In recent years, the global industrial competition landscape has undergone significant adjustments, with intelligent manufacturing emerging as a major trend and core focus for the future development of the manufacturing industry. Modern intelligent manufacturing models demand higher performance from industrial robots, requiring them to handle increasingly complex tasks with greater sensitivity and precision.
Compared to traditional industrial robots, collaborative robots offer distinct advantages such as lightweight design, enhanced safety, and advanced intelligence. These robots can work closely with human operators to accomplish intricate production tasks. As application scenarios expand and work tasks grow more complex, industrial production has raised the bar for the performance of six-axis robot motion control systems. For instance, processes like precision manufacturing, assembly, and welding now impose stricter requirements on motion control accuracy.
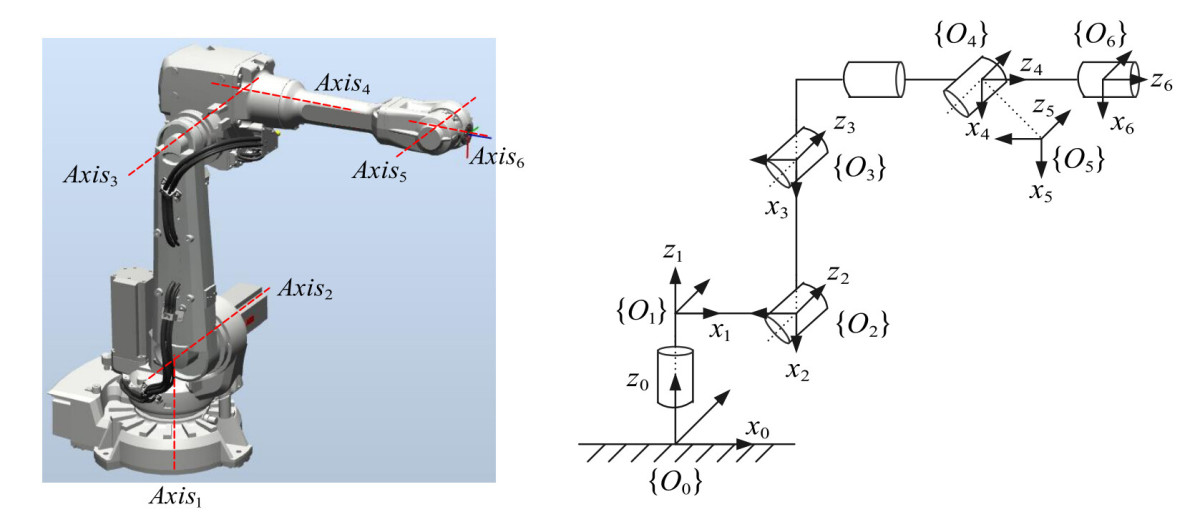
What Is a Six-Axis Robot?
A six-axis robot is an open-chain mechanism comprising six rotating joints and their associated connecting rods in series. It achieves precise control through motor drives and sensor feedback systems, enabling the robot’s end effector (e.g., gripper, welding torch) to move along a predetermined trajectory to a specified position and operate in a specific orientation.
The Importance of Robot Joints in Six-Axis Robots
From a kinematic perspective, six-axis robots feature an open-chain structure that maximizes workspace while minimizing mechanism size. The robot’s own weight and external loads are primarily supported by its joints.
Six-axis robots employ flexible transmission devices between joints, which not only allow for a larger range of motion with greater torsion angles but also provide a wider speed range, enhancing adaptability and flexibility. This flexibility enables robots to perform complex industrial tasks with higher precision, particularly in scenarios requiring delicate operations, such as precision manufacturing and assembly.
