China Planetary Gear Box Manufacturer
HONPINE planetary gearboxes are manufactured using processes borrowed from Nabtesco RV gearboxes in Japan. Our gear heat treatment technology is identical to Nabtesco's, a unique technology that underpins HONPINE's planetary gearbox production advantages, ensuring high precision, high strength, and long service life. HONPINE planetary gearboxes boast numerous patented manufacturing technologies, including an integrated housing design, an integrated sun gear input shaft design, and an integrated frame design for the planetary carrier and output shaft. The use of chromium-manganese-titanium alloy steel as the gear material further enhances the product's precision, dynamic response, torque, and speed compared to competitors. HONPINE is a leading high-end planetary gearbox manufacturer in China.
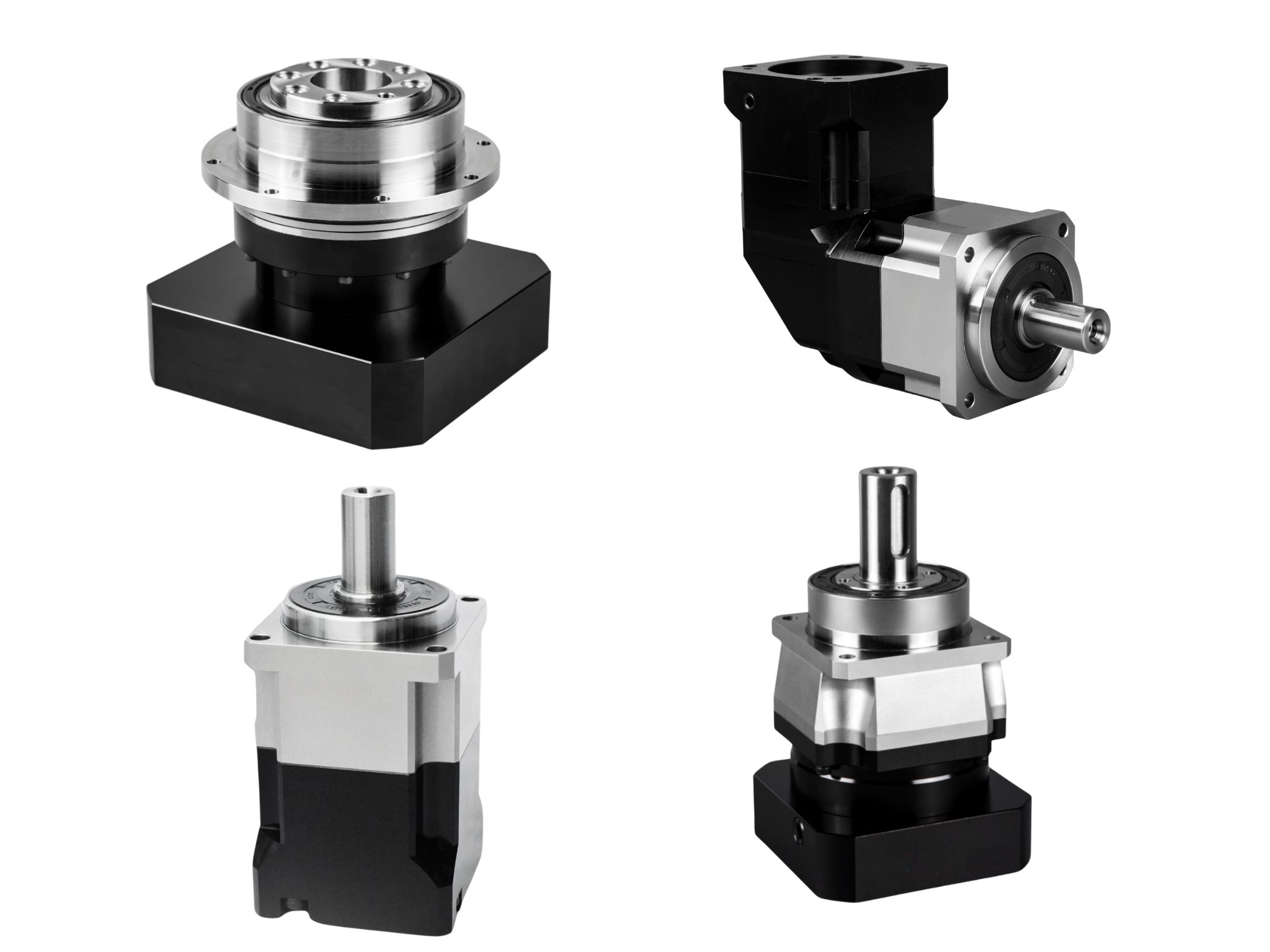
HONPINE Precision Planetary Reducer Gearbox
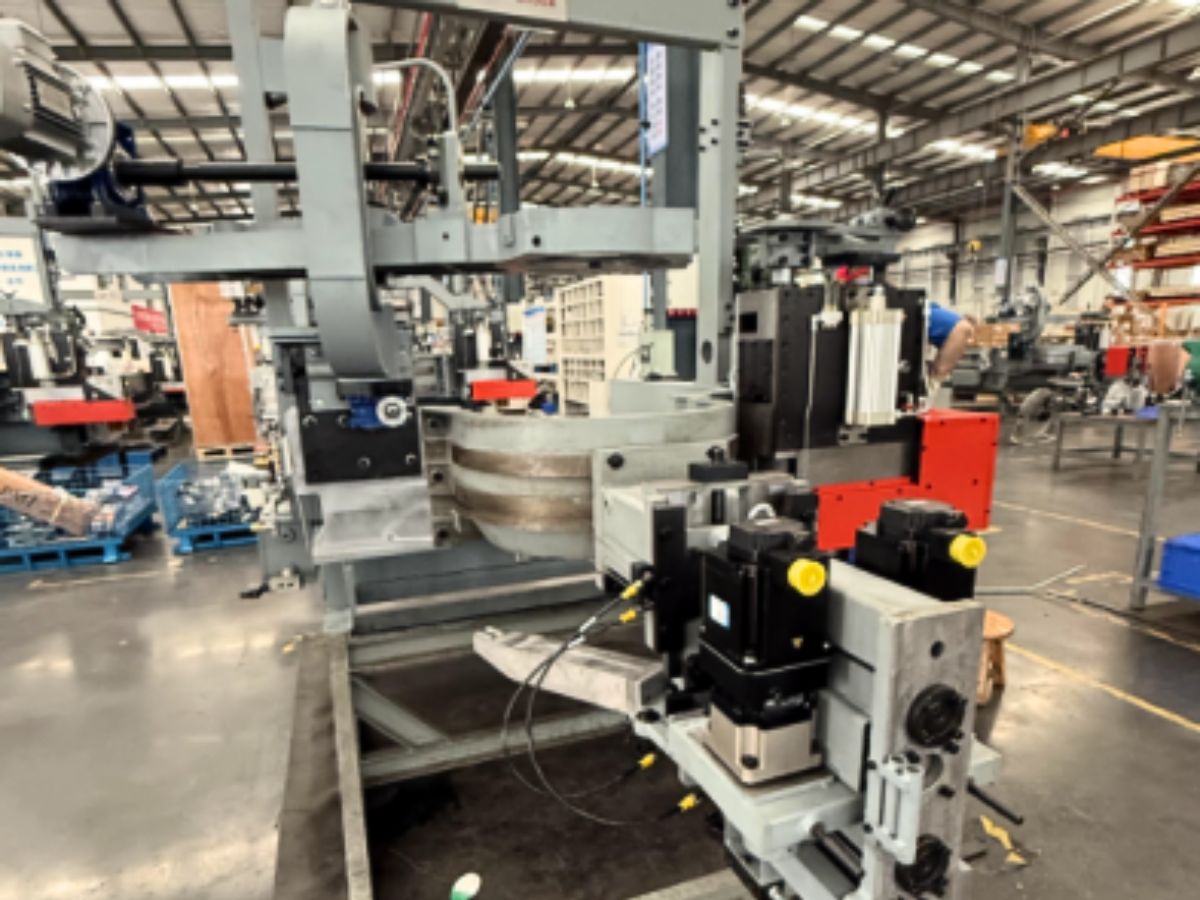
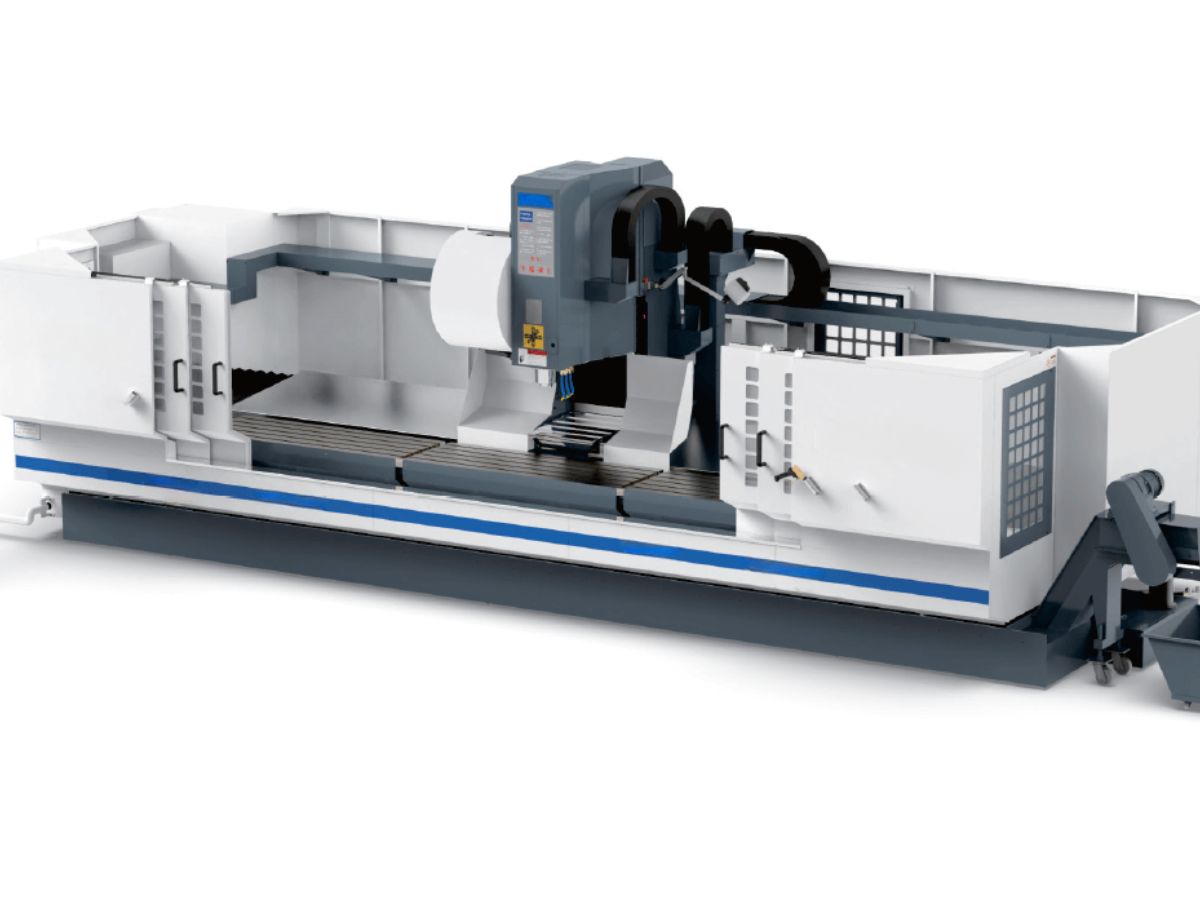
The HONPINE Planetary Reducer Gearbox is a product that blends Japanese precision engineering with Chinese manufacturing processes. It is currently widely used in packaging machinery, CNC machine tools, CNC gantry machining centers, CNC boring and milling machining centers, industrial robot joints, machine tool rotary tables, precision positioning platforms, semiconductor equipment, satellite antenna pointing mechanisms, UAV gimbals, radar optoelectronic pods, missile servo control systems, medical robot joints, imaging equipment, high-end measurement and monitoring equipment, solar tracking systems, high-precision radar antennas, and precision instruments.
