Why Is It So Difficult for the Price of High-Performance Humanoid Robots to Decrease?And Why Are Harmonic Joint Modules Still Irreplaceable?
When Will Humanoid Robots Be Commercialized, and Why Is Their Price So Hard to Reduce?
With massive capital pouring into the humanoid robotics industry, humanoid robots are clearly moving toward large-scale mass production. Yet a fundamental question remains: why is their price still so difficult to bring down?
Even China—often called the world’s factory—has not been able to produce truly low-cost humanoid robots.
For example, Unitree H1 is priced at around RMB 650,000, while Unitree G1, which removes the expensive dexterous hands (and therefore cannot strictly be considered a full humanoid robot) and significantly reduces degrees of freedom, still costs RMB 99,000.
The core reason lies in one unavoidable requirement: high degrees of freedom.
High DOF is essential for humanoid robots, and this directly leads to joint modules accounting for a consistently high proportion of total system value.
What Makes Humanoid Robots So Expensive?
In humanoid robots, joints account for approximately 60%–70% of the total cost.
Taking Tesla Optimus as a representative example:
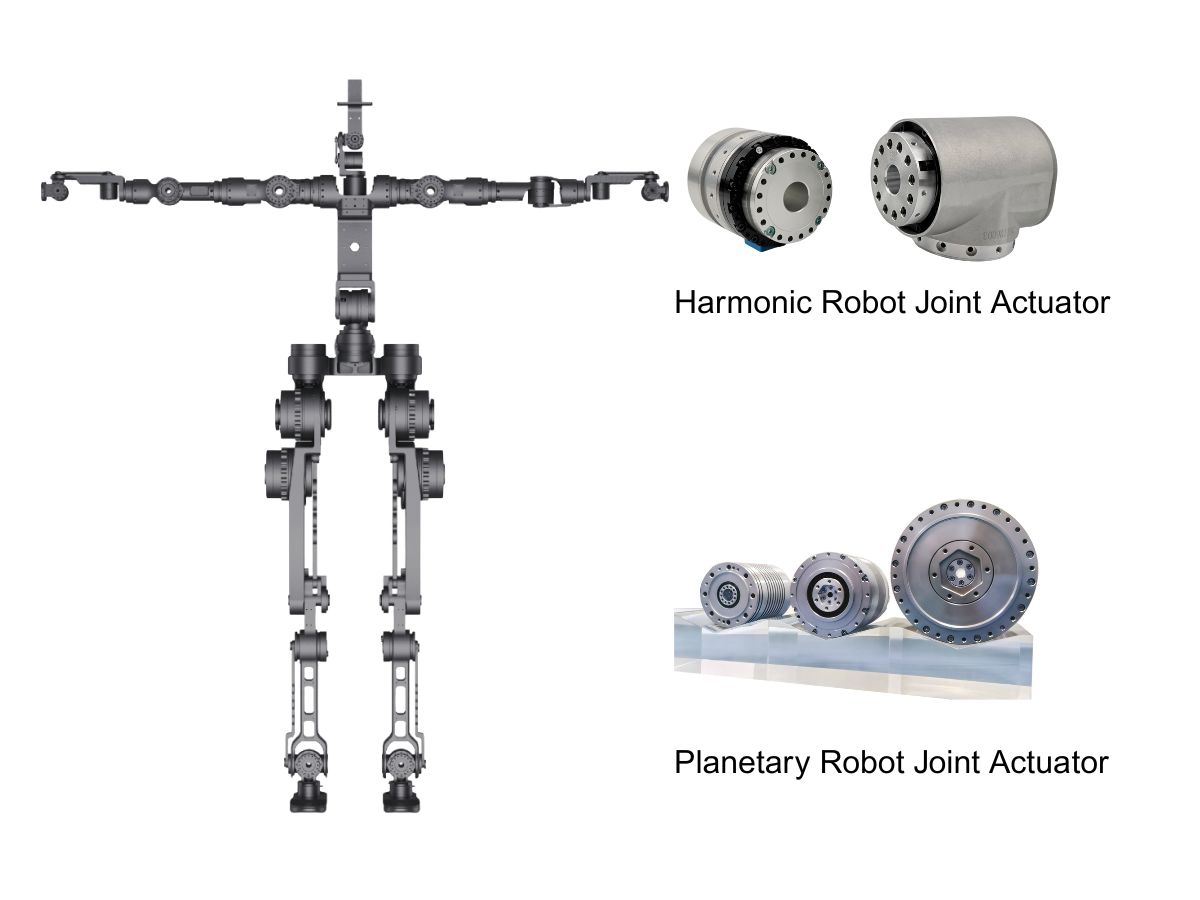
A typical humanoid robot features 28 actuators, evenly split between linear actuators and rotary actuators.
