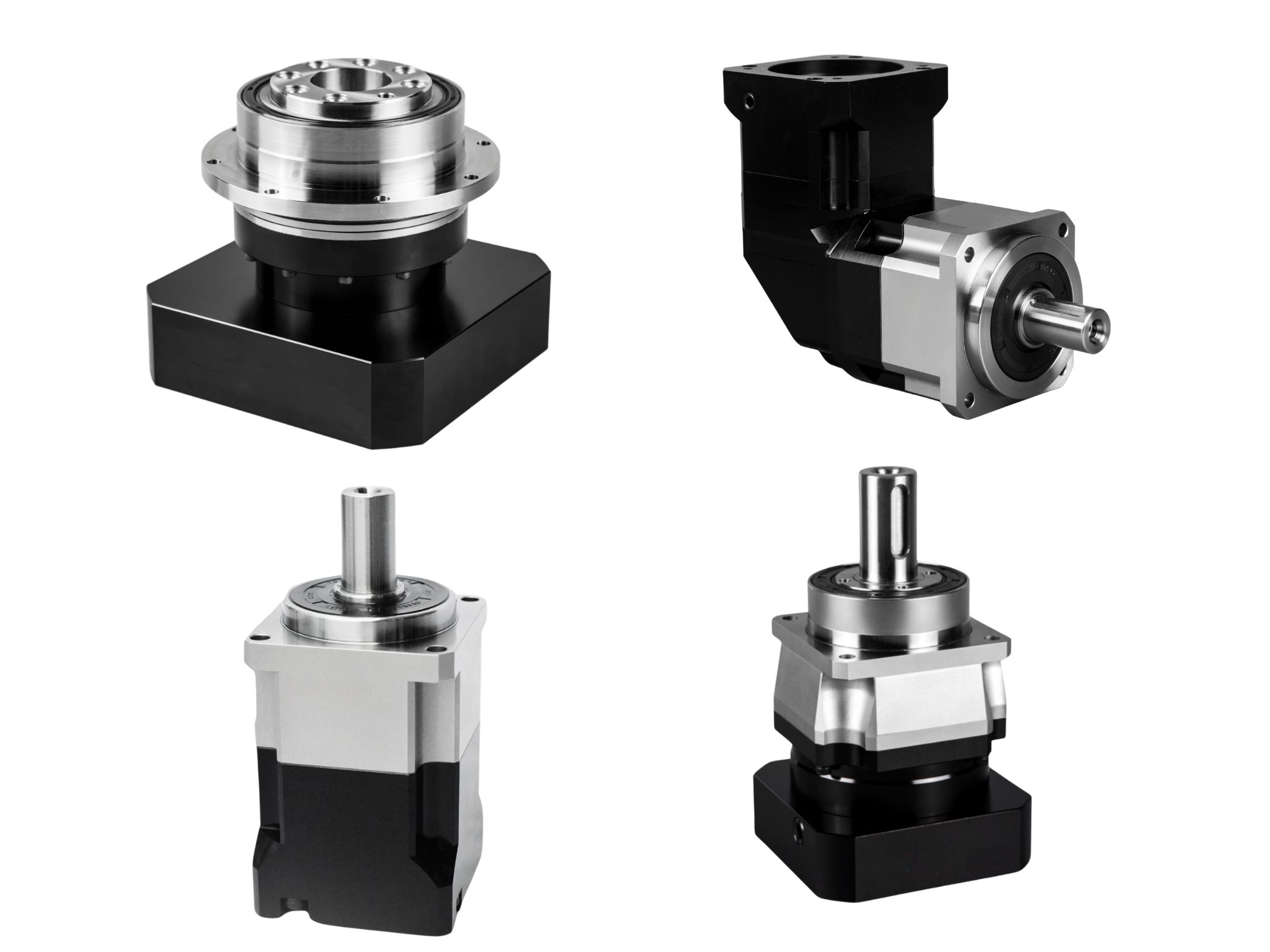
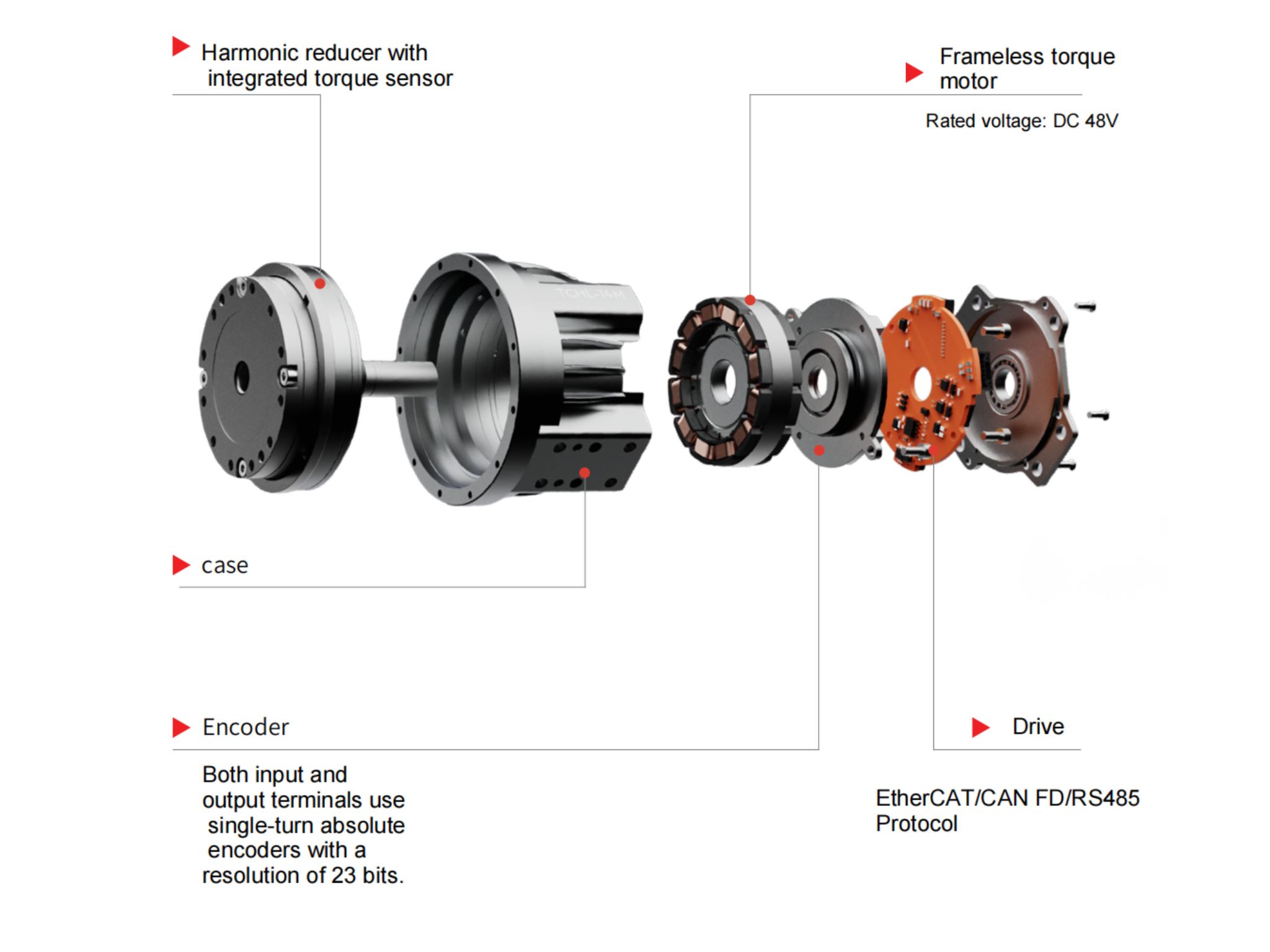
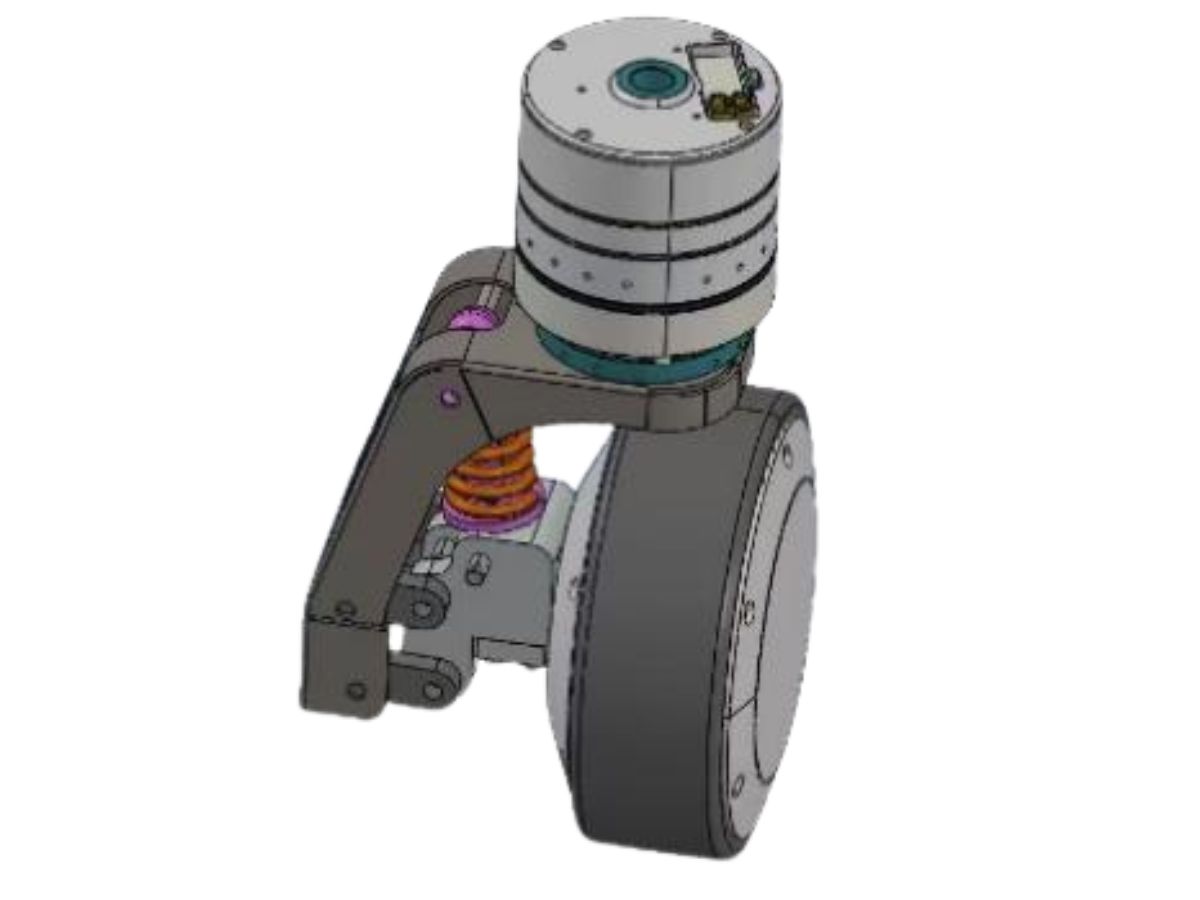