- 00
0000-00
Why Planetary Gearboxes Are Well Suited for Industrial Packaging Machines?![Why Planetary Gearboxes Are Well Suited for Industrial Packaging Machines? Why Planetary Gearboxes Are Well Suited for Industrial Packaging Machines?]()
- 00
0000-00
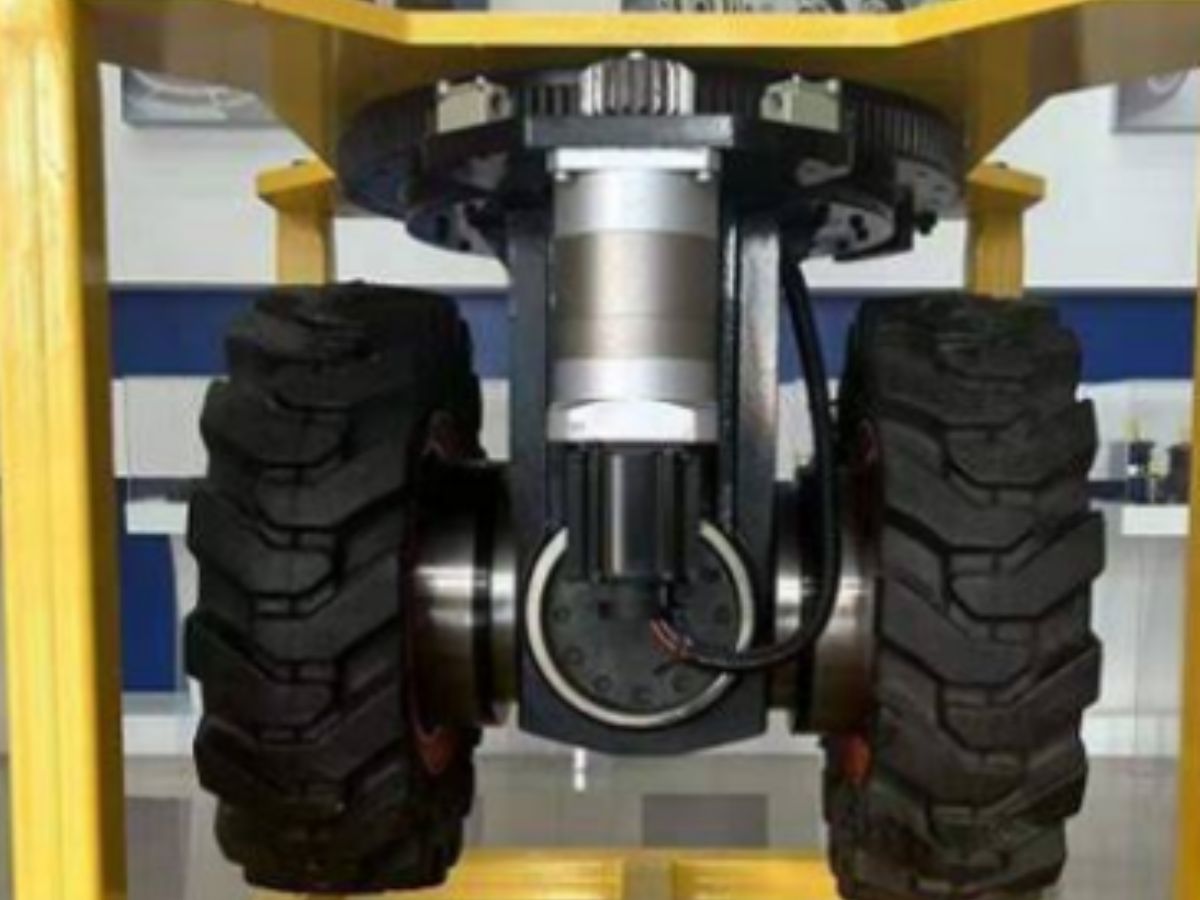
Why Planetary Gearboxes Are Perfectly Suited for AGV Drive Wheels?![Why Planetary Gearboxes Are Perfectly Suited for AGV Drive Wheels? Why Planetary Gearboxes Are Perfectly Suited for AGV Drive Wheels?]()
- 00
0000-00
How Planetary Gearboxes Enhance CNC Servo Motor and Stepper Motor Performance?![How Planetary Gearboxes Enhance CNC Servo Motor and Stepper Motor Performance? How Planetary Gearboxes Enhance CNC Servo Motor and Stepper Motor Performance?]()
- 00
0000-00
Differences Between Spur Gear Planetary Gearboxes and Helical Gear Planetary Gearboxes![Differences Between Spur Gear Planetary Gearboxes and Helical Gear Planetary Gearboxes Differences Between Spur Gear Planetary Gearboxes and Helical Gear Planetary Gearboxes]()
