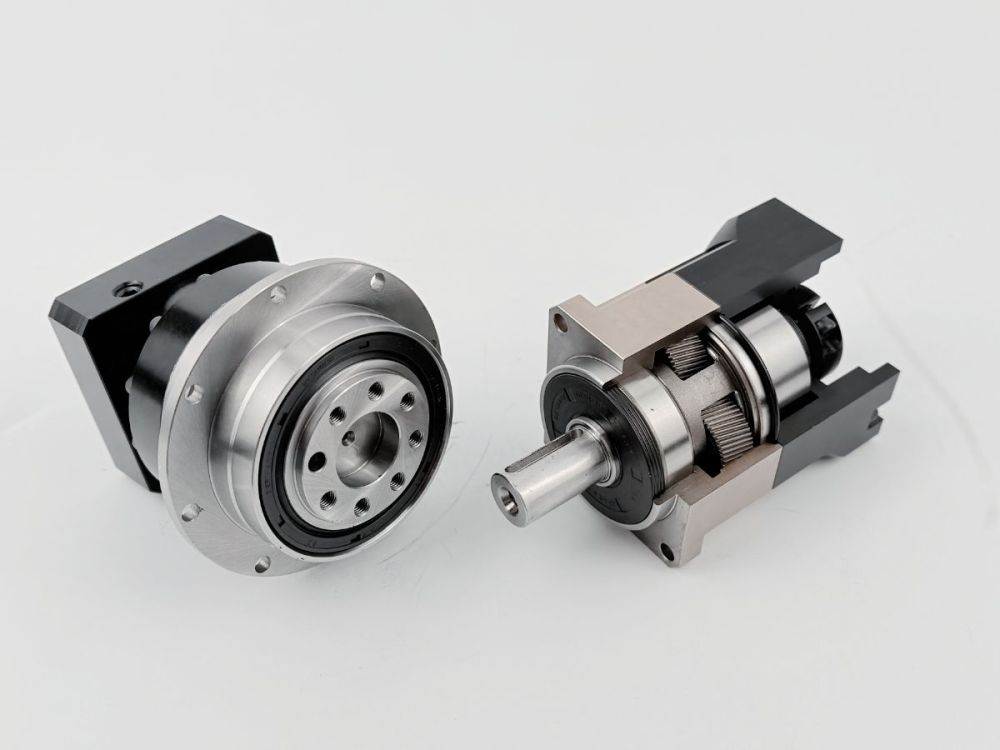
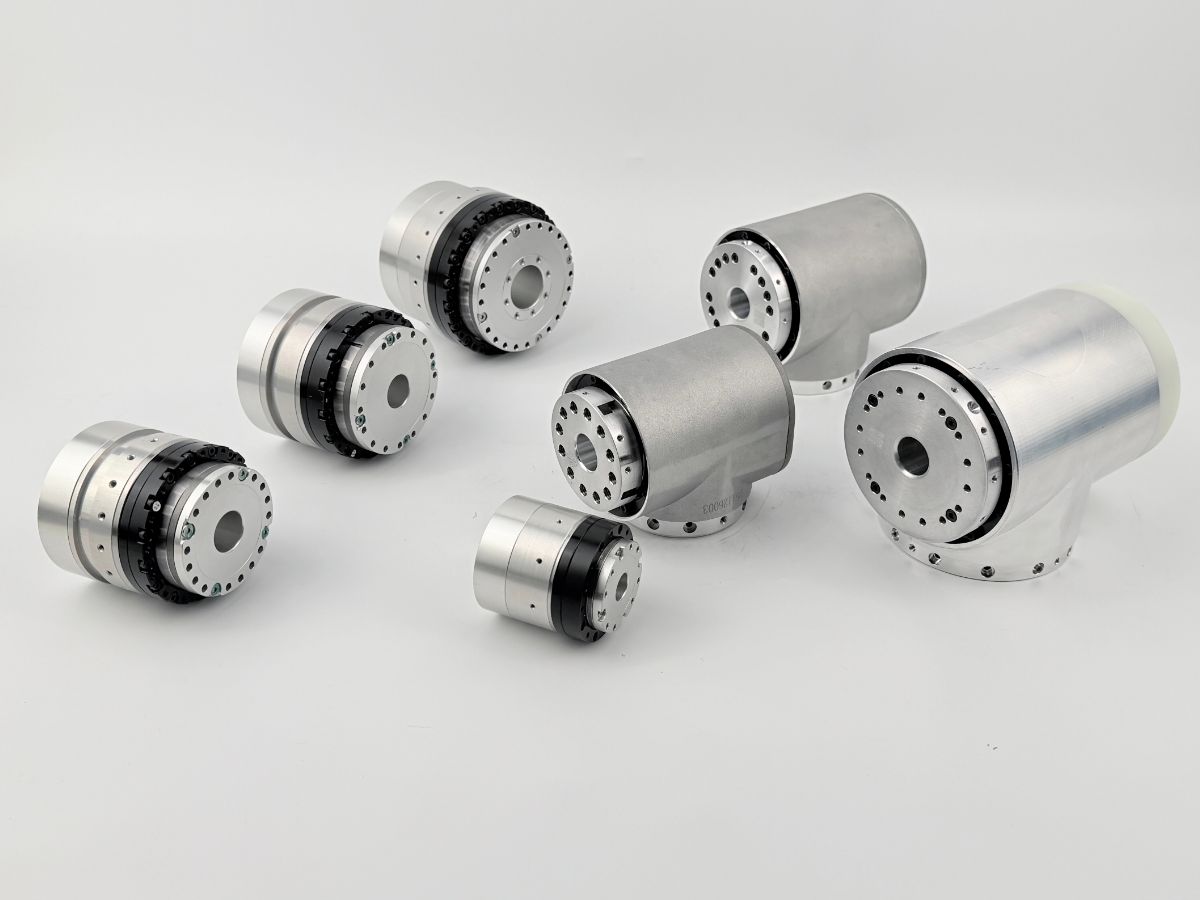
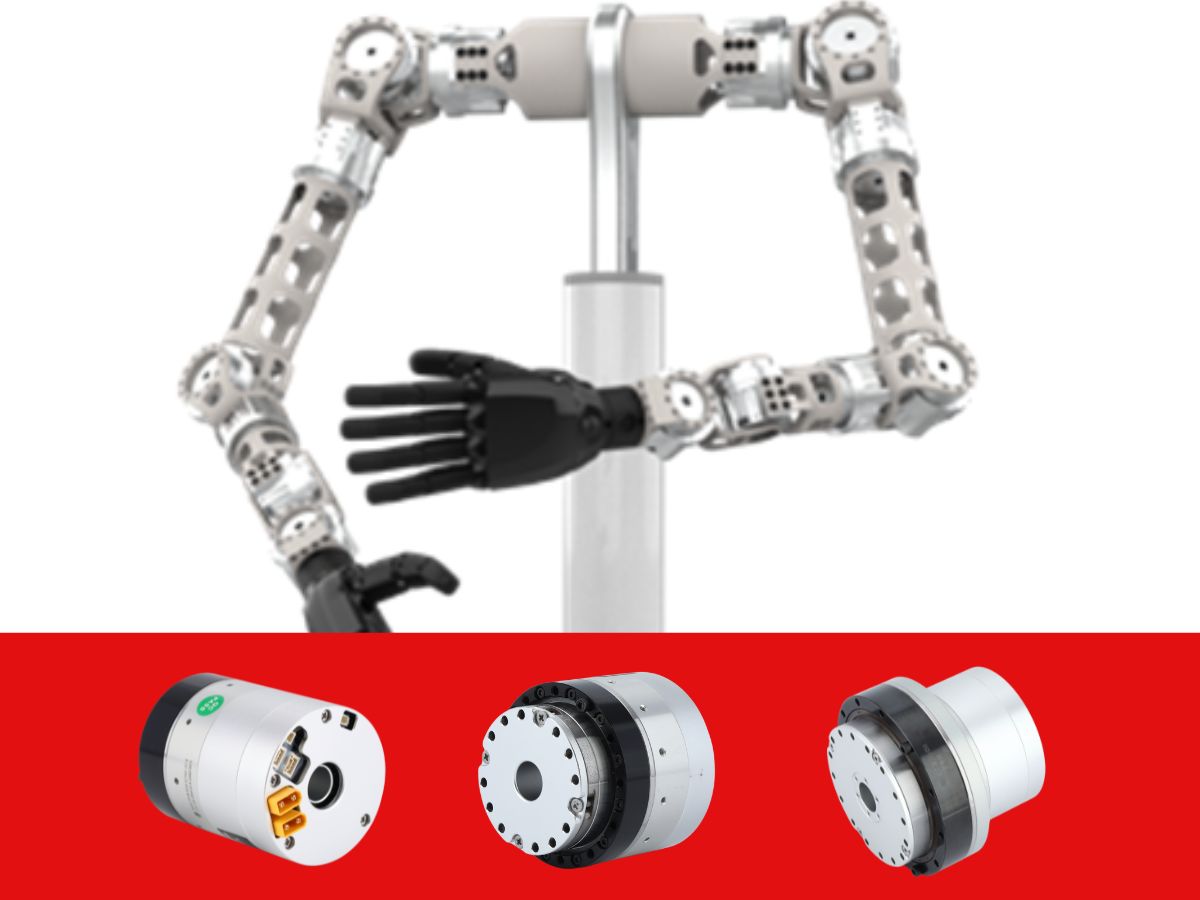
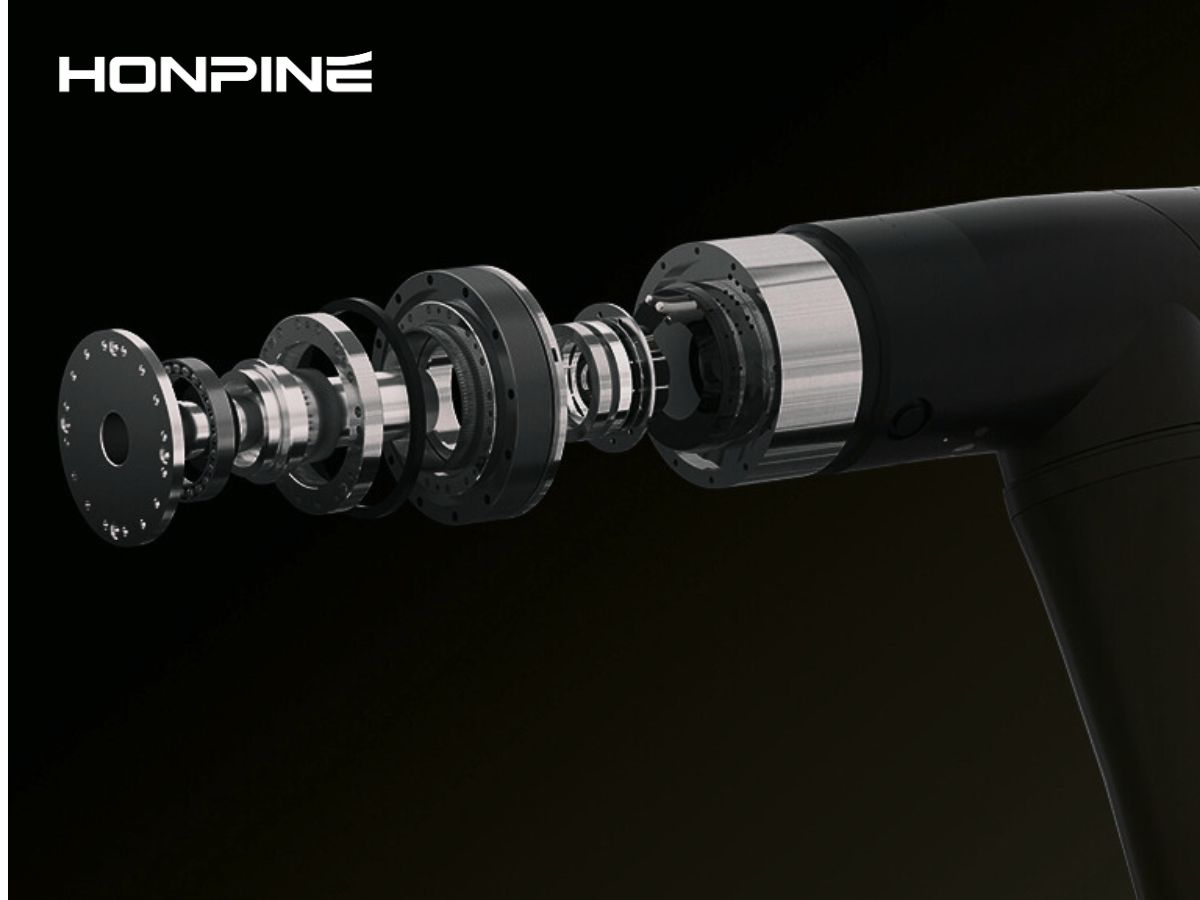
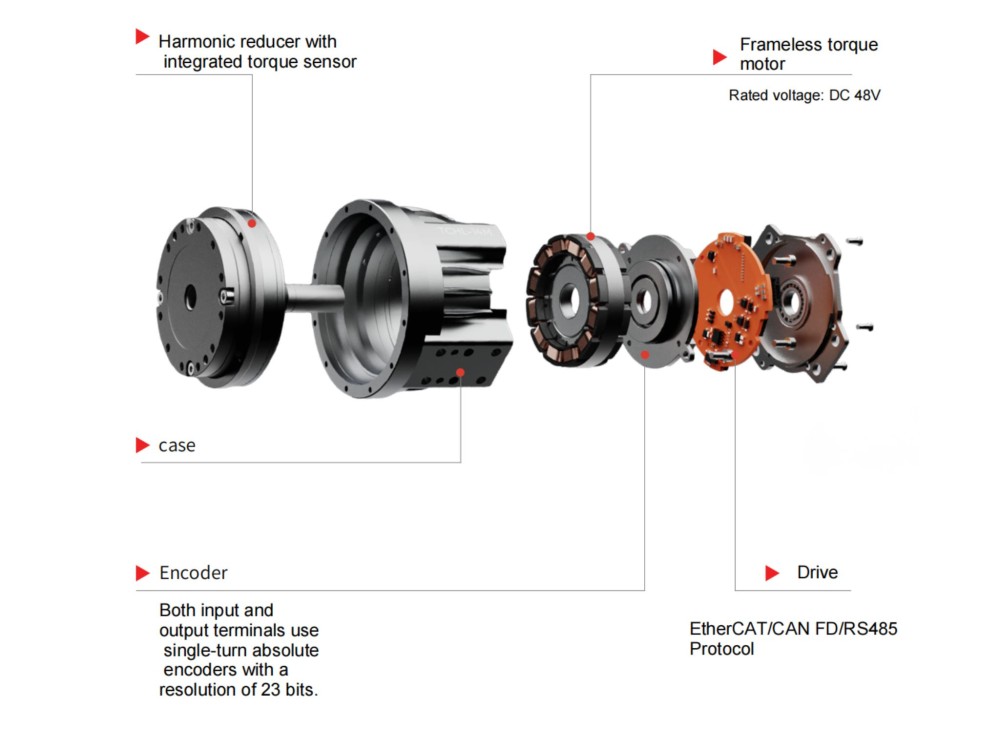
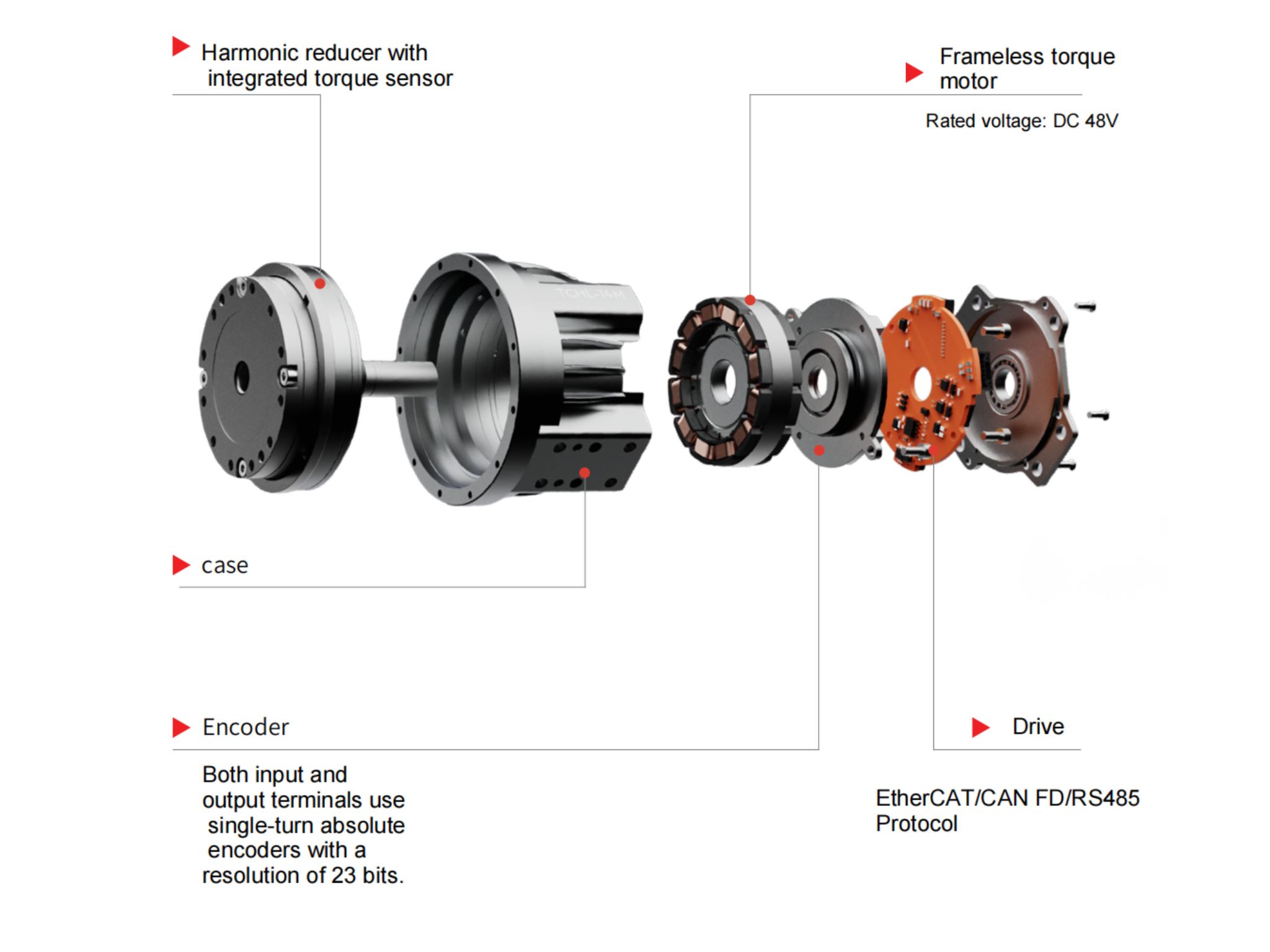
Communication Challenges of Harmonic Rotary Actuator: Can EtherCAT and CAN Be Used Together?
During the development and integration of humanoid robots, the compatibility of communication protocols in robot joint actuatordirectly impacts the control accuracy, system stability, and flexibility for future expansions. Recently, we’ve received several inquiries from engineers asking whether our robot's core hardware harmonic robot rotary actuator can simultaneously support both EtherCAT