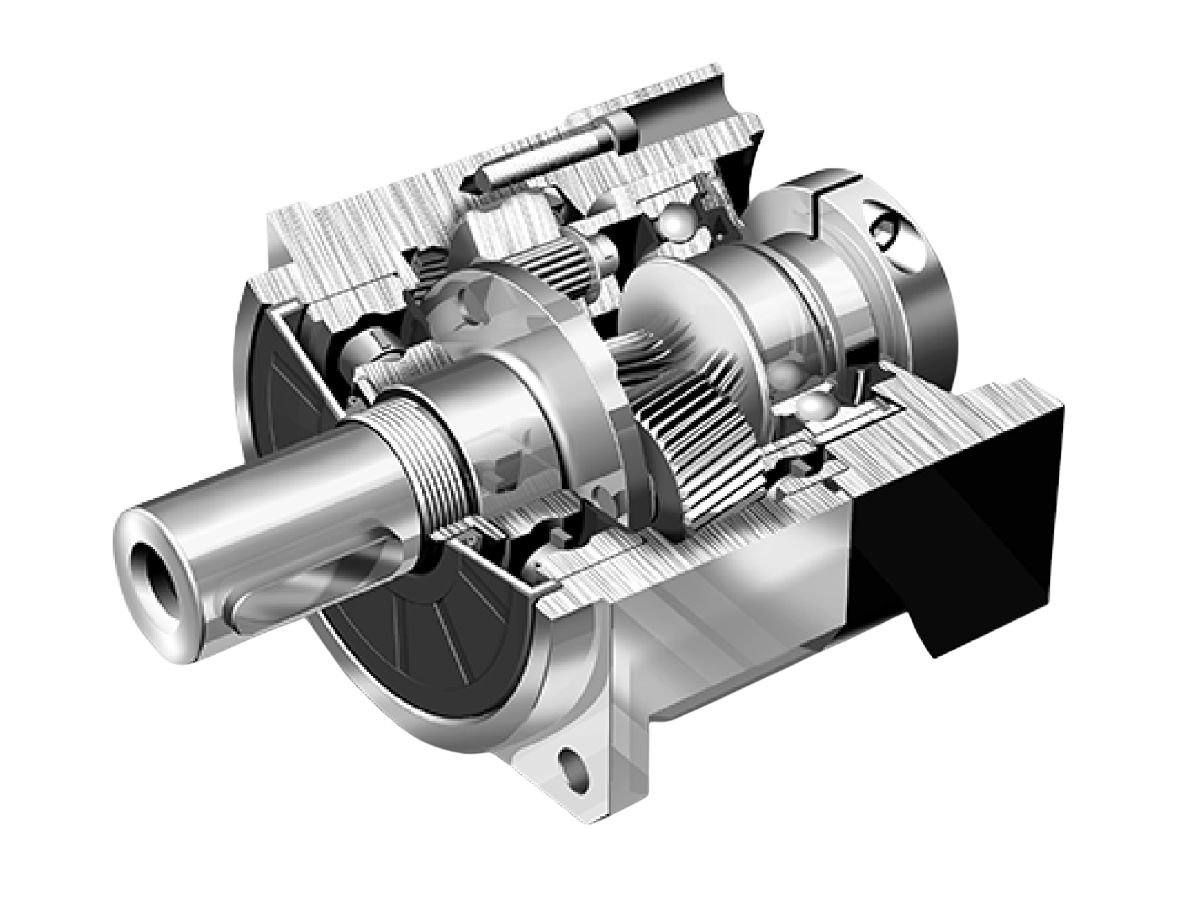
How HONPINE Dual Circular Spline Harmonic Drive