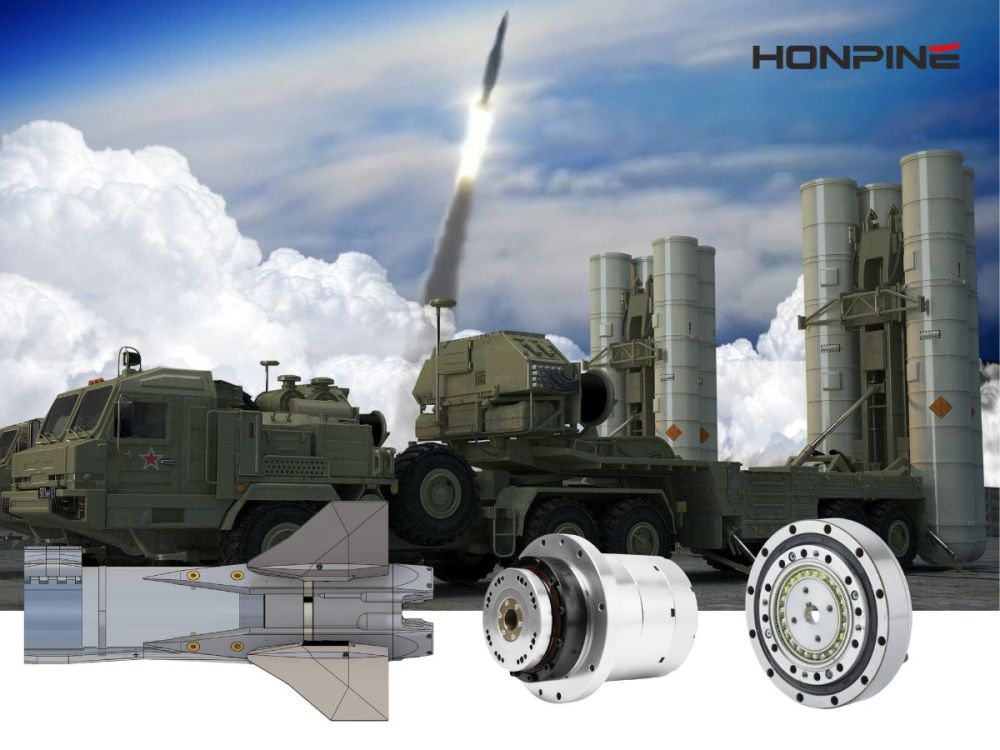
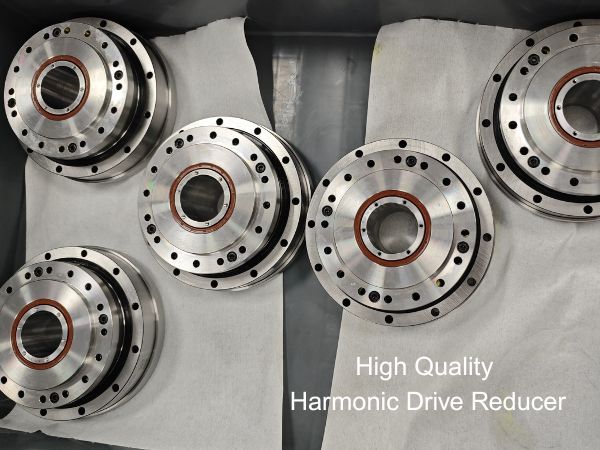
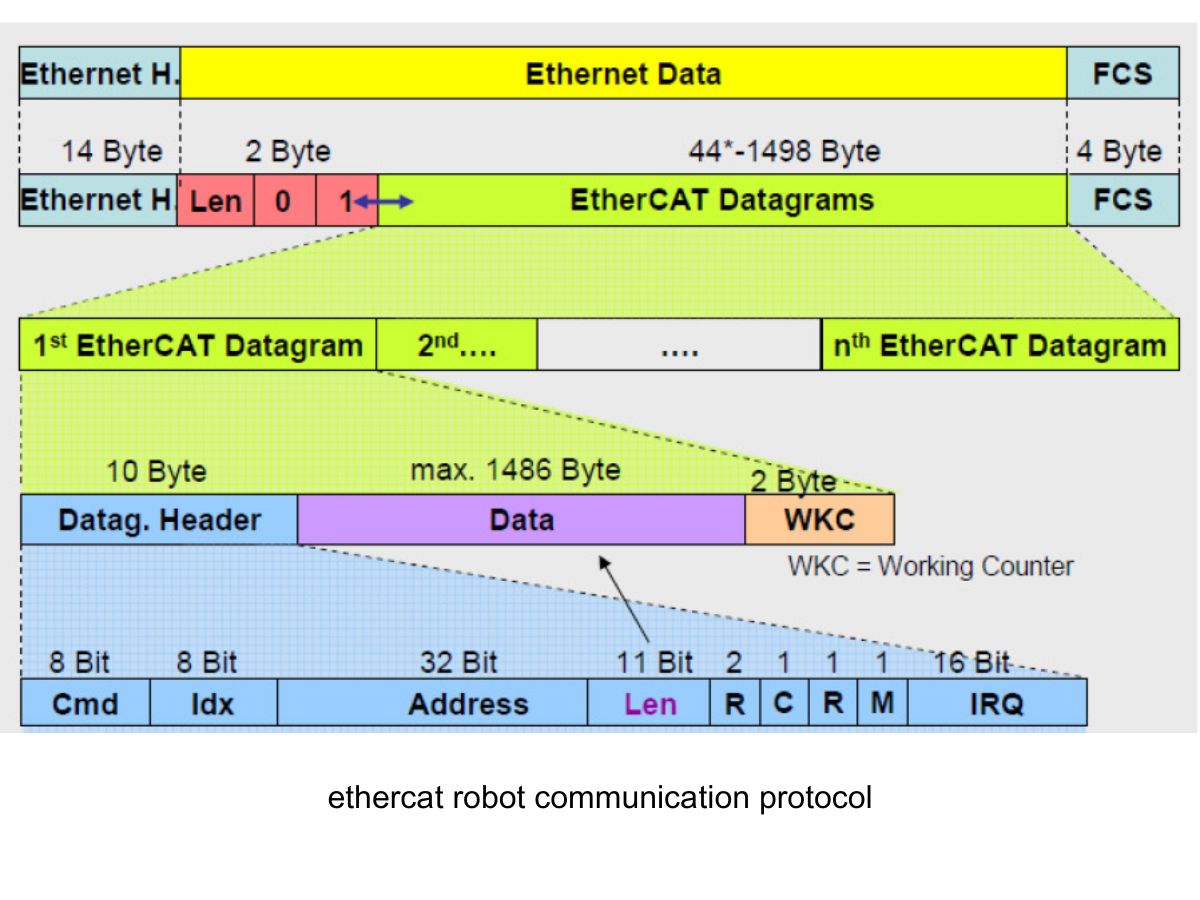
How High-Precision Reducers Drive the Development of Intelligent Manufacturing Technology
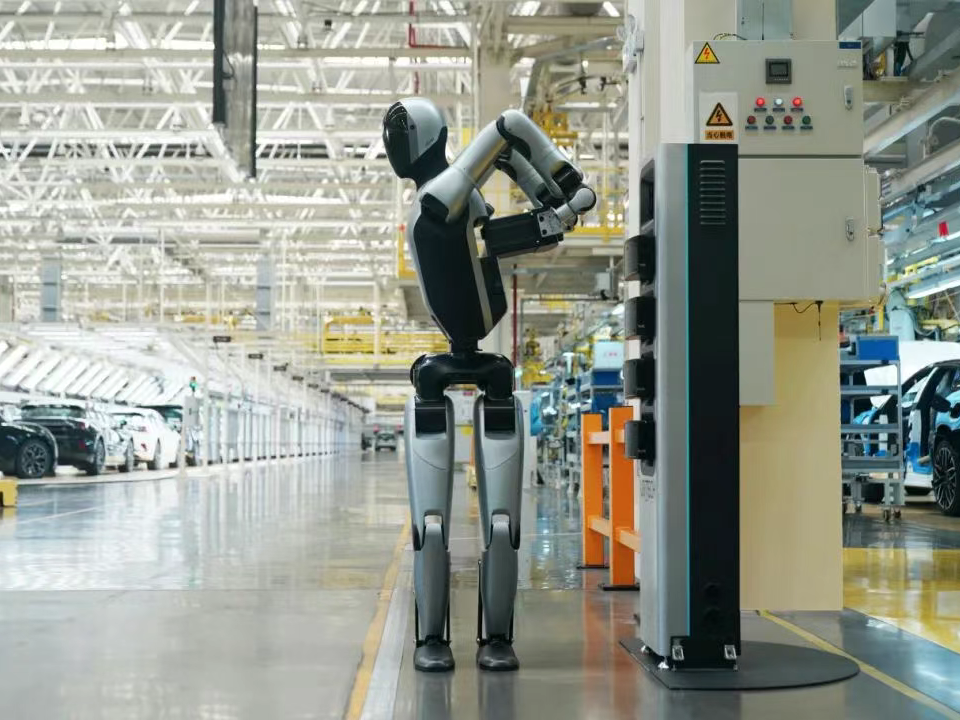
Research on key robotic technologies in intelligent manufacturing is a critical direction for promoting the intelligent upgrading of the manufacturing industry, among which high-precision robot positioning is a fundamental focus.
In the field of high-precision positioning technology, laser navigation and visual navigation are two commonly used and well-established