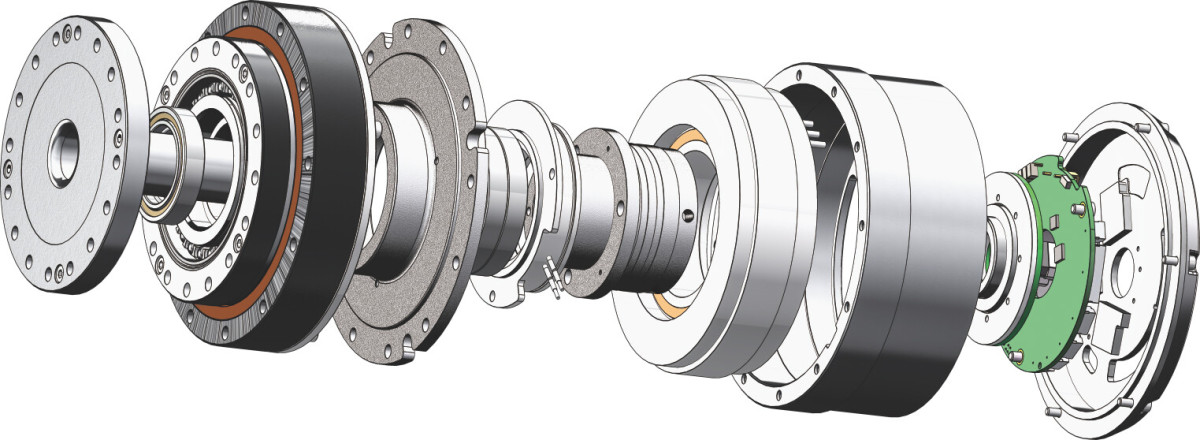
The mechanical structure of a robot joint typically includes the following key components:
1,Actuator: Primarily composed of servo motors, it provides power to drive joint movement and adjusts speed and torque based on control signals. The actuator is usually equipped with an encoder for precise motion feedback and control.
2,Transmission Device: Components such as harmonic reducers, belts, or chains convert the high-speed, low-torque rotation of the servo motor into the low-speed, high-torque output required for joint operation, meeting diverse torque and speed demands.
3,Load: Refers to the next link or end effector driven by the joint, along with any attached objects.
HONPINE’s Solutions
HONPINE provides tailored solutions for customers, whether they require complete joint modules or individual components. Our team offers one-on-one technical support to meet your specific needs.
Precision Control in Six-Axis Robots
Industrial production demands increasingly high precision from six-axis robots, particularly in motion control. Many manufacturing sectors, such as aerospace, microelectronics, and medical device assembly, impose stringent standards for part machining, assembly accuracy, and positioning. These industries require robots to execute tasks with exceptional precision to ensure product quality and performance.
As industrial automation advances, robots are increasingly integrated into production lines, necessitating seamless coordination with other automated equipment. This places greater emphasis on high-precision robot control to ensure efficient collaboration and optimize overall production line efficiency.
Compared to traditional gear systems (e.g., planetary or RV reducers), harmonic reducers stand out for their high precision and torque capabilities, making them the preferred choice for six-axis robots.
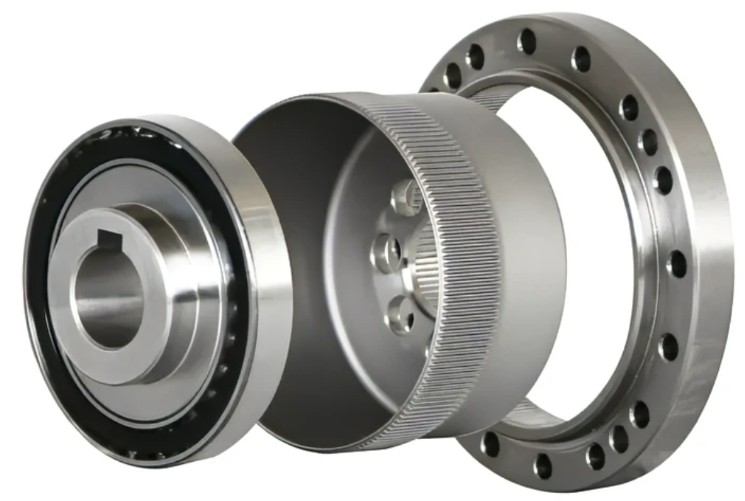

Robot Joints: The Heart of Robotics
Since 2018, HONPINE has delivered over 20,000 robot joint solutions, specializing in precision transmission systems. We provide dedicated technical consultation to help you select the ideal harmonic reducer or joint module for your application.
Contact us today to learn more about our harmonic reducers and joint modules!
