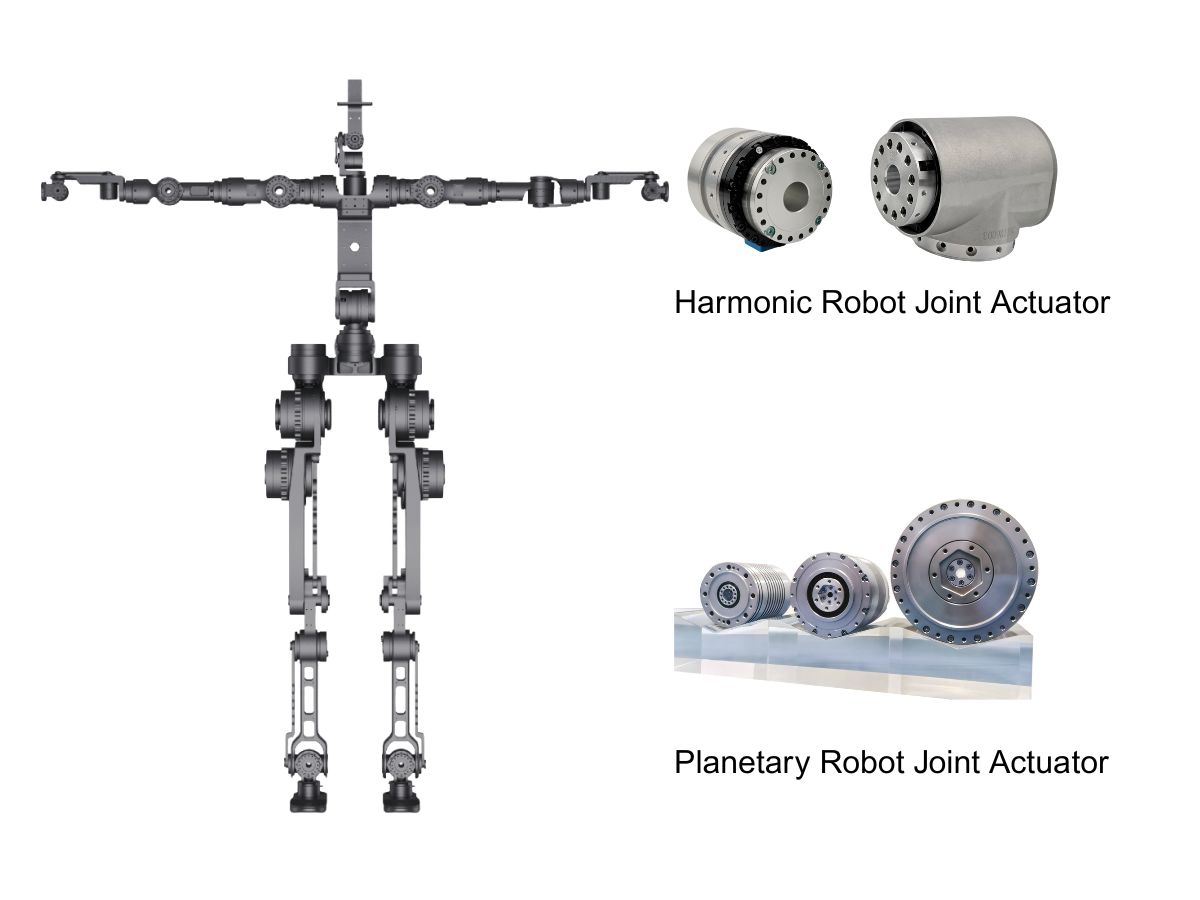
For example, due to their compact structure, harmonic reducers can increase torque density to 3–5 times that of traditional planetary gearboxes, enabling collaborative robots to achieve agile motion with a 7 kg payload. Continuous torque and peak torque must be matched to application requirements: material-handling robots emphasize continuous torque, while high-speed pick-and-place applications rely on short-term peak torque to support acceleration and deceleration.