Rotary actuators mainly consist of:
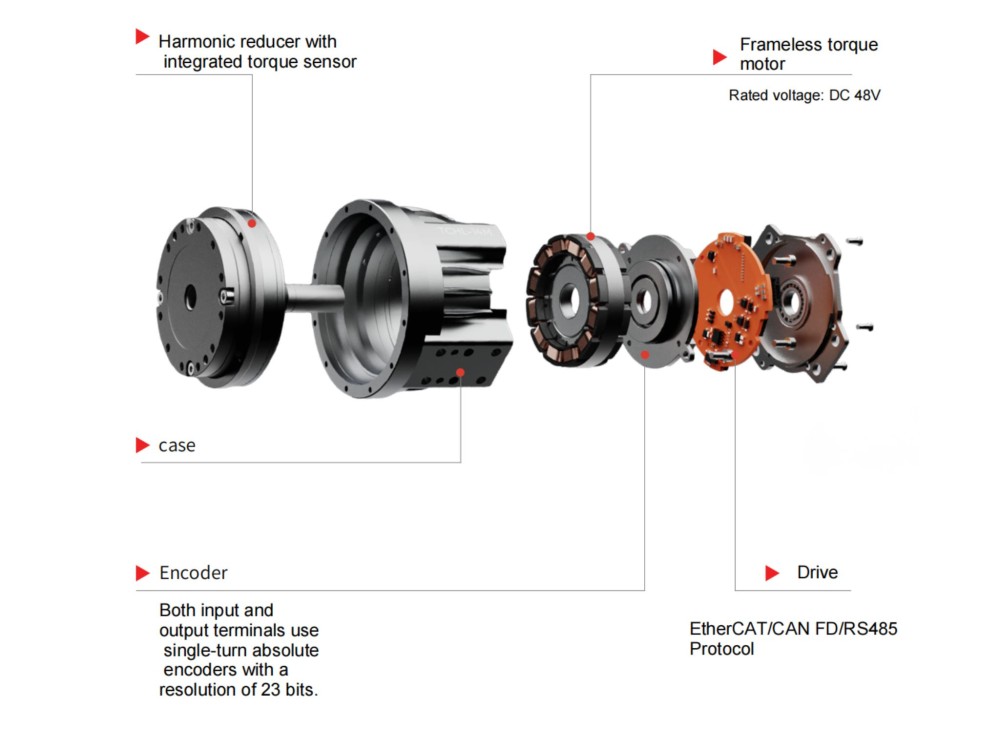
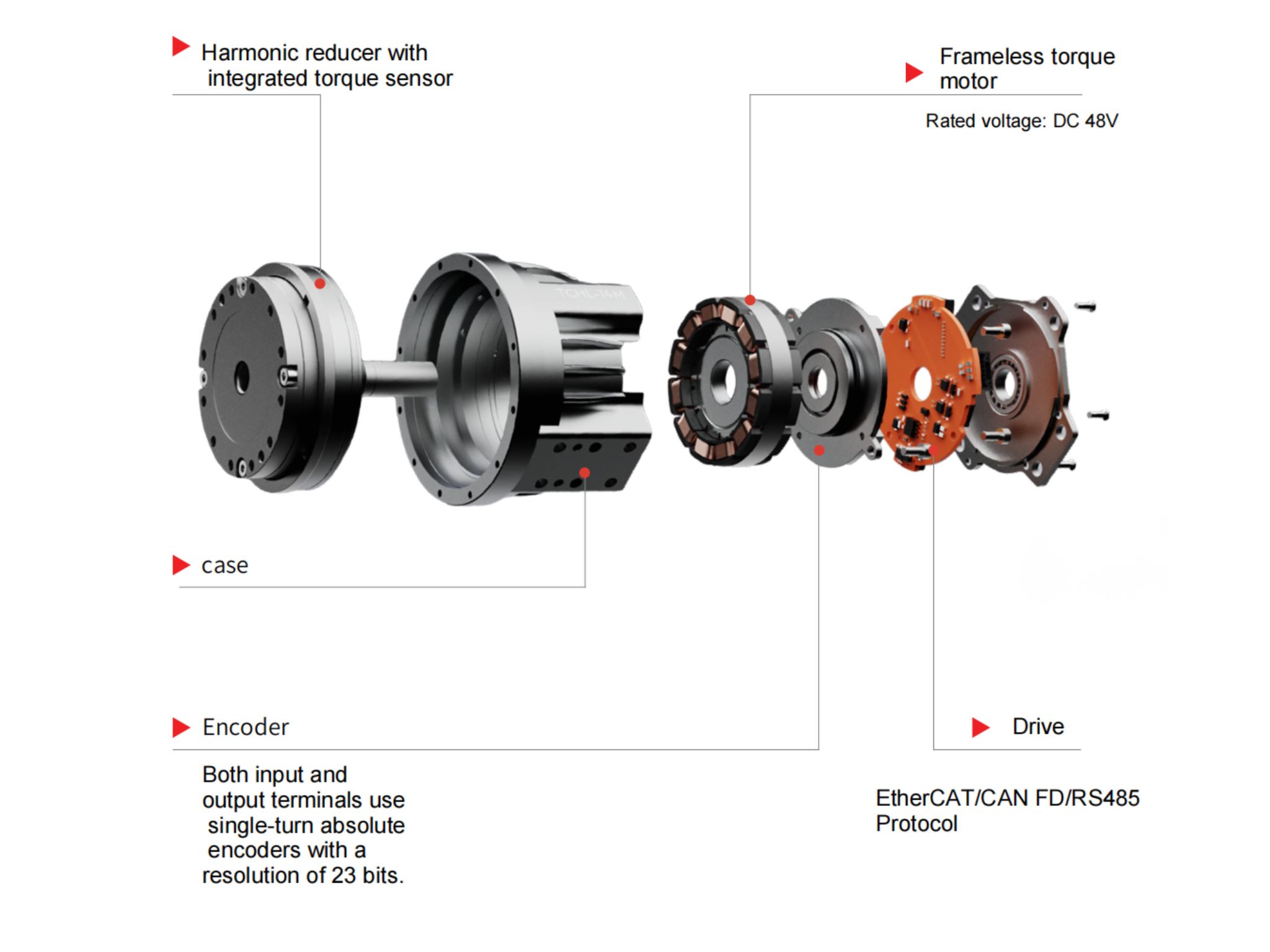
frameless servo motor + harmonic reducer + motor driver + clutch + force sensor + encoder
Linear actuators, similar to human muscles, mainly consist of:
frameless servo motor + planetary roller screw / trapezoidal screw + motor driver + force sensor + encoder
All 28 joints of Tesla Optimus use frameless torque motors as the primary power source.
Among them:
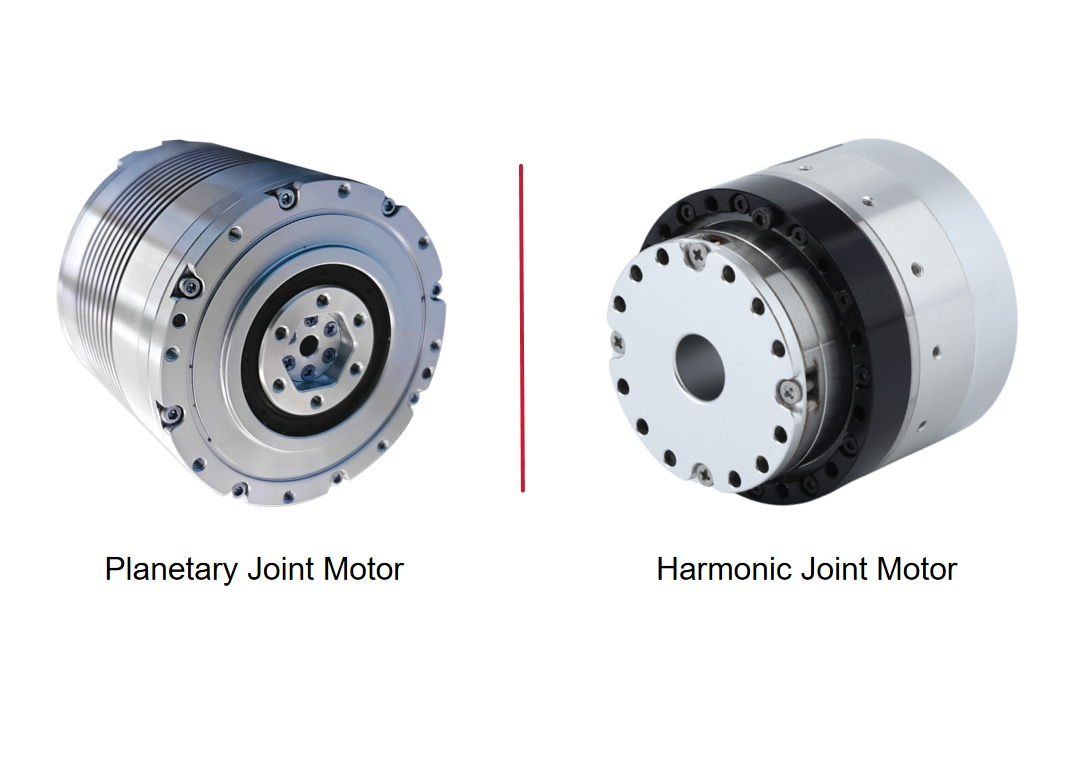
14 rotary joints adopt frameless torque motor + harmonic reducer
