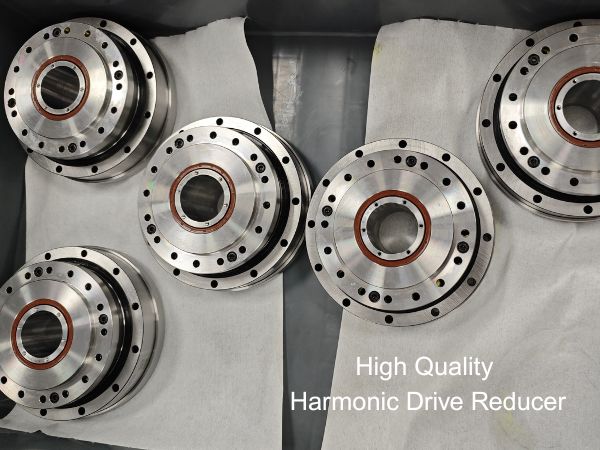
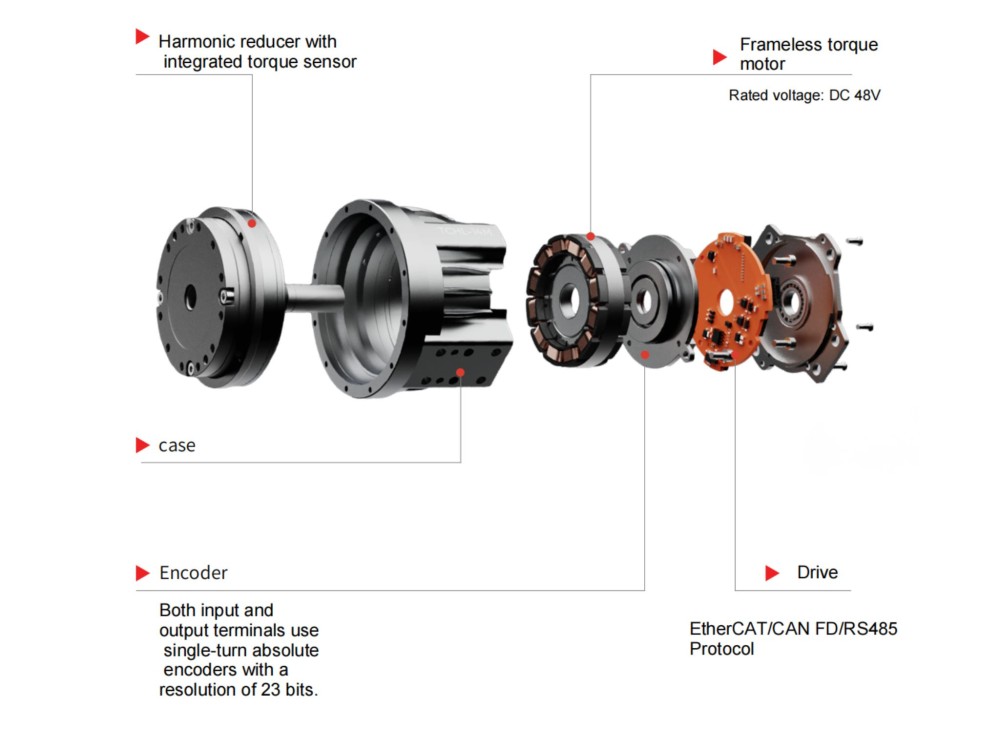
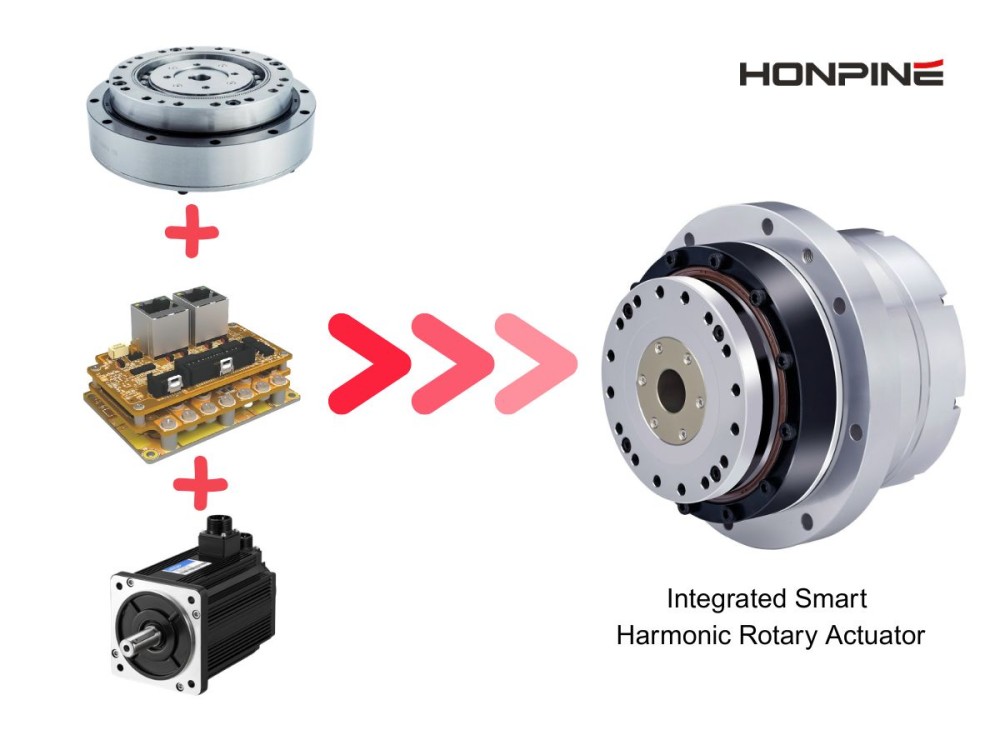
Top-Hat Type Harmonic Drive Reducer: Innovative Design Prolongs Service Life
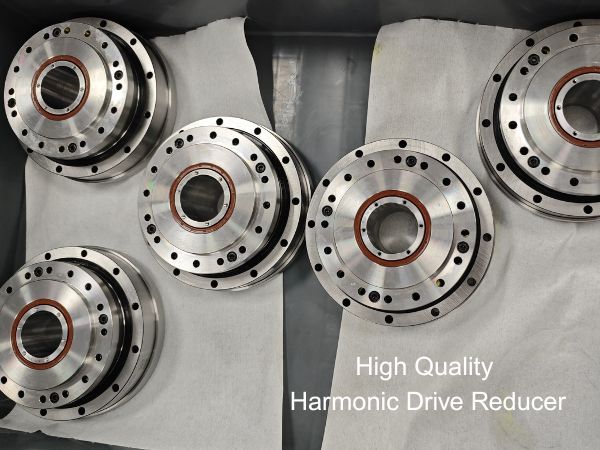
The harmonic drive reduceris a high-performance reducer featuring a compact structure, large transmission ratio, light weight, minimal backlash, and high transmission accuracy. It is widely used in high-precision fields such as industrial robotics, medical equipment, aerospace, and intelligent manufacturing. As a key core component of industrial robots, its performance directly affects motion control accuracy, operational stability, and energy efficiency. The top-hat type harmonic drive reducer is developed based on the conventional harmonic drive reducer, with enhanced rigidity and extended service life.
1. Key Performance Advantages of Harmonic Drive Reducers
High-quality harmonic drive reducers enable high-precision motion transmission, allowing robots to precisely control position, speed, and force during complex operations, thereby significantly improving efficiency and product quality. Its advantages include:
High-precision positioning: Near-zero backlash ensures accurate control
Superior motion stability: Compact structure with smooth transmission reduces vibration and noise
Energy efficiency and environmental protection: Optimized design lowers energy consumption and improves efficiency
Extended equipment lifespan: High-strength materials and structural design enhance durability and reliability
2. Drawbacks of Traditional Fixing Methods
Traditional harmonic drive reducers are typically fixed using bolts on the rigid wheel. However, over long-term operation, bolt connections are prone to loosening, which can compromise the reducer's performance. This may lead to failure in the connection between the rigid wheel and the cross-roller bearing, reducing overall transmission accuracy and stability.