Captures Market Share in Industrial Automation?
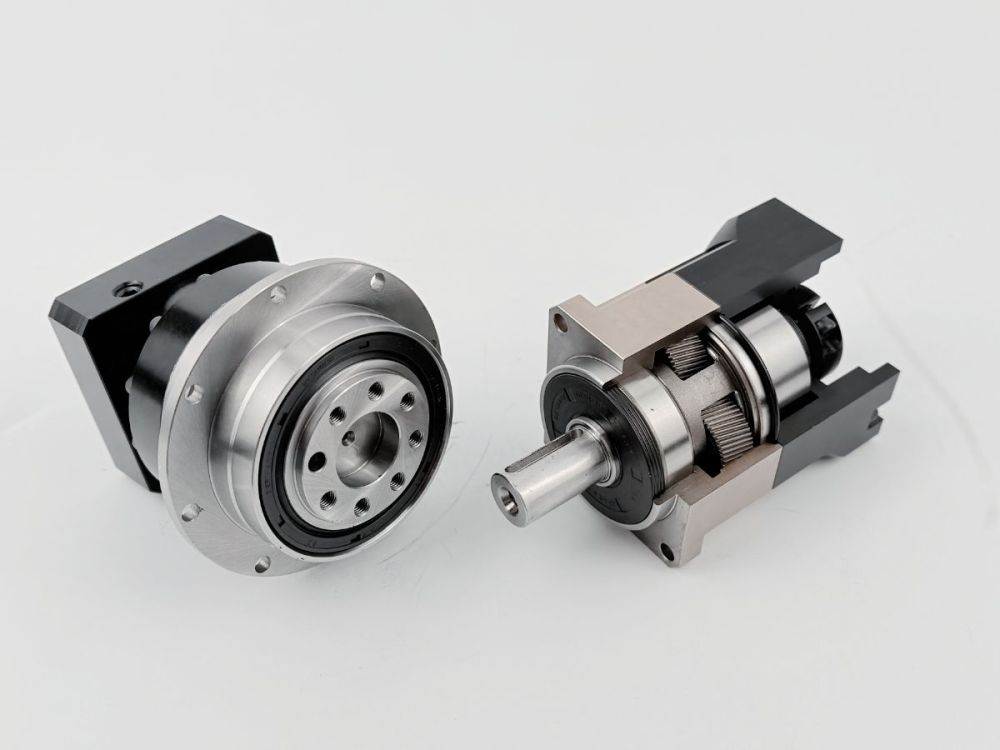
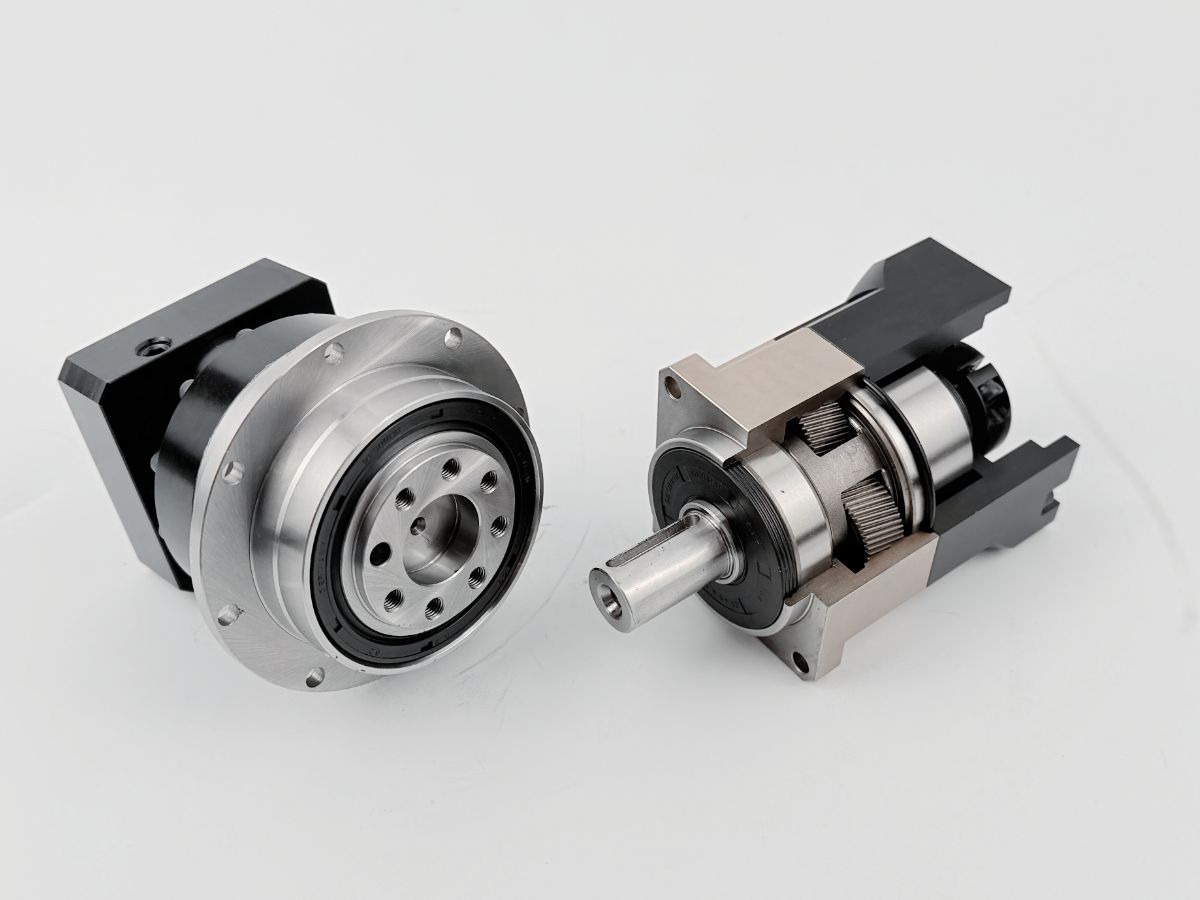