14 linear joints adopt frameless torque motor + planetary roller screw
The Unitree G1 basic version is equipped with 23 frameless motors, each priced at approximately USD 190–285, resulting in a total joint motor cost of around USD 4,300–6,900.
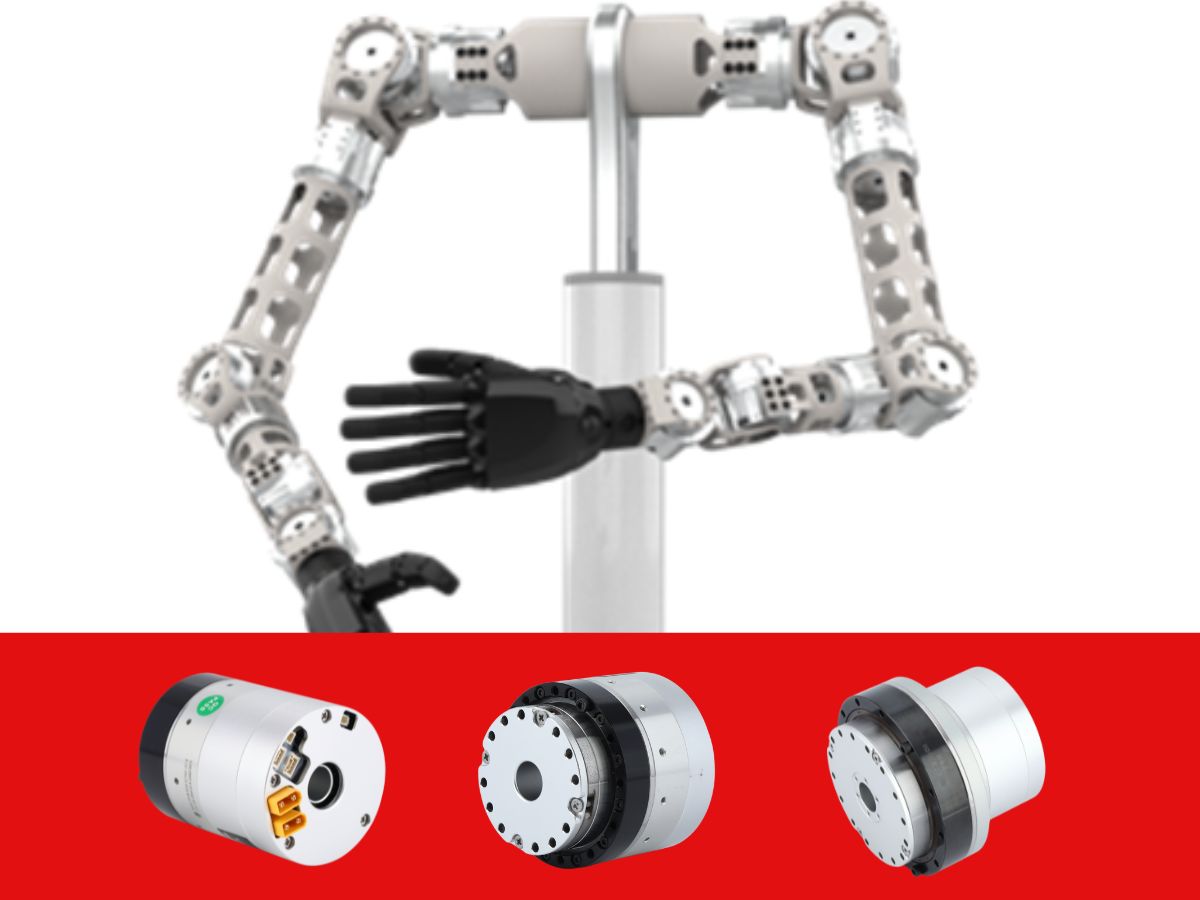
Why Are Joints So Critical in Humanoid Robots?
