Why the Joint Module is Called the "Power Heart" of the Robot
Robot joints are one of the most basic components that constitute the mechanical structure of the robot. All the actions of the robot are completed by the connecting rods and joints that make up the entire system. The performance of the robot joints will directly affect the overall performance of the robot, such as joint stiffness, hysteresis, positioning accuracy, speed, and noise during operation and other performance indicators.
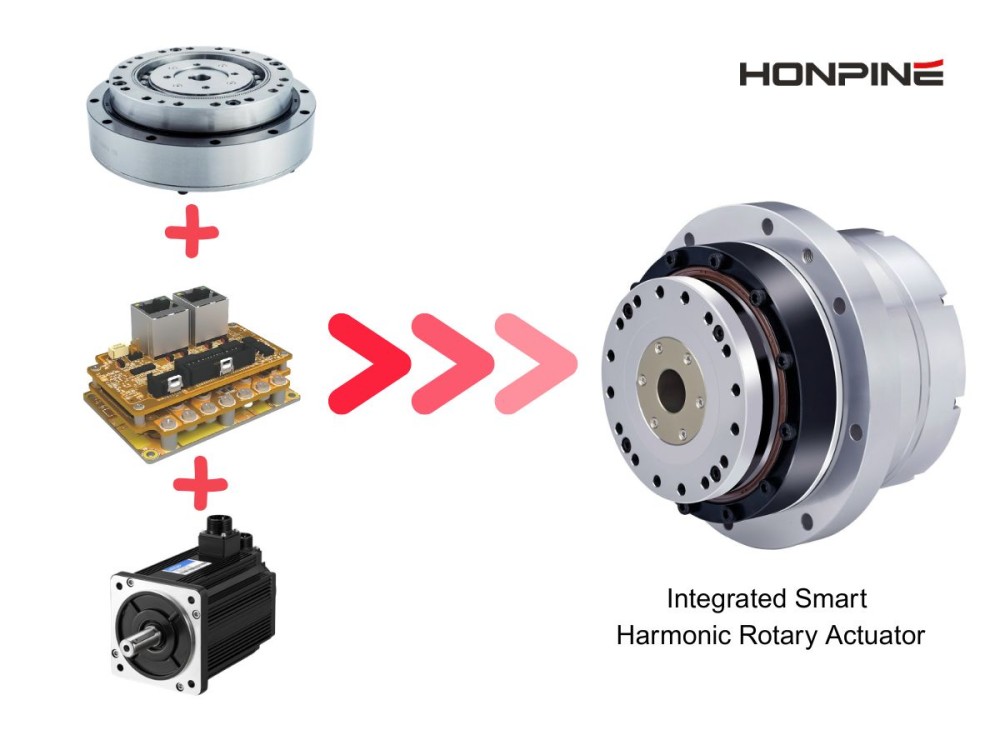
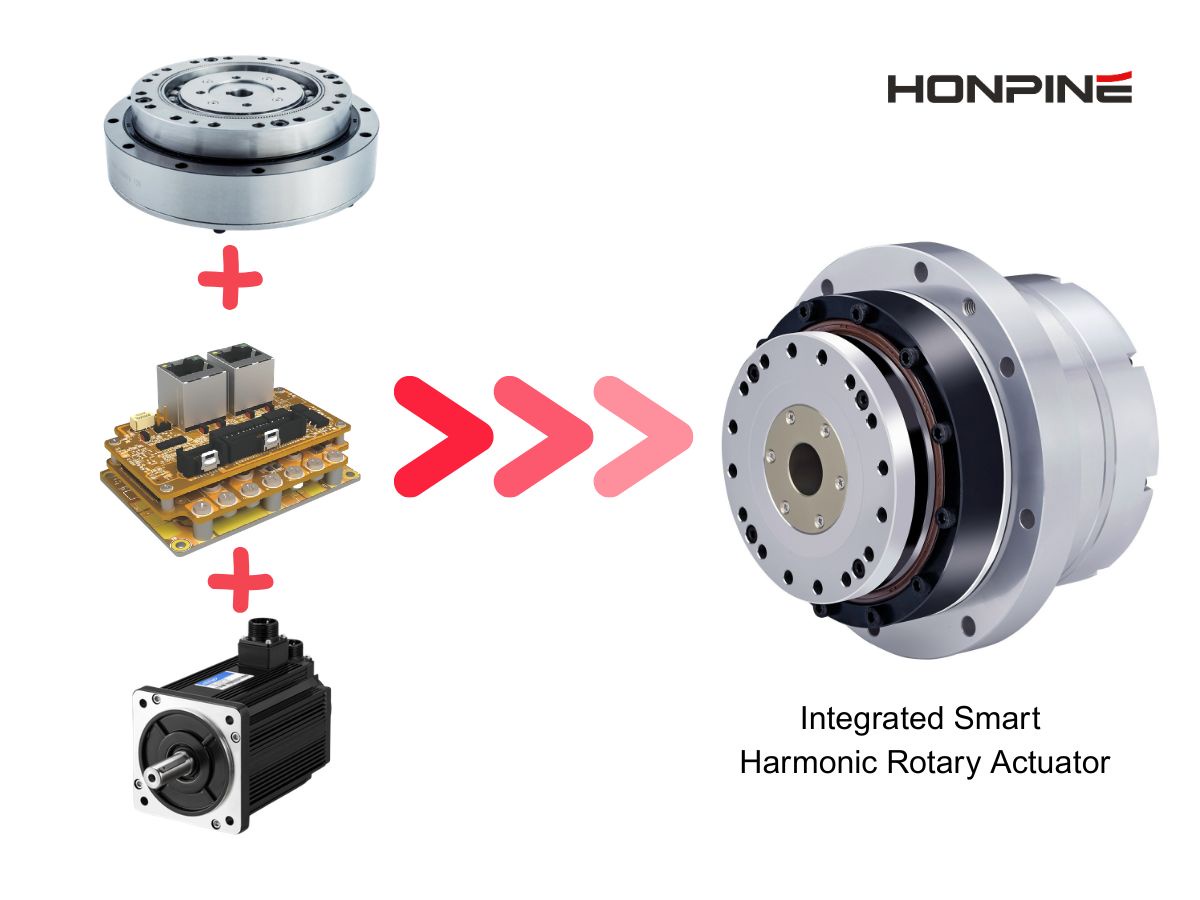
The robot joint module is a precision component that integrates drive, transmission, sensing and control. Its function is similar to the musculoskeletal system in an organism, and it is responsible for driving and controlling the movement of various joints and components of the robot. The power is provided by the motor, and after the speed is changed and the torque is increased by the reducer, the encoder provides feedback on the position information, and finally the driver achieves precise control. This article will help us unlock the robot joint module together.