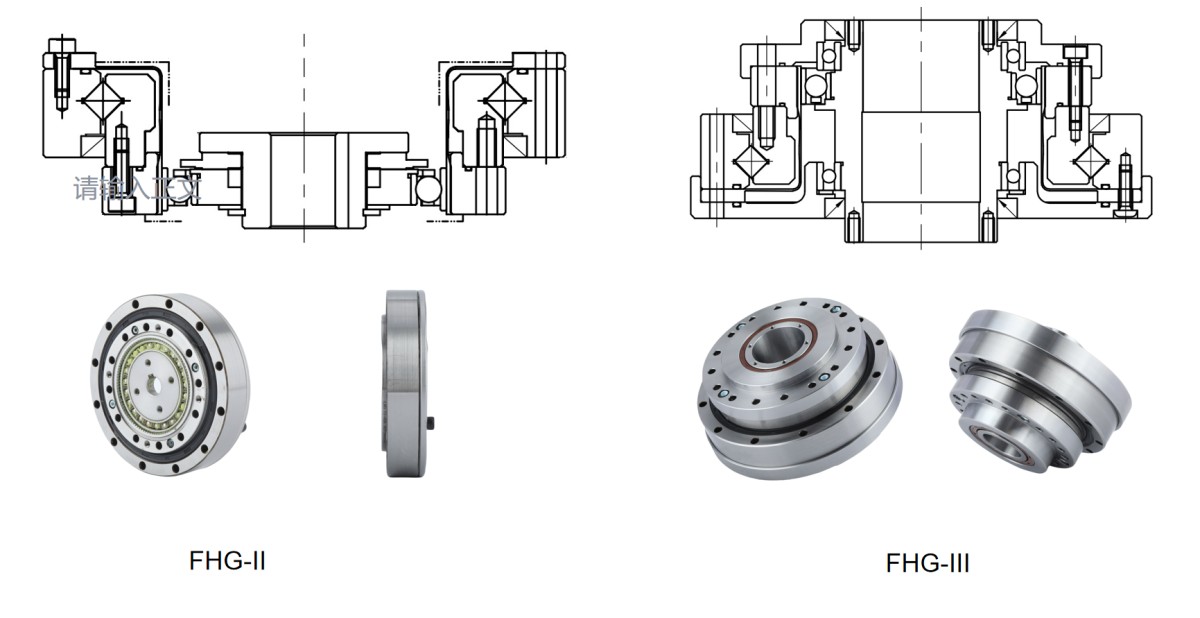
3. Structural Innovations of the Top-Hat Type Harmonic Reducer
To address the limitations of traditional designs, the top-hat type harmonic drive reducer was developed. Resembling a "top hat" in appearance, it incorporates comprehensive structural and material innovations, offering significant improvements in accuracy, load capacity, and service life.
A. Optimized Flexible Wheel Design
The flexible wheel (flexspline) is a core component of a harmonic drive reducer. Compared to the traditional thin-walled cylindrical structure, the top-hat type has been optimized as follows:
Flexible ring design: The wave generator transmits deformation through a flexible ring rather than acting directly on the cup body, reducing fatigue damage.
Extended service life: The flexible ring cushions impact loads, enhancing longevity under complex working conditions
Lower damage risk: More uniform stress distribution on the outer gear ring reduces gear wear and crack formation
B. Support Ring Fixing Structure
The top-hat type adopts a support ring instead of the traditional bolt-on rigid wheel connection, enabling higher precision and more stable transmission by increasing the contact area with the cross roller bearing:
Tighter connection and improved stability
Larger contact area enhances shock resistance
Simplified assembly and reduced installation error
C. Four-Point Contact Flexible Bearing Design
Using four-point contact bearings with the flexible wheel enlarges the force-bearing area and increases load capacity, allowing the reducer to handle higher loads within a smaller volume. This meets the dual requirements of compactness and rigidity in high-precision robotics.