methods. Laser navigation employs laser sensors to emit laser beams and receive reflected signals. By processing these signals, the relative position between the robot and its surrounding environment is calculated. This method offers advantages such as high precision and strong anti-interference capability, making it particularly suitable for structured environments like factory workshops and warehouses. Visual navigation, on the other hand, uses cameras to capture environmental images and applies image processing algorithms to extract feature information, thereby achieving robot positioning. Visual navigation is characterized by rich information and high flexibility, especially suited for unstructured or dynamically changing environments. Precision reducers serve as a bridge connecting the accurate algorithms of the digital world with the precise motion of the physical world.
Precision reducers directly determine whether a robot in a laser navigation system can accurately reach the target point calculated by the algorithm.
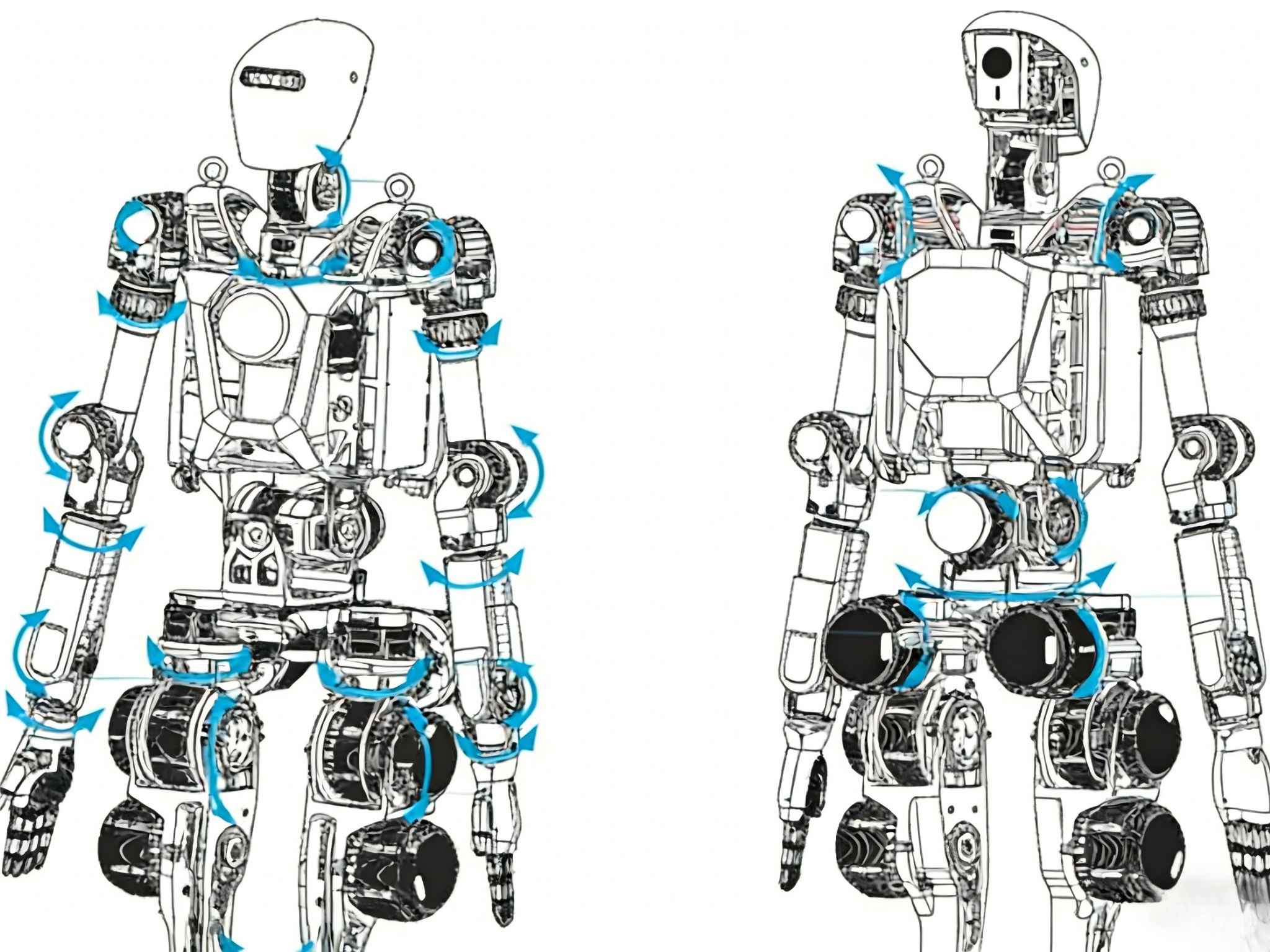
Precision planetary reducers provide driving power to the wheels.
Planetary reducers ensure precise linear velocity control by accurately regulating the speed of the drive