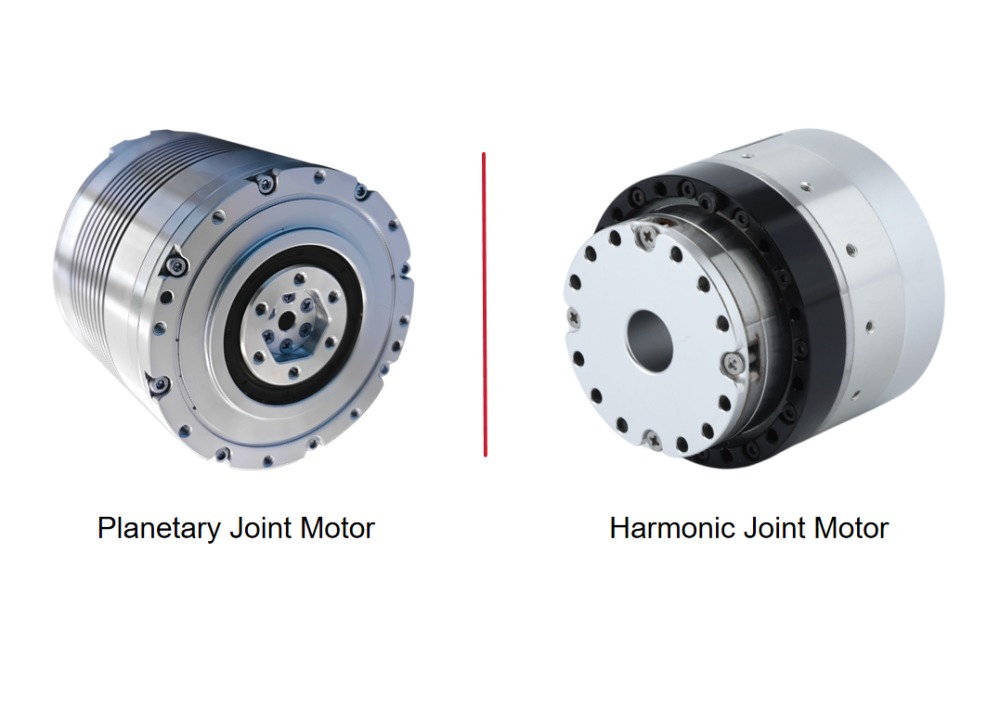
What is a Dual Circular Spline Harmonic Drive?