Robot joints are the core enablers of humanoid motion.
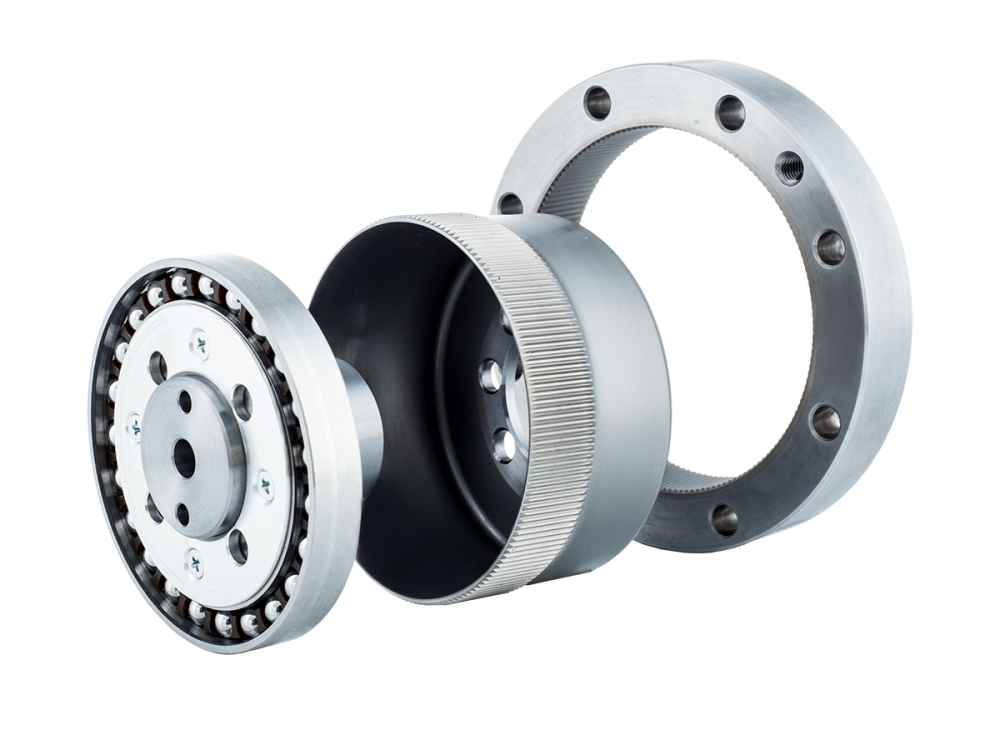
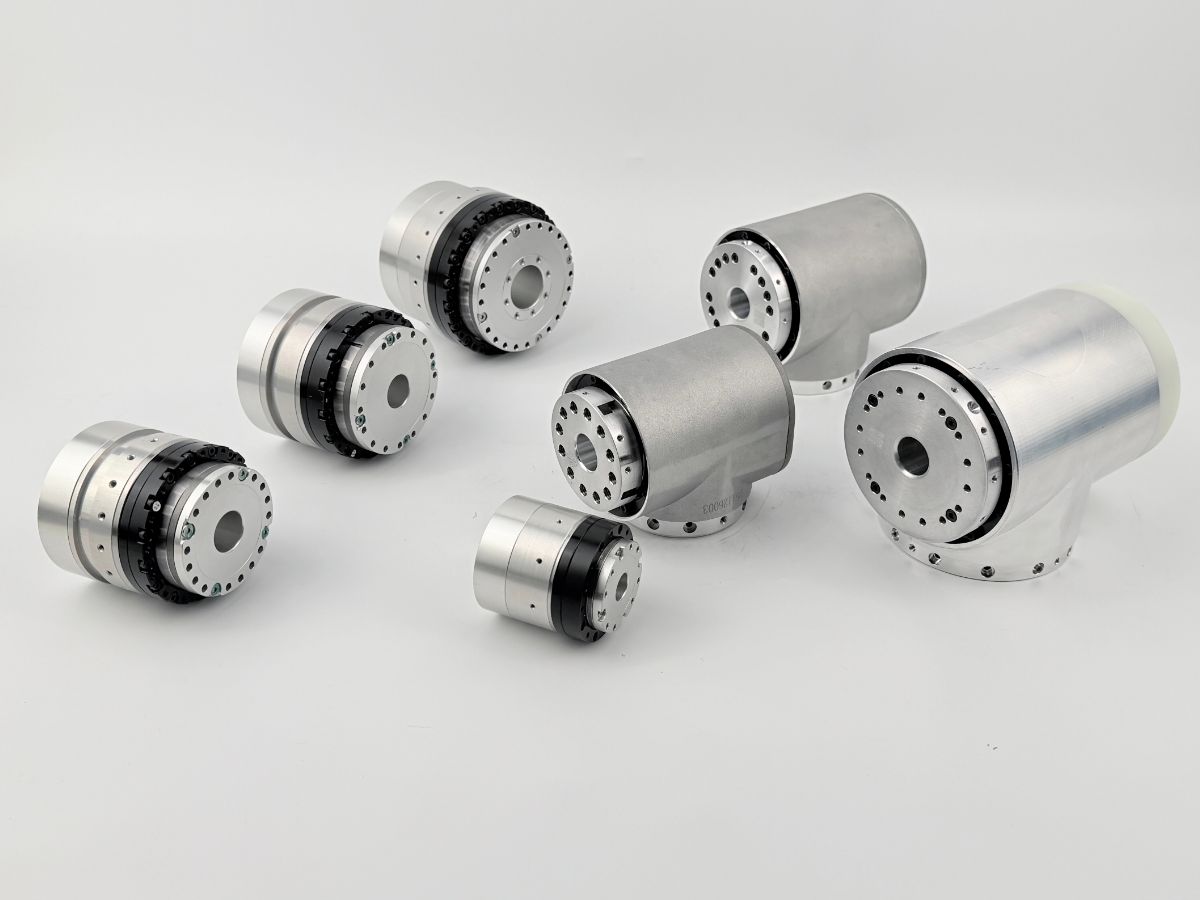
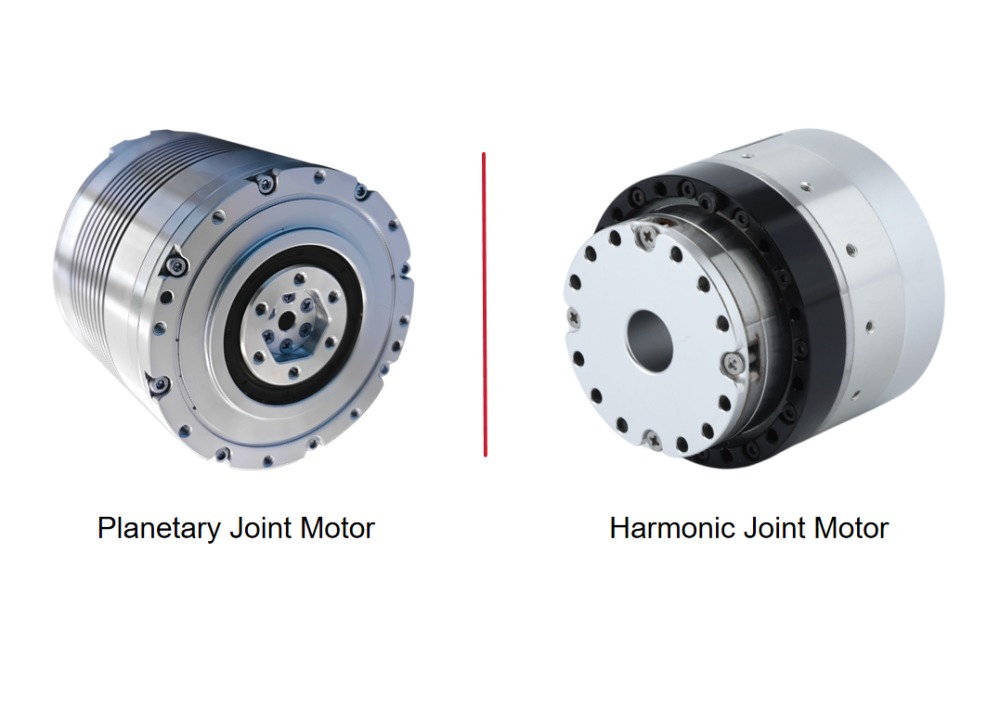
Only joint modules with ultra-high reduction ratios, extremely high torque density, and near-zero backlash—namely harmonic joint modules—can enable truly humanoid, natural movements.