The Composition and Function of the Joint Module
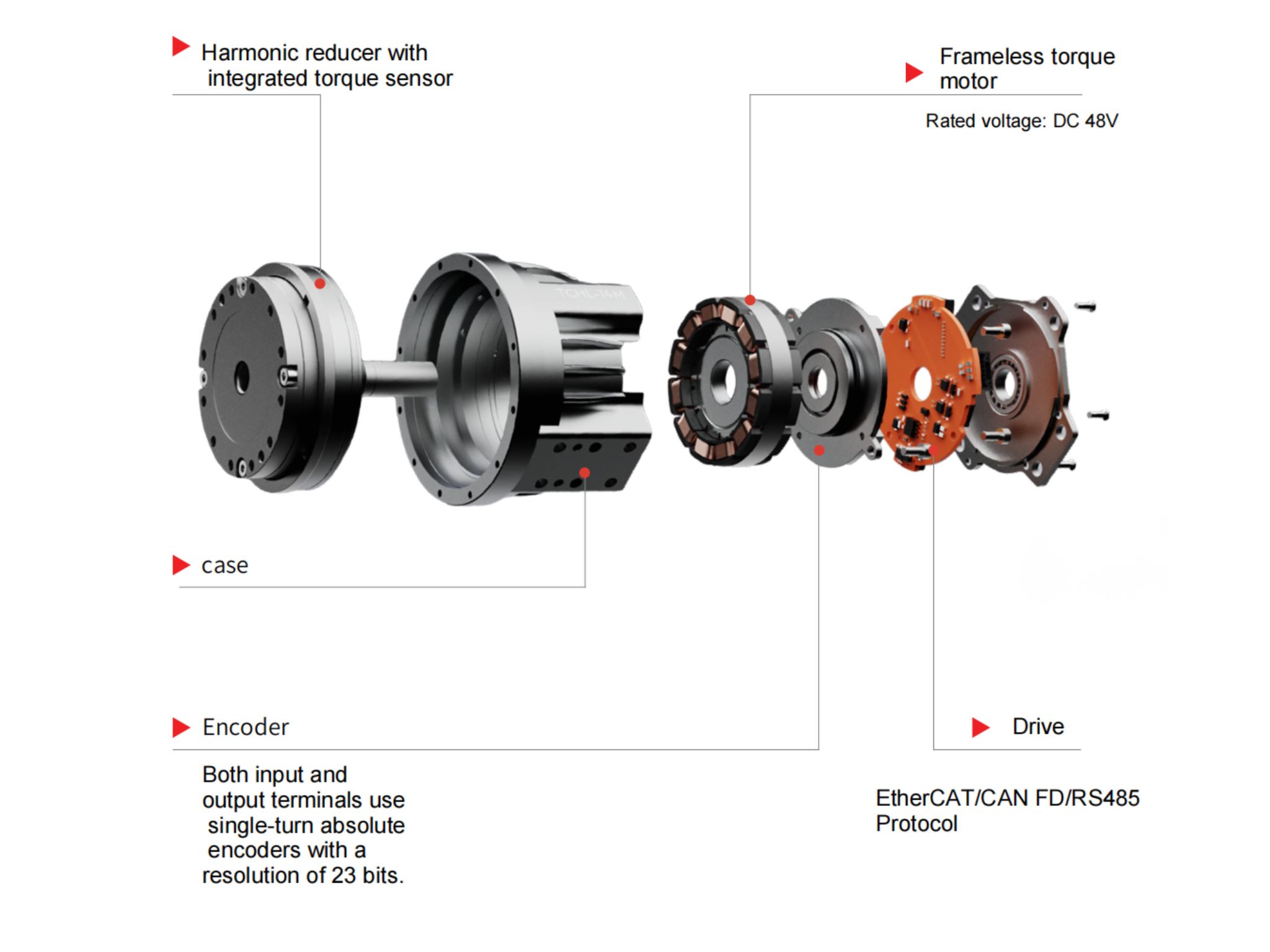
Magnetoelectric Encoder:
The main part is composed of a read head board and a magnetic grid. The magnetic grid is engraved with small magnetic poles, and the sensor detects the change of the magnetic field when the disk rotates. The read head board chip can be a Hall-effect device that senses voltage changes, or a magnetoresistive device that senses magnetic field changes. The signal is multiplied, divided or interpolated to produce the required output to achieve the measurement purpose.
Photoelectric Encoder:
It is composed of a light source, an optical code disk and a photosensitive element. The grating is actually a disk engraved with transparent and opaque lines. The light flux received by the photosensitive element changes synchronously with the transparent lines. The output waveform of the photosensitive element is shaped and becomes a pulse signal. One pulse is output for each revolution. According to the change of the pulse, the displacement of the equipment can be accurately measured and controlled to reflect the current speed of the equipment.