wheels, enabling the robot to travel smoothly along the path and speed planned by the navigation system. This avoids speed fluctuations that could increase the corrective pressure on the positioning algorithm. Low-backlash planetary reducers guarantee consistency between speed commands and output speed. During starting, stopping, and load-bearing uphill climbing, they deliver smooth and powerful torque to prevent slipping or jitter, as even minor sliding can introduce positioning errors.
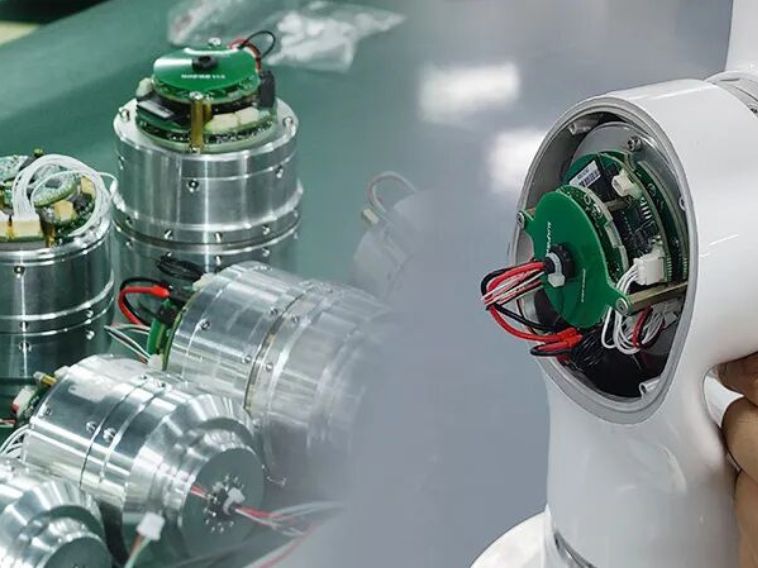
Harmonic reducers are responsible for high-precision positioning of the steering wheel.