3. Response Speed and Bandwidth
Response speed and bandwidth reflect dynamic performance. Bandwidth refers to the frequency range over which a joint can effectively track command signals. Higher bandwidth enables faster response and smoother trajectory tracking.
Servo motor power density, reducer torsional stiffness, and control algorithm latency jointly constrain bandwidth. Industrial robot joints typically require bandwidths in the 10–50 Hz range to meet high-speed trajectory planning demands.
4. Reliability and Service Life
Reliability and service life directly impact long-term operating costs. Key indicators include Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and the fatigue life of transmission components such as reducers and bearings.
For example, failures in harmonic reducers are often caused by flexspline fatigue. High-quality products can achieve service lives ranging from several thousand to tens of thousands of operating hours, supported by material reinforcement (such as titanium alloy flexsplines) and optimized lubrication.
5. Integration and Compatibility
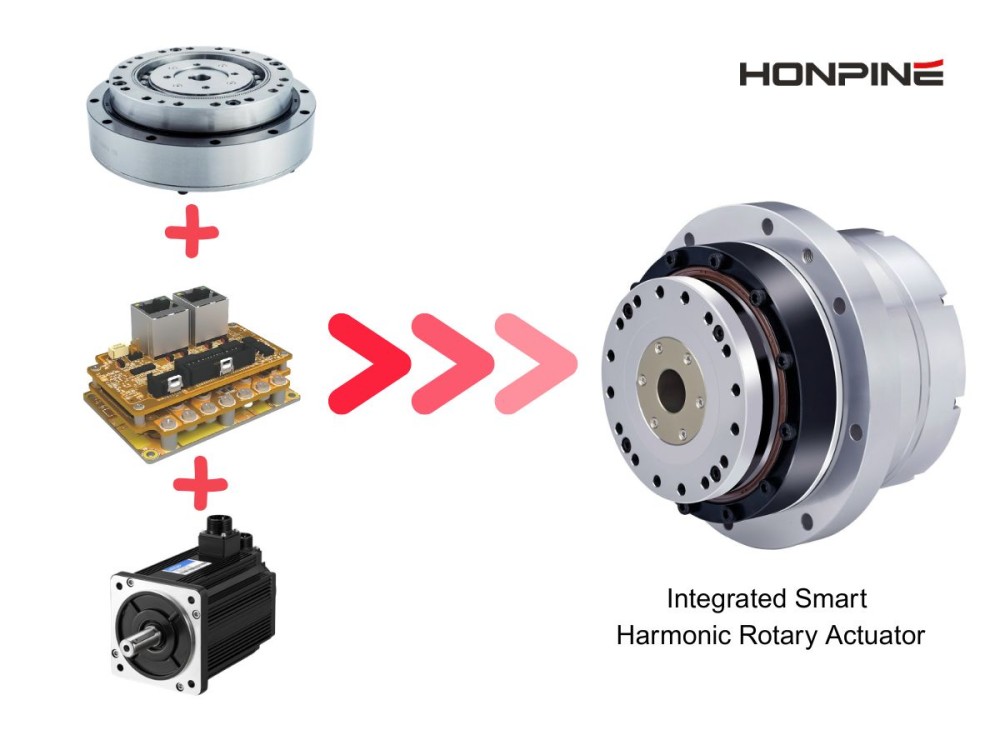
In addition, integration and compatibility influence development efficiency. Highly integrated modules—combining the motor, driver, and encoder—reduce wiring complexity and shorten deployment cycles. Open interfaces supporting mainstream protocols such as EtherCAT and CAN facilitate seamless coordination with higher-level control systems.
If you are looking for a robot joint motor supplier, please contact us to obtain comprehensive product documentation and professional technical support.
Read More
Learn more about the story of HONPINE and industry trends related to precision transmission.
Double Click
We provide harmonic drive reducer,planetary reducer,robot joint motor,robot rotary actuators,RV gear reducer,robot end effector,dexterous robot hand