Incremental Encoder:
The incremental encoder directly uses the principle of photoelectric conversion to output three sets of square wave pulses A, B and Z phases; the phase difference between A and B pulses is 90°, so that the direction of rotation can be easily determined, and the Z phase is one pulse per rotation, which is used for reference point positioning. Its advantages are a simple principle and structure, an average mechanical life of more than tens of thousands of hours, strong anti-interference ability, high reliability, and suitability for long-distance transmission. Its disadvantage is that it cannot output the absolute position information of the shaft rotation.
Absolute Encoder:
The absolute encoder is a sensor that directly outputs digital data. There are several concentric code disks on its circular code disk along the radial direction. Each track is composed of light-transmitting and light-impermeable sectors. The number of sectors of adjacent code tracks is doubled. The number of code tracks on the code disk is the number of bits of its binary digits. On one side of the code disk is the light source, and on the other side there is a photosensitive element corresponding to each code track. When the code disk is in different positions, each photosensitive element converts the corresponding level signal according to whether it is illuminated or not, forming a binary number. The characteristic of this encoder is that it does not require a counter, and a fixed digital code corresponding to the position can be read at any position of the rotating shaft. Obviously, the more code tracks there are, the greater the accuracy.
DC Drive and Temperature Sensor
The DC drive can change the motor voltage to control the brushless DC speed.
(Control motor rotation)
The temperature sensor can sense the temperature and convert it into a usable output signal.
(Collect current temperature feedback)
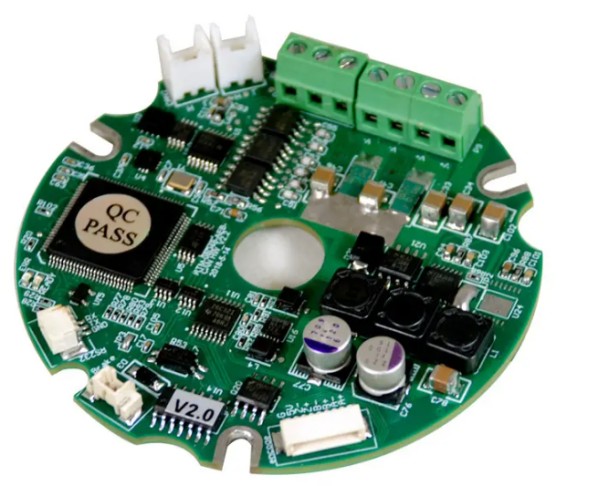

Servo Drive Module:
The high-performance, compact and fully digital universal servo drive designed and produced by the integrated research and development of joint modules can well meet the requirements of your collaborative robot for high precision, smooth operation, fast response and torque control. It is suitable for high-precision working scenarios such as collaborative robots, exoskeleton robots, medical and automation equipment.
(Control the motor to rotate with torque, current and absolute position)


Brake Retainer:
The retaining brake is an electromagnetic device, which consists of an electromagnet, a brake pad, a pressure plate, and a spring. When the motor stops running, the electromagnet is energized to generate a magnetic field, which attracts the brake pad to contact the pressure plate. At the same time, the pressure plate compresses the spring, causing friction between the brake pad and the motor rotor, thereby maintaining the position of the motor.