- 00
0000-00
The Most Comprehensive Guide to Planetary Gearbox Selection and Common Pitfalls![The Most Comprehensive Guide to Planetary Gearbox Selection and Common Pitfalls The Most Comprehensive Guide to Planetary Gearbox Selection and Common Pitfalls]()
0000-00
Planetary Gear Reducer - FAQ
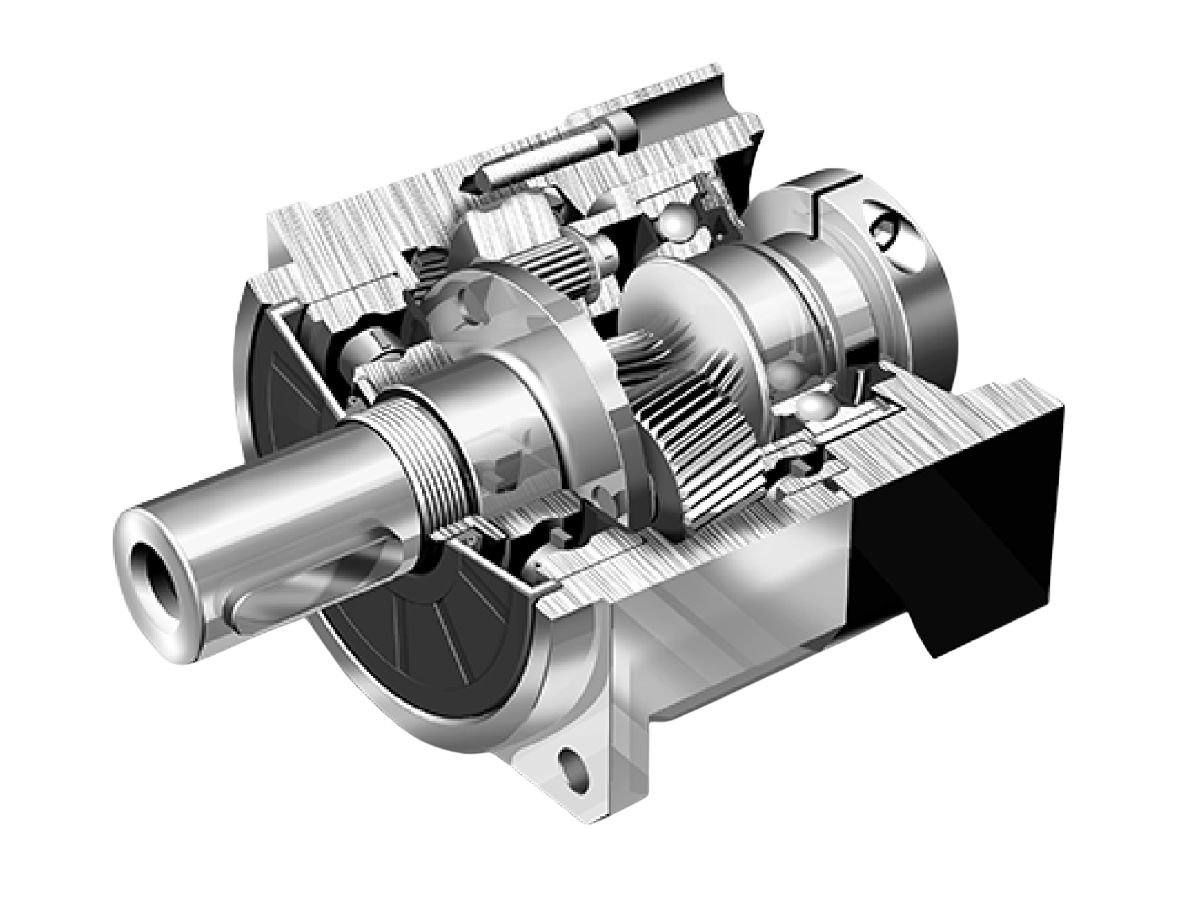
A planetary gear reducer is the most common type of motor reducer. It consists of four main components: the sun gear, planet gears, planet carrier, and ring gear. In typical operation, torque is input through the sun gear, the ring gear is fixed, and the planet gears are mounted on the planet carrier. The sun gear drives the planet gears to rotate on their own axes while also causing the planet carrier to revolve around the sun gear. Torque is then output through the planet carrier.