Laser navigation requires the steering wheel to accurately turn to the commanded angle (e.g., with a precision of 0.01°). The near-zero backlash characteristic of harmonic reducers ensures that the angle rotated by the steering motor is transmitted to the tire without any loss, avoiding "backlash error." This allows the robot to move accurately along a straight line or perform precise right-angle turns.
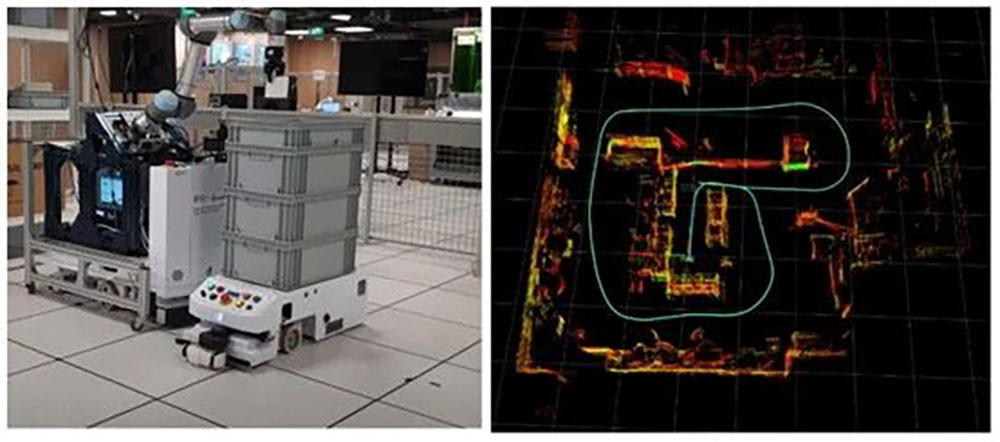
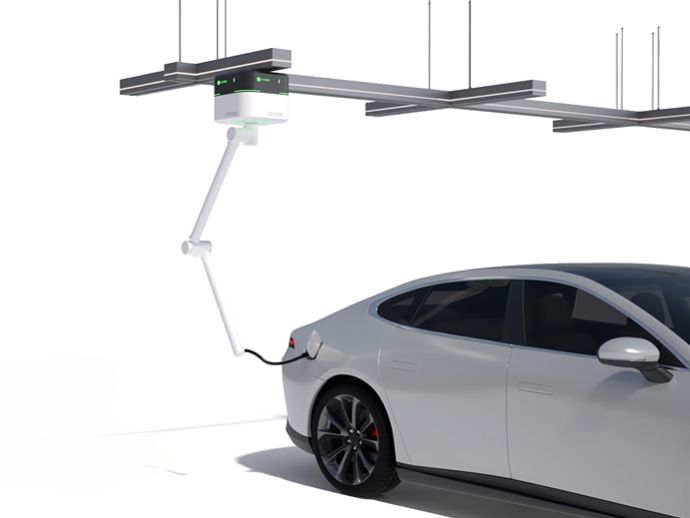
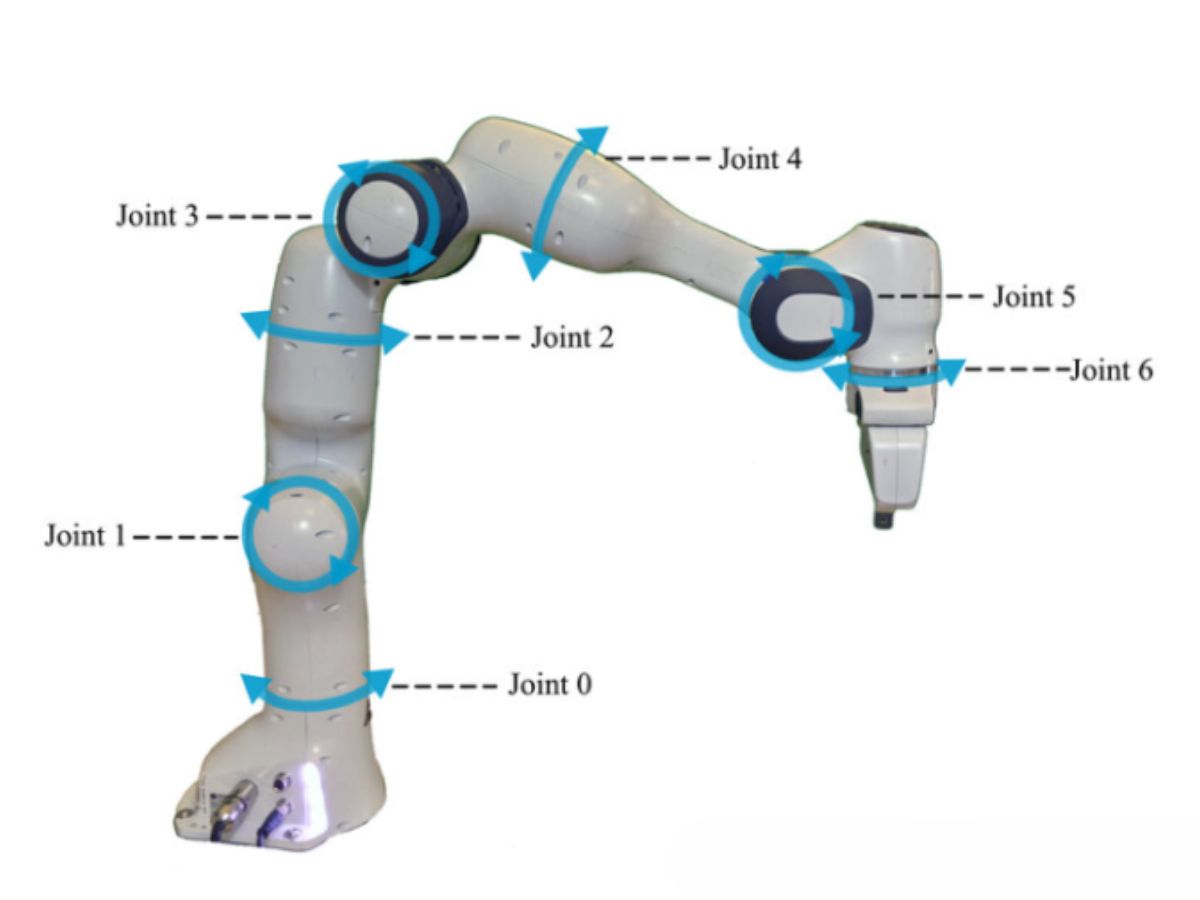
Precision reducers enable vision systems to correctly guide robotic arms.
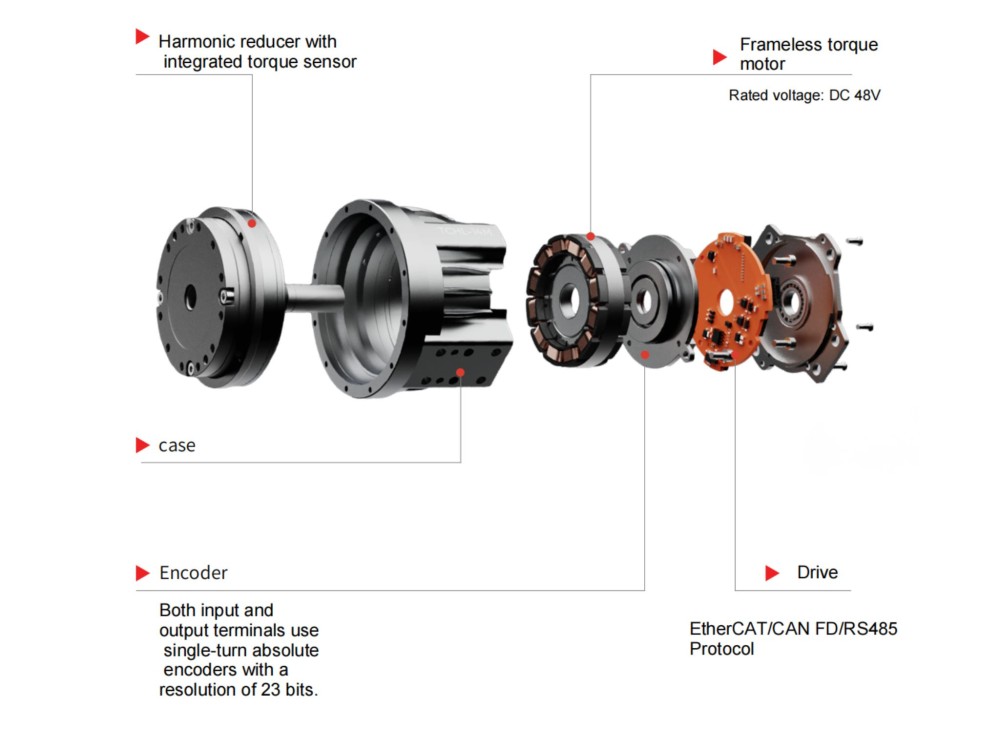