and CAN protocols. What are the functional differences between these two connection methods? Let’s take a deep dive into these questions today
1. Separate Connections: Both EtherCAT and CAN Can Achieve Full Control
Whether connected solely via EtherCAT or CAN, our robot joint actuator can independently achieve full functionality, meeting the needs of various usage scenarios:
Only connected to EtherCAT: Leveraging the high-speed, real-time communication features of EtherCAT, the system can precisely transmit control commands such as position, velocity, and torque. It supports microsecond-level synchronization, making it perfect for high-precision, high-dynamics motion control applications (e.g., precision assembly robots, collaborative robots). This ensures rapid motion responses with minimal error.
Only connected to CAN: For scenarios with lower bandwidth requirements, or where cost control is more important (e.g., AGV robots, low-load material handling robots), a single CAN connection can reliably transmit control commands and feedback on motor status, offering a balance between practicality and cost-effectiveness.
2. Simultaneous Connections: EtherCAT Takes Priority, CAN Switches to Monitoring Mode
When both EtherCAT and CAN are connected to the robot joint actuator simultaneously, the system will automatically trigger the “EtherCAT priority” mechanism to prevent command conflicts between the two buses while maximizing the advantages of both protocols:
Control rights belong to EtherCAT: At this point, only the EtherCAT bus has permission to send control commands, enabling high-precision motion control while ensuring the real-time and exclusive nature of the core control loop, unaffected by other buses.
CAN switches to monitoring mode: The CAN bus automatically switches to a "monitoring mode" to continuously provide feedback on key motor statuses, such as motor speed, winding temperature, operating current, and fault codes. This allows engineers to keep track of the system’s operational condition, facilitating debugging, maintenance, and fault troubleshooting, ensuring the system's stable operation.
If your project needs to balance high-precision control and multi-dimensional status monitoring, consider using the EtherCAT + CAN simultaneous connection approach. However, if your application requires only basic control functions, choosing either protocol alone will be sufficient.
If you encounter any issues during protocol selection or connection configuration, or would like to learn about specific adaptation cases in certain scenarios, feel free to leave a comment below. Our technical team will be happy to assist you!
Read More
Learn more about the story of HONPINE and industry trends related to precision transmission.
Double Click
We provide harmonic drive reducer,planetary reducer,robot joint motor,robot rotary actuators,RV gear reducer,robot end effector,dexterous robot hand