Although joint modules contribute significantly to the overall cost, at the current stage of technology, harmonic joint modules remain the only solution that achieves the optimal balance between size, weight, precision, and torque. This makes them irreplaceable.
Why Are Frameless Torque Motors So Important in Humanoid Robot Joints?
The humanoid robotics industry almost exclusively uses frameless motors in joints.
A frameless torque motor is a type of permanent magnet synchronous motor that retains only the torque- and speed-generating core of a traditional motor—without a shaft, bearings, housing, or end caps.

A frameless motor consists of only two parts:
Rotor: an internal rotating steel ring with permanent magnets, mounted directly onto the machine shaft
Stator: an external component with laminated steel and copper windings, mounted tightly inside the mechanical housing to generate electromagnetic force
Unlike conventional servo motors, which are evaluated mainly by output power, frameless torque motors are evaluated by output torque.
Powered by a drive unit, the driver controls the UVW three-phase currents to generate a magnetic field that drives the permanent-magnet rotor. Feedback can be provided via Hall sensors or external encoders, allowing the drive to compare actual feedback with target values and precisely adjust rotor position to achieve servo control.
The key advantage of frameless motors lies in their high torque and power density and excellent volume and weight efficiency.
By increasing stator slot fill (embedding more copper windings) and optimizing structural design (lightweight, thin profiles), frameless motors deliver powerful torque within limited space—making them ideal for humanoid robots, where size, weight, and dynamic performance are critical.
Their high-density characteristics include:Higher power output within the same volume,Smaller size for the same power level,Lower temperature rise
Thanks to integrated design and optimized potting processes, energy efficiency and reliability are also significantly improved.
Why Are Gear Reducers So Important in Humanoid Robot Joints?
When comparing harmonic reducers, RV reducers, and planetary reducers, harmonic reducers are currently the optimal solution for humanoid robot upper-limb joints.
In harmonic drives:30%–50% of the total teeth are engaged simultaneously,Errors are averaged across multiple teeth, providing mutual compensation,Transmission accuracy is extremely high, with backlash controllable within 1 arc-minute,Under the same gear accuracy grade, transmission error is roughly one-quarter that of conventional cylindrical gear systems.
By slightly adjusting the radius of the wave generator to increase flexspline deformation, backlash can be reduced to near zero, or even completely eliminated—making harmonic drives especially suitable for frequent reversing motion.
How Harmonic Drives Reducers Work?
Harmonic transmission is based on the interaction between the wave generator and the flexible gear.
As the wave generator rotates, its elliptical profile causes periodic elastic deformation of the flexspline. Because the flexspline and circular spline differ in tooth count (typically by two teeth), the meshing position shifts continuously.
For every 180 degrees of wave generator rotation, the flexspline’s engagement position moves by one tooth pitch along the circumference. This accumulated relative displacement creates a speed difference between the flexspline and circular spline.
As a result, when the wave generator completes one full rotation, the flexspline rotates only
(tooth difference / circular spline teeth) × 360 degrees,
achieving a very high reduction ratio.
The harmonic reducer is a critical component of the harmonic joint module.
Motor and harmonic reducer must be properly power-matched—neither undersized nor oversized. In joint design, the reducer’s parameters (torque, speed) must be determined first, and then the motor is selected accordingly.

The high price of humanoid robots is not caused by brand premiums, but by engineering complexity and the difficulty of precision manufacturing.
Each joint in a humanoid robot must simultaneously achieve:High precision,Lightweight design,High torque output,Long-term reliability.
Only when every joint meets these stringent requirements can the entire robot operate smoothly, safely, and naturally.This is the fundamental reason why the cost of high-performance humanoid robots remains difficult to reduce.
Read More
Learn more about the story of HONPINE and industry trends related to precision transmission.
Double Click
We provide harmonic drive reducer,planetary reducer,robot joint motor,robot rotary actuators,RV gear reducer,robot end effector,dexterous robot hand