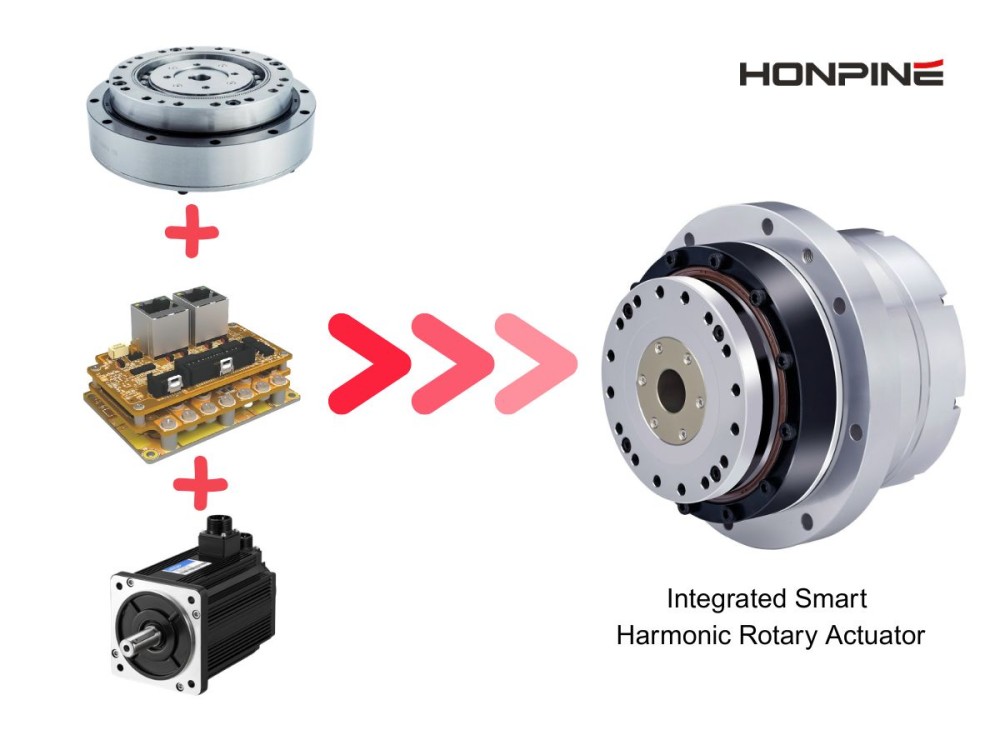
Harmonic reducers and RV reducers ensure that robotic arms can repeatedly reach the same spatial point with high repeatability. Vision cameras identify the position and orientation of the workpiece (X, Y, Z, Rx, Ry, Rz). This six-dimensional coordinate is sent to the robotic arm controller. Each joint of the robotic arm requires a harmonic reducer to convert the motor's rotation into minute and precise angular changes of the joint, thereby driving the end effector (e.g., suction cup or gripper) to move to the target point without any deviation. Backlash or error in any joint will be amplified at the end, leading to grasping or operational failure.
In practical applications, high-precision positioning technology must be selected and optimized based on the specific intelligent manufacturing environment. Machinery manufacturers can choose the most suitable precision reducer according to the required torque, accuracy, rigidity, and other factors in specific scenarios.
Read More
Learn more about the story of HONPINE and industry trends related to precision transmission.
Double Click
We provide harmonic drive reducer,planetary reducer,robot joint motor,robot rotary actuators,RV gear reducer,robot end effector,dexterous robot hand