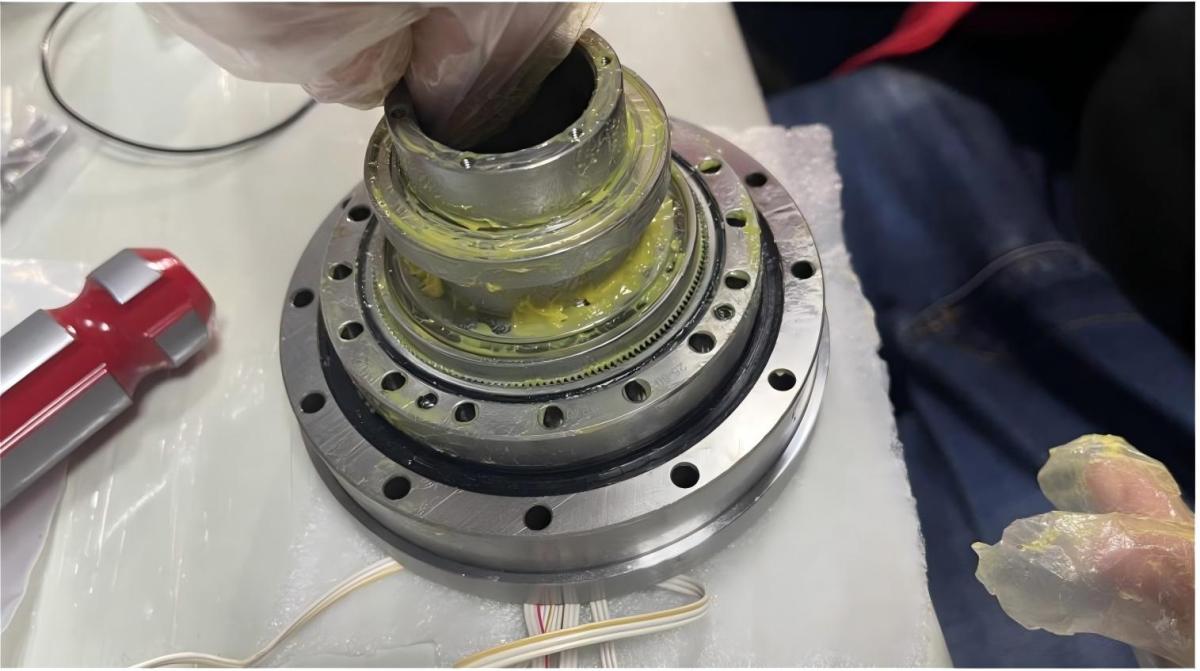

D. Elastomer Cavity Structure
An elastomer-filled cavity is integrated into the flexible wheel:
Provides damping and vibration reduction, improving overall strength
Elastomer is injected via through-hole design to ensure tight bonding
Enables multi-part synchronous molding to enhance manufacturing efficiency and consistency
4. Simplified Structure for Stress Analysis
As the bottom flange of the top-hat flexible wheel is connected to the output end, it is significantly thicker than the cylindrical section, making the overall geometry complex. To facilitate stress analysis (such as Finite Element Method, FEM), the flexible wheel structure is often simplified to better identify stress concentrations, fatigue points, and critical stress zones.
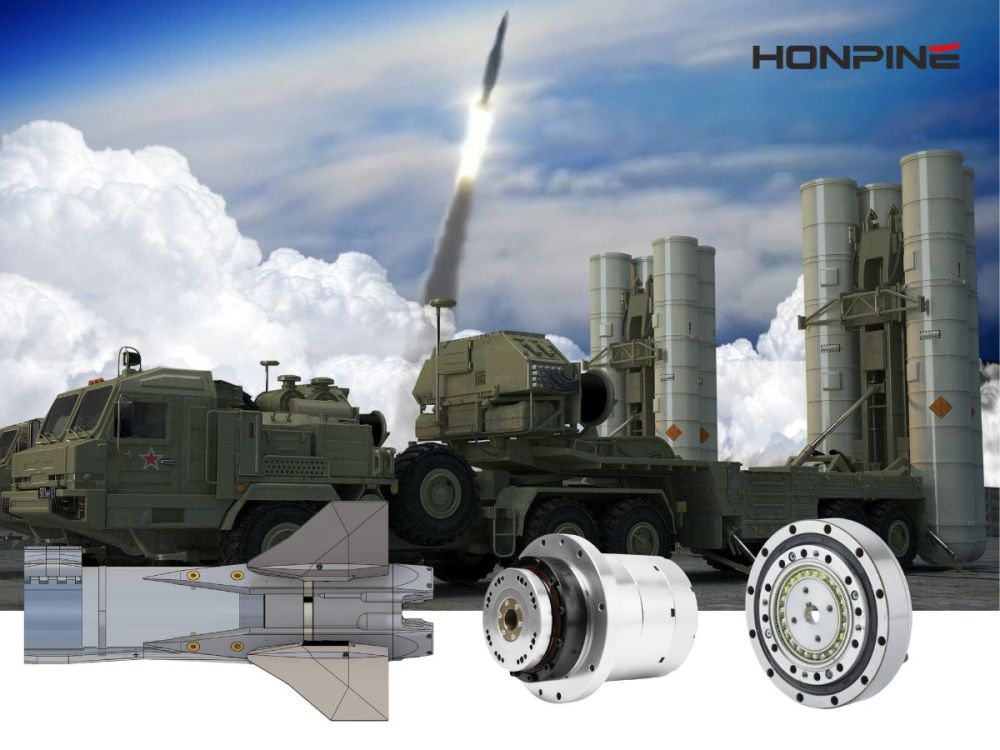
5. Applications and Development Trends of Harmonic Drives
Top-hat type harmonic drive reducers perform exceptionally well in high-precision robotic applications, especially in:
Collaborative robots (Cobots)
Medical robots (surgical/rehabilitation)
Semiconductor manufacturing equipment
Visual inspection and automated assembly systems
Aerospace and defense equipment
As the robotics industry moves toward more compact, intelligent, and precise motion systems, top-hat type harmonic drive reducers are poised to become a key transmission technology for the future.
Read More
Learn more about the story of HONPINE and industry trends related to precision transmission.
Double Click
We provide harmonic drive reducer,planetary reducer,robot joint motor,robot rotary actuators,RV gear reducer,robot end effector,dexterous robot hand