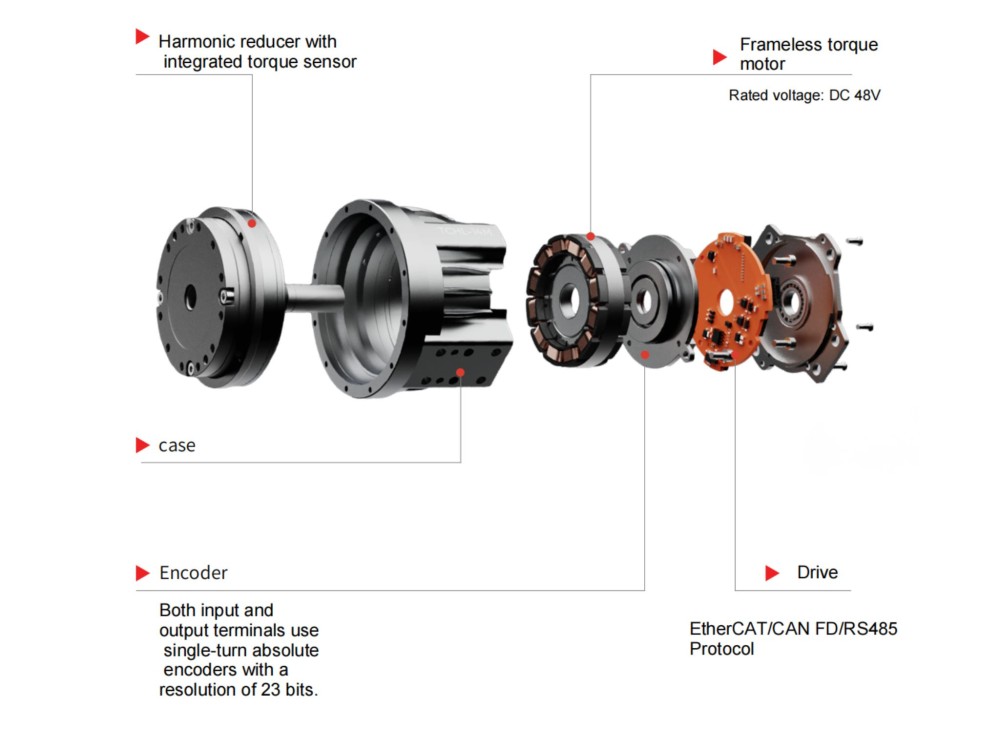
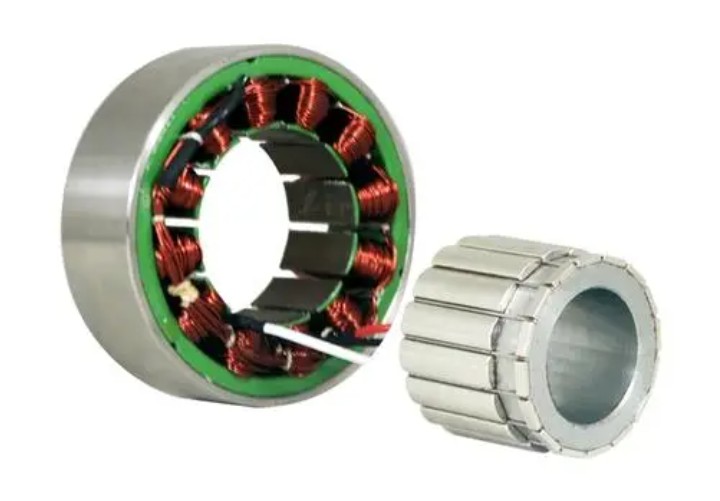
Frameless Torque Motor:
Torque motors can continue to operate even when the motor is at low speed or even stalled (i.e., the rotor cannot rotate), without causing damage to the motor. In this working mode, the motor can provide a stable torque to the load (hence the name torque motor). Torque motors can also provide torque in the opposite direction of operation (braking torque). The shaft of a torque motor does not output power at a constant power but at a constant torque.

Torque Sensor:
The torque sensor, also called torque transducer or torque meter, is divided into two categories: dynamic and static. Dynamic torque sensor can also be called torque sensor, torque speed sensor, non-contact torque sensor, rotation torque sensor, etc. The torque sensor is a detection device of the torsional torque applied on various rotating or non-rotating mechanical parts.