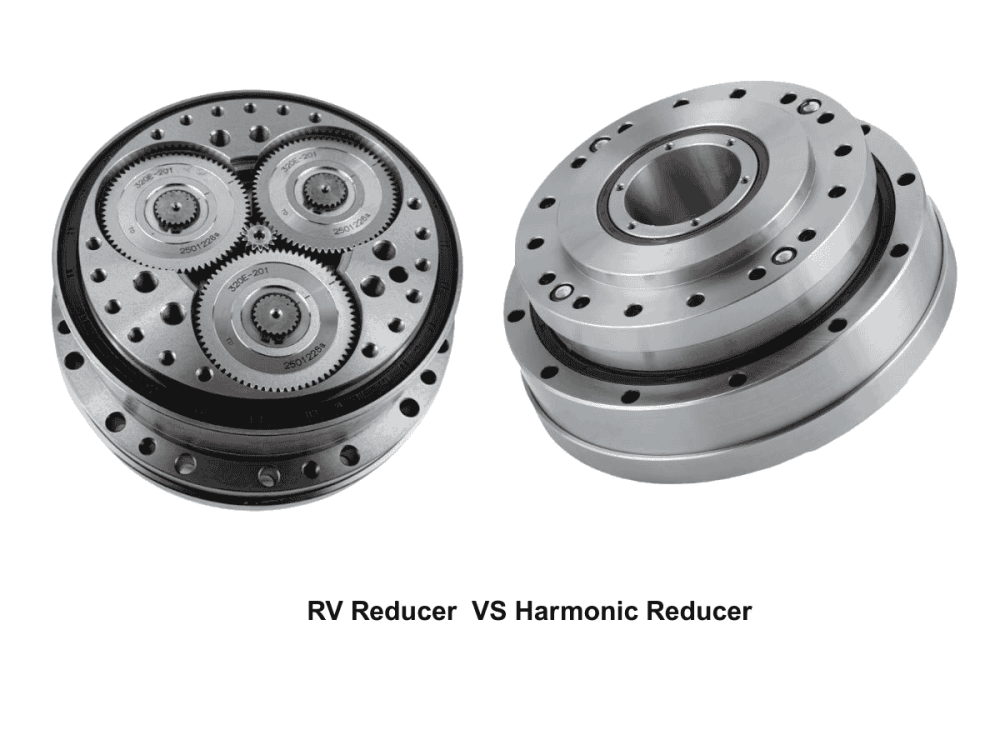
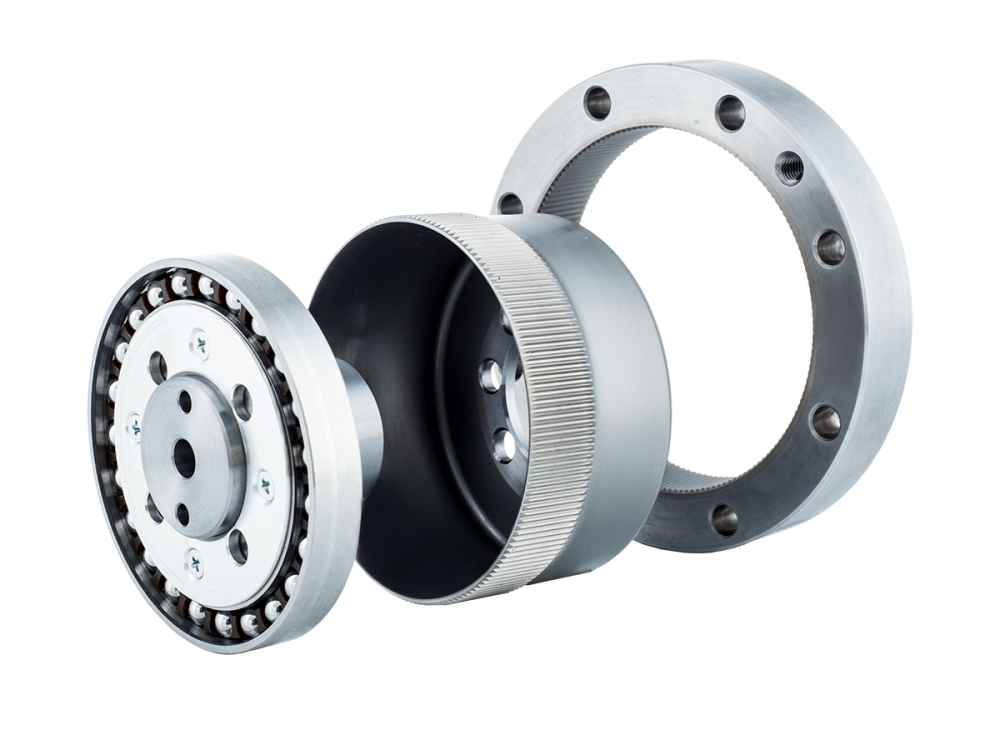
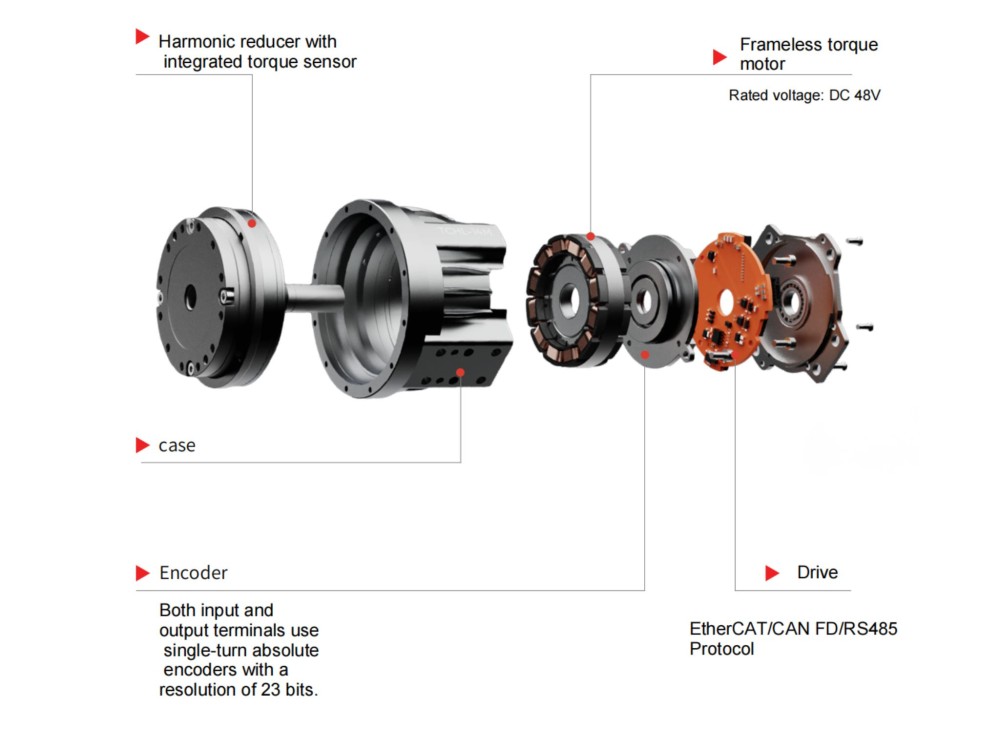
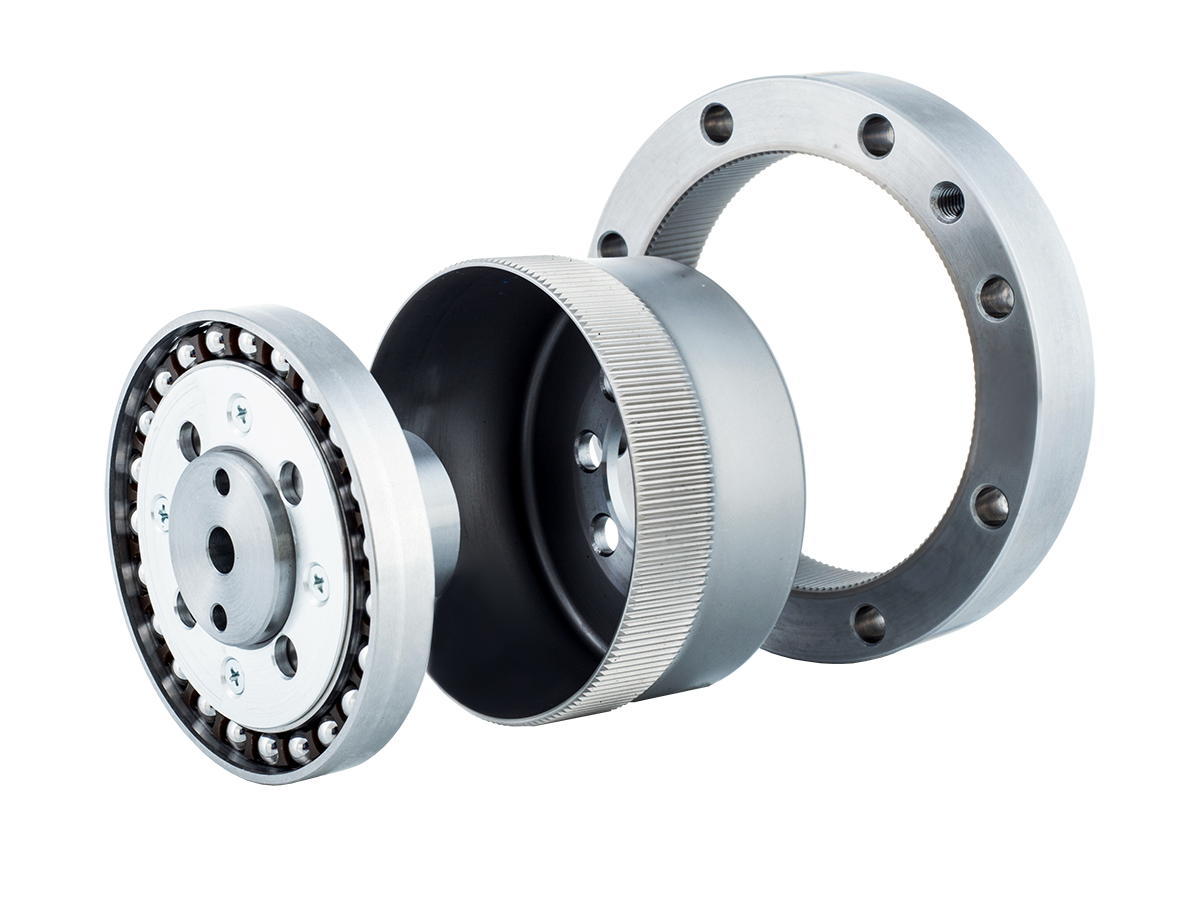
Common harmonic drives feature two types of flexsplines: the cup type and the hat type. In addition to the straight gear portion, both the inner flange of the cup type and the outer flange of the hat type are used to drive the output rotation. The term "dual circular spline" refers to the presence of two circular splines. The first circular spline, the flexspline, and the wave generator operate similarly to a standard harmonic drive: the circular spline has two more teeth than the flexspline, resulting in the flexspline rotating backward by two teeth per revolution of the wave generator. The key difference lies in the flexspline of the dual circular spline harmonic drive, which is a straight cylindrical structure without a flange to drive the output. Hence, a second circular spline is introduced. This second circular spline has the same number of teeth as the flexspline, meaning it rotates by the exact same angle as the flexspline.