Adding a reducer to a servo motor increases torque. When the load is high, the planetary reducer protects the motor during transmission by bearing most of the torque. In case of overload, only the overload divided by the reduction ratio is transmitted to the motor, preventing potential motor damage that might occur if the motor directly handled the load.
The planetary reducer in the main drive system of a CNC machining center is a core component requiring high torsional rigidity. From a mechanical perspective, torsional rigidity refers to an object's ability to resist torsional deformation. During operation, the reducer must withstand torque from the motor and reactive forces generated during machining. If torsional rigidity is insufficient, internal components may experience significant elastic deformation under torque.
Planetary reducers provide cost-effective solutions for the laser cutting industry. Advanced manufacturing processes and materials help control costs, allowing customers to avoid high expenses during purchase and use. The introduction of planetary reducers significantly reduces production costs, greatly enhancing market competitiveness.
1.High Torque and Impact Resistance:
Planetary gears achieve 360-degree load distribution across contact surfaces, avoiding the risk of single-point overload and breakage common in traditional point-contact drives. This structure offers high torque capacity and impact resistance.
2.Compact Size and Light Weight:
Traditional gear reducers require significant meshing distance between gears, occupying more space. Planetary reducers allow for compact stacking, effectively improving space utilization.
3.High Efficiency and Low Backlash:
Planetary gears enable multi-point uniform meshing, with the ring gear and planet gears tightly engaged, enhancing reducer efficiency.
Selecting the right reducer is key to maximizing performance and requires a holistic system-level approach:
1.Match Reduction Ratio and Load:
Calculate the appropriate reduction ratio based on output torque, acceleration requirements, and duty cycle (continuous or intermittent operation), avoiding oversized or overloaded applications.
2.Define Precision Requirements:
Choose the appropriate backlash level based on motion control needs—high-precision applications like machining or robot joints require low backlash (e.g., ≤3 arc-min), while standard conveying equipment may allow more flexibility.
3.Ensure Compatibility with Installation Dimensions and Structure:
Verify input/output shaft specifications and mounting flange dimensions to ensure compatibility with the motor and load layout. Standardized designs (e.g., inline or right-angle) are recommended to simplify integration.
4.Consider Operating Environment and Supplier Capabilities:
For harsh environments (high temperature, du
Helical gears offer smoother engagement, more stable torque transmission, higher load capacity, and smaller backlash compared to spur gears. They are ideal for applications requiring smooth operation, low noise, and high positioning accuracy, such as CNC machine tools, industrial robot joints, and medical equipment.
1. Basic Calculation Method
The reduction ratio is the ratio of input speed to output speed. The formula is:
i = n₁ / n₂
where n₁ is the input speed and n₂ is the output speed.
Example: If the input speed is 1500 rpm and the output speed is 25 rpm, the reduction ratio is:
i = 1500 / 25 = 60:1
2. Gear Train Calculation Method
For multi-stage gear reducers, divide the driven gear teeth by the driving gear teeth for each meshing pair, then multiply the results.
Example: In a planetary gear set, let the sun gear teeth be z₁, planet gear teeth be z₂, and ring gear teeth be z₃. The reduction ratio is calculated as:
i = z₃ / z₁ × z₂ / z₁