It is precision measuring equipment for measuring various torques, speeds and mechanical powers
(Used to measure motor torque, generally using incremental and absolute encoders instead)

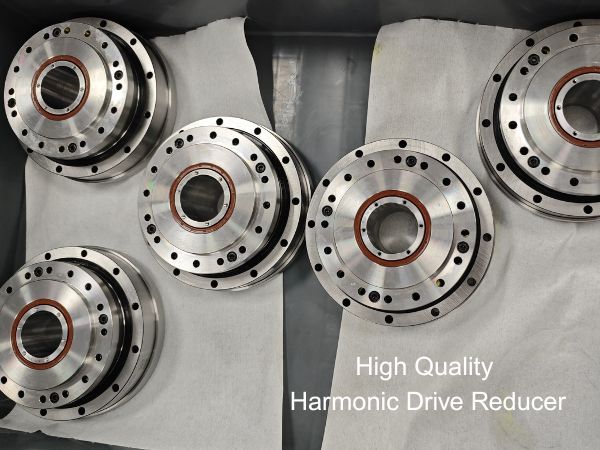
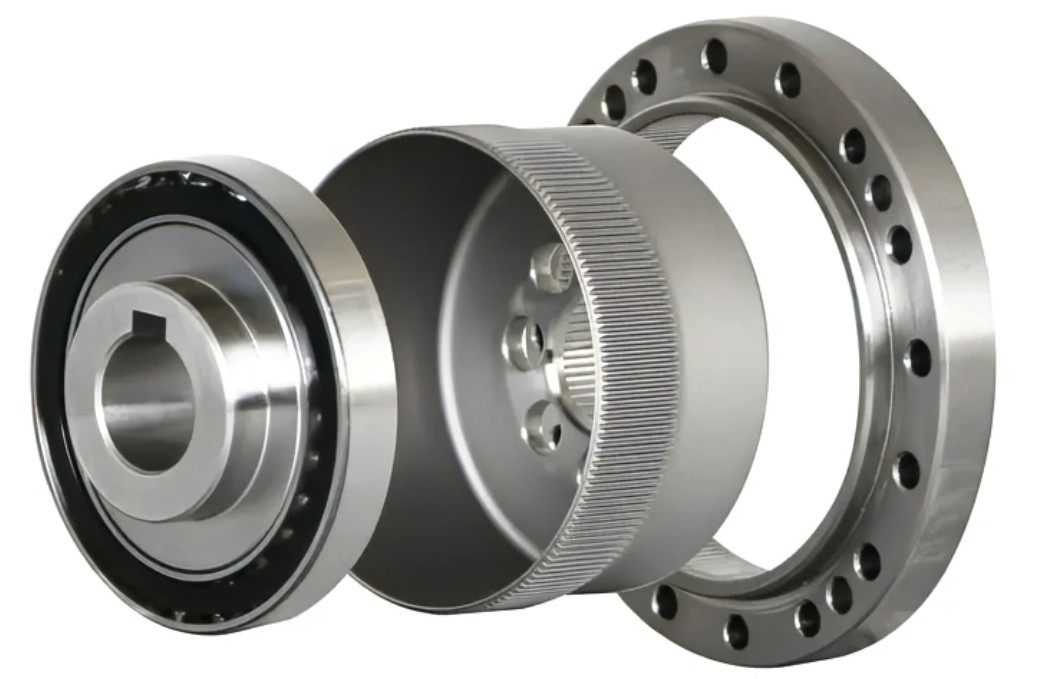
Harmonic Reducer:
The harmonic gear reducer is a reduction device consisting of three basic components: a fixed internal gear, a flexible wheel (i.e., an elastic thin-walled sleeve whose base is connected to the driven shaft "making a gear ring on the generatrix at the beginning of the flexible wheel"), and a wave generator that causes radial deformation of the flexible wheel.
(The motor running speed is reduced through different reduction ratios)

What are the advantages of joint modules?
Modularity
Integrated joint modules typically feature modular designs, allowing them to be freely combined to form multi-degree-of-freedom robotic arms or service robot skeletons.
Shorten construction period and reduce costs
They reduce personnel and time investments in mechanical selection and assembly. They simplify comprehensive supply chain management and quality control costs, while reducing robot R&D and production cycles.