Development Background of the Dual Circular Spline Harmonic Drive
To address limitations in the transmission ratio range and high costs associated with traditional harmonic gear drives, and to meet the engineering demands of robotic joints for "miniaturization, lightweight design, fast response, and high precision," technological breakthroughs were required through transmission scheme redesign and performance enhancement of key components. In the dual circular spline harmonic drive, the ring-type flexspline offers excellent load-bearing capacity and a simple structure. Under the action of the wave generator, it undergoes no axial deformation, and tooth profile design does not need to consider interference issues caused by axial warping.
Features of the Dual Circular Spline Harmonic Drive
Lightweight, Compact Size, High Torque, Improved Weight-to-Torque Ratio
The dual circular spline harmonic drive has a more compact structure, allowing for a smaller size compared to traditional harmonic drives. The maximum outer diameter can be reduced by 17%, weight by up to 24%, and reducer inertia by up to 42%. This reduces the torque required for acceleration and deceleration, lowering overall robot power consumption by up to 29%. The dual circular spline harmonic drive is more suitable than single circular spline versions for high-torque load applications such as industrial automation equipment.
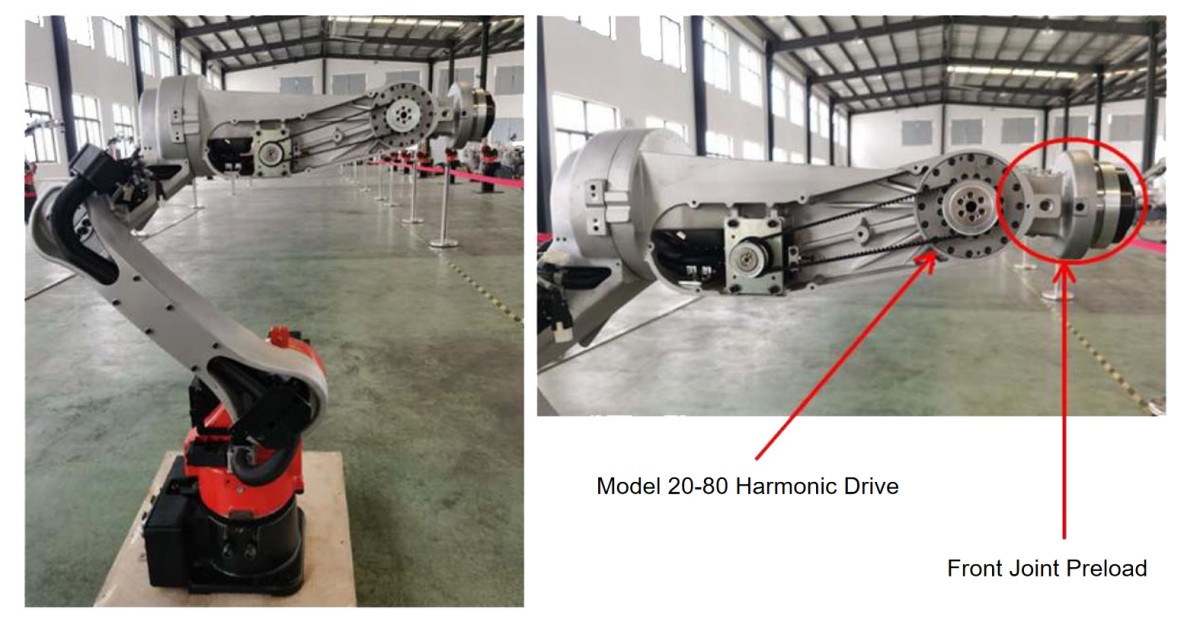

Faster Torque Response Than Traditional Harmonic Drives
In other harmonic drives, torque is transmitted through the teeth of the flexspline to the connecting flange (cup or hat type), with a cylindrical section between the gears and the flange. This causes slight torsion in the flexspline. The straight cylindrical design significantly improves this, eliminating intermediate flexible transmission for faster response and higher rigidity.