Function expansion
Additional sensor devices can be integrated to enhance high-precision movement coordination and ensure motion safety.
Mass production
Establishing standardized production systems helps reduce costs. Implementing standardized quality control and inspection systems ensures consistent robot joint quality.
Where will the future of joint modules go?
Mechatronic joints have only a few decades of development history since Carnegie Mellon University developed the world's first mechatronic joint prototype for NASA in 1988.
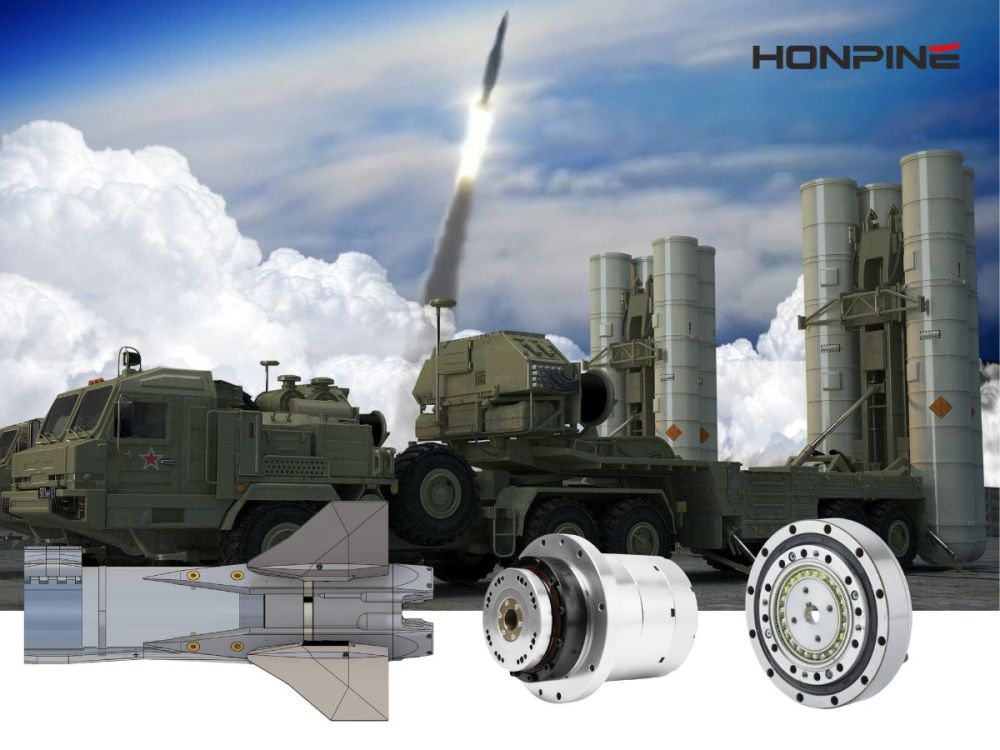
Currently, joint modules have been successfully applied in:Aerospace,Automated packaging machinery,Industrial laser cutting systems,Industrial robot automation components,Medical robotic equipment,Measurement and testing devices,Media and communication equipment,Mobile humanoid robots,Optical equipment and telescopes,Photovoltaic systems,PCB manufacturing,Semiconductor production Artificial intelligence, robotics, and digital technologies are transforming global workplace safety and health standards.




These technologies improve worker well-being by:Automating hazardous tasks,Optimizing logistics,Enhancing monitoring capabilitiesThe future development of joint modules will expand with emerging applications, supporting customization in:Materials,Structural designs,Precision levels
HONPINE is committed to providing customers with comprehensive services and solutions.
Read More
Learn more about the story of HONPINE and industry trends related to precision transmission.
Double Click
We provide harmonic drive reducer,planetary reducer,robot joint motor,robot rotary actuators,RV gear reducer,robot end effector,dexterous robot hand