Higher Rigidity and Longer Lifespan Than Other Harmonic Drives
The dual circular spline harmonic drive offers better rigidity than traditional harmonic drives, primarily due to the replacement of balls in the wave generator with rollers and the longer contact line enabled by the straight cylindrical flexspline. In single circular spline harmonic drives, the cup or hat-type flexspline has a 90° bend between the gear ring surface and the flange, which is the weakest point. This area has poor impact resistance and is prone to twisting deformation under sudden high torque. The dual circular spline design replaces the flexspline flange with a dynamic circular spline, evolving the flexspline into a straight cylindrical structure. This eliminates the 90° bend, greatly enhancing impact resistance and extending service life.
Easier Installation
The flexspline of the dual circular spline harmonic drive has adjustable clearance with both circular splines, making assembly easier.
How HONPINE Overcomes Production Challenges of Dual Circular Spline Harmonic Drives
The dual circular spline harmonic drive has two circular splines and two sets of meshing teeth, each requiring precision and efficiency considerations, making machining more challenging. Due to the straight cylindrical flexspline, special attention must be paid to the dimensional tolerances of the ellipse. HONPINE adopts an integrated design of the bearing inner ring and the circular spline, reducing part count, minimizing size and inertia, shortening assembly time, and improving coaxiality. HONPINE's well-established supply chain system also plays a crucial role in this process.

Machining errors and assembly deviations in the components of the dual circular spline harmonic drive are the main factors introducing periodic stiffness variations. If the flexspline or circular spline has installation eccentricity during machining, the gears will exhibit cumulative pitch error. When such gears mesh internally, the torsional stiffness of the dual circular spline harmonic drive will fluctuate periodically, though at a relatively low frequency. Based on tooth profile design theory, HONPINE innovatively developed the "P" tooth profile. The P-type tooth has a low tooth height, wide tooth width, and large root curvature, with minimal radial deformation. This reduces alternating stress during flexspline deformation, lowering the risk of root fracture and thereby enhancing flexspline fatigue life. However, the P-type tooth has a smaller meshing depth, resulting in fewer meshing teeth during transmission compared to S-type teeth, slightly reducing stiffness and load-bearing capacity.
Why Choose HONPINE Dual Circular Spline Harmonic Drives?
HONPINE is a company focused on growth, customer feedback, and R&D investment. Since 2018, HONPINE has been investing in the development of dual circular spline harmonic drives, breaking the monopoly of Japan's Harmonic Drive Systems in this field and becoming one of the earliest companies in China to dedicate efforts to this technology.
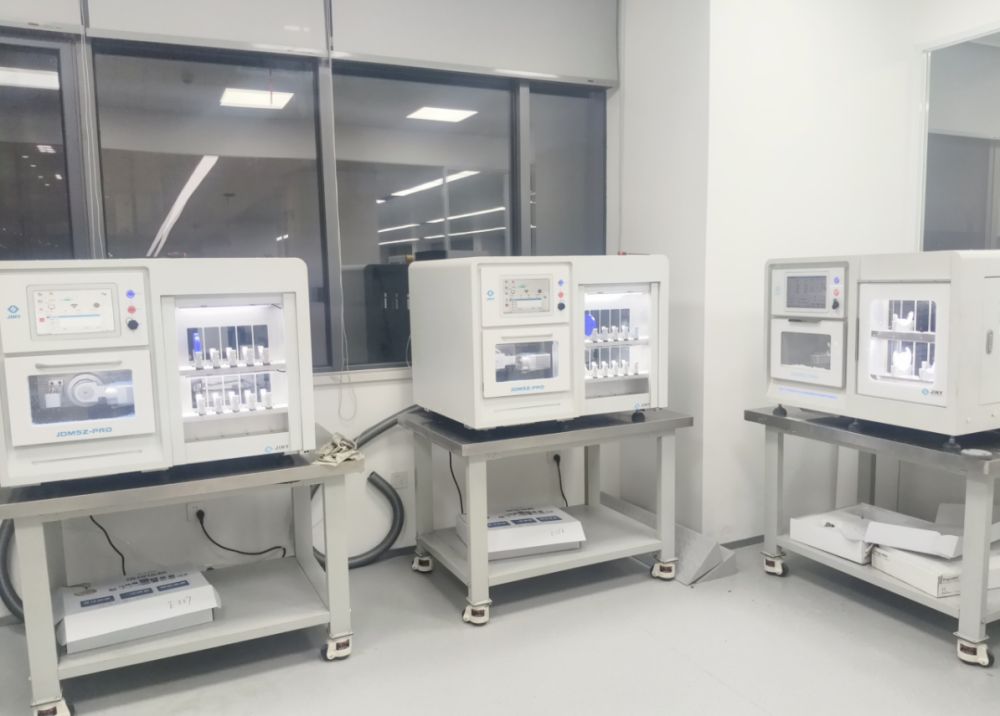
While emphasizing R&D, we equally prioritize product quality assurance. Every harmonic drive undergoes rigorous testing before leaving the factory, including torsional vibration tests and torsional buckling tests. Through multi-dimensional functional testing, we ensure product quality while gaining deeper insights into the strengths and weaknesses of our dual circular spline harmonic drives, continuously refining our R&D direction.
Currently, HONPINE dual circular spline harmonic drives have been validated in the market, primarily for industrial automation equipment. They have undergone testing and use by multiple customers, receiving highly positive feedback.
Read More
Learn more about the story of HONPINE and industry trends related to precision transmission.
Double Click
We provide harmonic drive reducer,planetary reducer,robot joint motor,robot rotary actuators,RV gear reducer,robot end effector,dexterous robot hand